Apps Script สำหรับ Google เอกสารช่วยให้คุณเข้าถึงเนื้อหาจากแท็บใดก็ได้ในเอกสาร
แท็บคืออะไร
Google เอกสารมีเลเยอร์การจัดระเบียบที่เรียกว่าแท็บ เอกสารช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สร้างแท็บอย่างน้อย 1 แท็บในเอกสารเดียวได้ คล้ายกับที่มีแท็บในชีตในปัจจุบัน แต่ละแท็บจะมีชื่อและรหัสของตัวเอง (ต่อท้ายใน URL) แท็บยังมีแท็บย่อยได้ด้วย ซึ่งเป็นแท็บที่ซ้อนอยู่ใต้แท็บอื่น
เข้าถึงแท็บ
เข้าถึงพร็อพเพอร์ตี้และเนื้อหาของแท็บได้โดยใช้ Document.getTabs() ซึ่งจะแสดงรายการ Tab ส่วนต่อๆ ไปจะแสดงภาพรวมคร่าวๆ ของคลาส Tab นอกจากนี้เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับคลาสแท็บยังมีข้อมูลโดยละเอียดเพิ่มเติมด้วย
คุณสมบัติของแท็บ
คุณสามารถเรียกข้อมูลพร็อพเพอร์ตี้แท็บได้โดยใช้เมธอดต่างๆ เช่น Tab.getId() และ Tab.getTitle()
เนื้อหาแท็บ
คุณสามารถเรียกข้อมูลเนื้อหาเอกสารภายในแต่ละแท็บได้โดยใช้ Tab.asDocumentTab()
ส่วนการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้างคลาสเอกสารอธิบายวิธีใช้
ลําดับชั้นของแท็บ
แท็บย่อยจะแสดงใน Google Apps Script ผ่าน Tab.getChildTabs()
การเข้าถึงเนื้อหาจากแท็บทั้งหมดต้องผ่าน "ต้นไม้" ของแท็บย่อย
ตัวอย่างเช่น ลองพิจารณาเอกสารที่มีลําดับชั้นแท็บดังต่อไปนี้
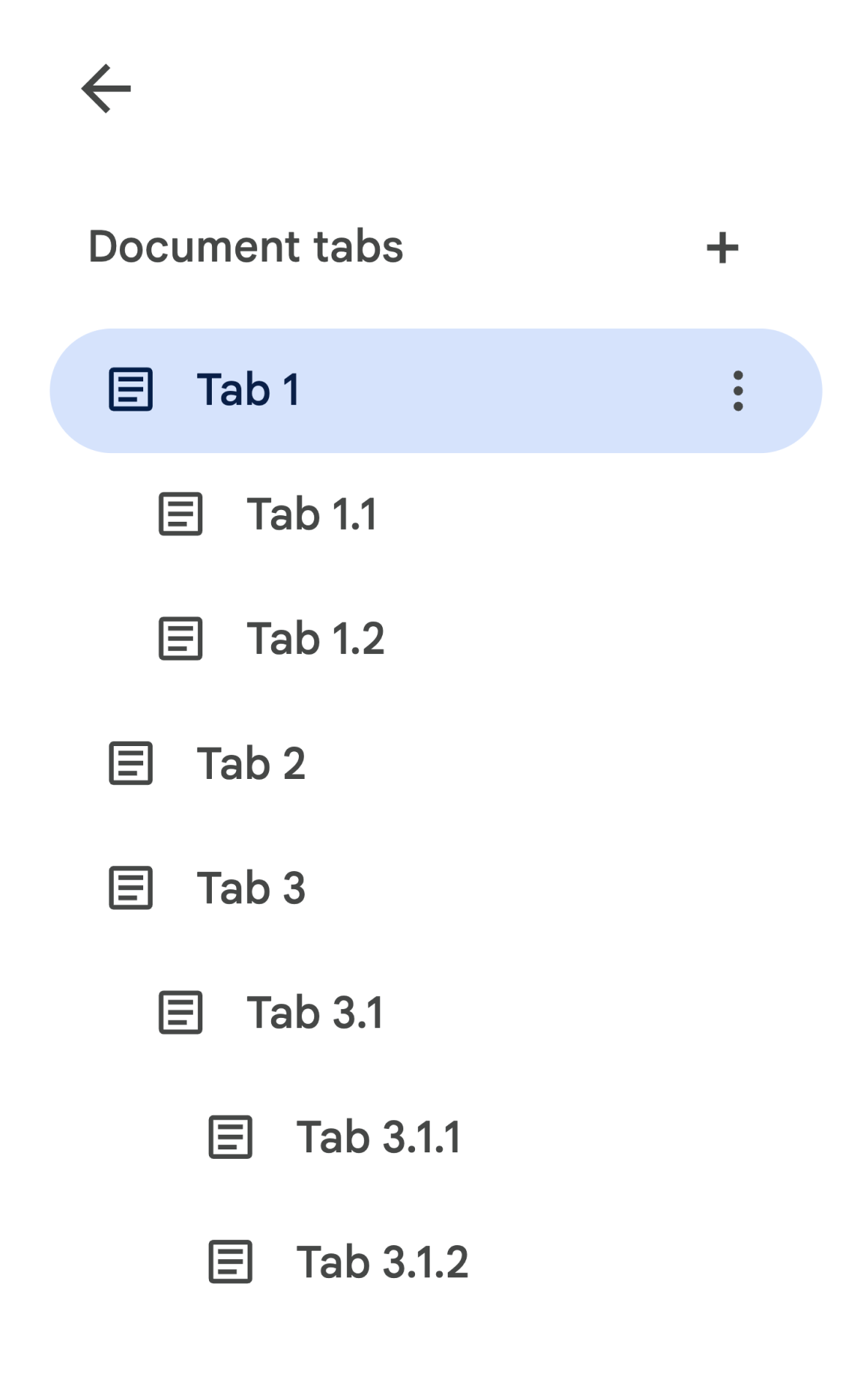
หากต้องการเข้าถึงแท็บ 3.1.2 ให้ทําดังนี้
// Print the ID of Tab 3.1.2. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const tab = doc.getTabs()[2].getChildTabs()[0].getChildTabs()[1]; console.log(tab.getId());
ดูบล็อกโค้ดตัวอย่างในส่วนถัดไป ซึ่งแสดงโค้ดตัวอย่างสำหรับการวนซ้ำในแท็บทั้งหมดในเอกสาร
วิธีอื่นๆ ในการเรียกข้อมูลแท็บ
การเรียกข้อมูลแท็บทำได้อีก 2 วิธีดังนี้
Document.getTab(tabId): แสดงแท็บที่มีรหัสที่ระบุDocument.getActiveTab(): แสดงแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้ ใช้ได้เฉพาะในสคริปต์ที่เชื่อมโยงกับเอกสาร ส่วนถัดไปจะอธิบายเรื่องนี้อย่างละเอียด
การเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้างชั้นเอกสาร
ก่อนหน้านี้ เอกสารไม่มีแนวคิดเรื่องแท็บ ดังนั้น Document Class จึงแสดงวิธีการเข้าถึงและแก้ไขเนื้อหาข้อความของเอกสารโดยตรง เมธอดต่อไปนี้จัดอยู่ในหมวดหมู่นี้
Document.addBookmark(position)Document.addFooter()Document.addHeader()Document.addNamedRange(name, range)Document.getBody()Document.getBookmark(id)Document.getBookmarks()Document.getFooter()Document.getFootnotes()Document.getHeader()Document.getNamedRangeById(id)Document.getNamedRanges()Document.getNamedRanges(name)Document.newPosition(element, offset)Document.newRange()
เมื่อเพิ่มลําดับชั้นเชิงโครงสร้างของแท็บแล้ว วิธีการเหล่านี้จะไม่แสดงเนื้อหาข้อความจากแท็บทั้งหมดในเอกสารตามความหมายอีกต่อไป ตอนนี้เนื้อหาข้อความจะแสดงในเลเยอร์อื่น โดยคุณจะเข้าถึงเมธอดข้อความที่กล่าวถึงข้างต้นทั้งหมดผ่าน DocumentTab
เมธอดที่มีอยู่เหล่านี้ในคลาส Document จะเข้าถึงหรือแก้ไขเนื้อหาจากแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ (ในสคริปต์ที่เชื่อมโยงกับเอกสารหนึ่งๆ) หรือแท็บแรก (หากไม่มีแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่)
เข้าถึงเนื้อหาข้อความภายในแท็บที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
เราขอแนะนำให้ใช้เมธอดที่มีอยู่ในคลาส DocumentTab แทนการใช้เมธอดข้อความจาก Document (ซึ่งใช้ได้ผ่านเมธอด Tab.asDocumentTab()) เช่น
// Print the text from the body of the active tab. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const documentTab = doc.getActiveTab().asDocumentTab(); const body = documentTab.getBody(); console.log(body.getText());
การเปลี่ยนแปลงตัวเลือกของผู้ใช้
วิธีการเลือกข้อความ
คลาส Document มี getter และ setter เพื่อจัดการตําแหน่งในข้อความที่ผู้ใช้เลือกภายในเอกสารที่ใช้งานอยู่ เมธอดเหล่านี้จะทํางานภายในบริบทของแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้ที่เรียกใช้สคริปต์
Document.getCursor(): แสดงตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์ของผู้ใช้ในแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่Document.getSelection(): แสดงผลช่วงการเลือกของผู้ใช้ในแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่Document.setCursor(position): กำหนดตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์ของผู้ใช้ในเอกสารที่ใช้งานอยู่ หากตำแหน่งอยู่ในแท็บที่ไม่ได้ใช้งาน ระบบจะเปลี่ยนแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้เป็นแท็บที่เชื่อมโยงกับตำแหน่งนั้นด้วยDocument.setSelection(range): ตั้งค่าช่วงการเลือกของผู้ใช้ในเอกสารที่ใช้งานอยู่ หากช่วงอยู่ในแท็บที่ไม่ใช้งาน ระบบจะเปลี่ยนแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้เป็นแท็บที่เชื่อมโยงกับช่วงนั้นด้วย
วิธีการและกรณีการใช้งานการเลือกแท็บ
เมื่อมีการเปิดตัวแท็บ คุณอาจต้องการรับและตั้งค่าแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้ที่เรียกใช้สคริปต์ ซึ่งทำได้โดยใช้วิธีการต่อไปนี้
Document.getActiveTab(): แสดงผลTabที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้ในเอกสารที่ใช้งานอยู่Document.setActiveTab(tabId): ตั้งค่าTabที่ผู้ใช้เลือกในเอกสารปัจจุบันเป็นแท็บที่มีรหัสที่ระบุ
"การเลือก" ของผู้ใช้โดยรวมประกอบด้วยแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ร่วมกับตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์ปัจจุบันหรือช่วงการเลือก รูปแบบ 2 แบบสําหรับการทํางานกับการเลือกที่ใช้งานอยู่คือการแก้ไขแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้เป็นแท็บที่เฉพาะเจาะจงอย่างชัดเจน หรือใช้แท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้
การเปลี่ยนแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้อย่างชัดเจนทำได้โดยใช้ Document.setActiveTab(tabId)
หรือจะเรียกใช้ Document.setCursor(position) หรือ Document.setSelection(range) ด้วย Position หรือ Range จากแท็บที่ไม่ได้ใช้งาน แท็บนั้นก็จะเริ่มทำงาน
หากลักษณะการทํางานที่ต้องการของสคริปต์คือการใช้แท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้โดยไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง ก็ไม่จําเป็นต้องใช้ Document.setActiveTab(tabId) วิธีการ Document.getCursor() และ Document.getSelection() จะทํางานในแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่โดยอิงตามแท็บที่ผู้ใช้เรียกใช้สคริปต์
โปรดทราบว่าเอกสารไม่รองรับการเลือกแท็บหลายรายการ ตำแหน่งหลายตำแหน่ง หรือช่วงหลายช่วงในแท็บต่างๆ ดังนั้น การใช้ Document.setActiveTab(tabId) จะล้างตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์หรือช่วงการเลือกก่อนหน้า
วิธีการเกี่ยวกับตําแหน่งและช่วงสําหรับแท็บที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
แท็บที่เฉพาะเจาะจงคือสิ่งที่ให้ความหมายแก่แนวคิดการเลือกข้อความของ Position และ Range กล่าวคือ ตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์หรือช่วงการเลือกจะมีความหมายก็ต่อเมื่อสคริปต์ทราบแท็บที่ตำแหน่งหรือช่วงนั้นอยู่
ซึ่งทำได้โดยใช้เมธอด DocumentTab.newPosition(element, offset) และ DocumentTab.newRange() ซึ่งจะสร้างตำแหน่งหรือช่วงที่กำหนดเป้าหมายไปยัง DocumentTab ที่เฉพาะเจาะจงซึ่งเรียกใช้เมธอด ในทางตรงกันข้าม Document.newPosition(element, offset) และ Document.newRange() จะสร้างตำแหน่งหรือช่วงที่กำหนดเป้าหมายไปยังแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ (หรือแท็บแรก หากสคริปต์ไม่ได้เชื่อมโยง)
ดูบล็อกโค้ดตัวอย่างในส่วนถัดไป ซึ่งแสดงโค้ดตัวอย่างสําหรับการทํางานกับรายการที่เลือก
รูปแบบการใช้งานทั่วไปสำหรับแท็บ
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้อธิบายวิธีต่างๆ ในการโต้ตอบกับแท็บ
อ่านเนื้อหาแท็บจากแท็บทั้งหมดในเอกสาร
โค้ดที่มีอยู่ซึ่งทําเช่นนี้ก่อนฟีเจอร์แท็บจะย้ายข้อมูลเพื่อรองรับแท็บได้โดยการสํารวจลําดับชั้นแท็บและเรียกใช้เมธอด getter จาก Tab และ DocumentTab แทน Document ตัวอย่างโค้ดบางส่วนต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีพิมพ์เนื้อหาข้อความทั้งหมดจากทุกแท็บในเอกสาร โค้ดการเรียกดูแท็บนี้สามารถปรับให้เข้ากับ Use Case อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่ไม่สนใจโครงสร้างจริงของแท็บ
/** Logs all text contents from all tabs in the active document. */
function logAllText() {
// Generate a list of all the tabs in the document, including any
// nested child tabs. DocumentApp.openById('abc123456') can also
// be used instead of DocumentApp.getActiveDocument().
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc);
// Log the content from each tab in the document.
for (const tab of allTabs) {
// Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab object.
const documentTab = tab.asDocumentTab();
// Get the body from the given DocumentTab.
const body = documentTab.getBody();
// Get the body text and log it to the console.
console.log(body.getText());
}
}
/**
* Returns a flat list of all tabs in the document, in the order
* they would appear in the UI (i.e. top-down ordering). Includes
* all child tabs.
*/
function getAllTabs(doc) {
const allTabs = [];
// Iterate over all tabs and recursively add any child tabs to
// generate a flat list of Tabs.
for (const tab of doc.getTabs()) {
addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs);
}
return allTabs;
}
/**
* Adds the provided tab to the list of all tabs, and recurses
* through and adds all child tabs.
*/
function addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs) {
allTabs.push(tab);
for (const childTab of tab.getChildTabs()) {
addCurrentAndChildTabs(childTab, allTabs);
}
}
อ่านเนื้อหาแท็บจากแท็บแรกในเอกสาร
ซึ่งคล้ายกับการอ่านแท็บทั้งหมด
/**
* Logs all text contents from the first tab in the active
* document.
*/
function logAllText() {
// Generate a list of all the tabs in the document, including any
// nested child tabs.
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc);
// Log the content from the first tab in the document.
const firstTab = allTabs[0];
// Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab object.
const documentTab = firstTab.asDocumentTab();
// Get the body from the DocumentTab.
const body = documentTab.getBody();
// Get the body text and log it to the console.
console.log(body.getText());
}
อัปเดตเนื้อหาแท็บในแท็บแรก
ตัวอย่างโค้ดบางส่วนต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีกําหนดเป้าหมายแท็บที่เฉพาะเจาะจงเมื่อทําการอัปเดต
/** Inserts text into the first tab of the active document. */
function insertTextInFirstTab() {
// Get the first tab's body.
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const firstTab = doc.getTabs()[0];
const firstDocumentTab = firstTab.asDocumentTab();
const firstTabBody = firstDocumentTab.getBody();
// Append a paragraph and a page break to the first tab's body
// section.
firstTabBody.appendParagraph("A paragraph.");
firstTabBody.appendPageBreak();
}
อัปเดตเนื้อหาแท็บในแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่หรือที่เลือก
ตัวอย่างโค้ดบางส่วนต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีกําหนดเป้าหมายแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่เมื่อทําการอัปเดต
/**
* Inserts text into the active/selected tab of the active
* document.
*/
function insertTextInActiveTab() {
// Get the active/selected tab's body.
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const activeTab = doc.getActiveTab();
const activeDocumentTab = activeTab.asDocumentTab();
const activeTabBody = activeDocumentTab.getBody();
// Append a paragraph and a page break to the active tab's body
// section.
activeTabBody.appendParagraph("A paragraph.");
activeTabBody.appendPageBreak();
}
ตั้งค่าตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์หรือช่วงการเลือกในแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่
ตัวอย่างโค้ดบางส่วนต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีอัปเดตตำแหน่งเคอร์เซอร์หรือช่วงการเลือกภายในแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้ การดำเนินการนี้เกี่ยวข้องกับสคริปต์ที่เชื่อมโยงเท่านั้น
/**
* Changes the user's selection to select all tables within the tab
* with the provided ID.
*/
function selectAllTables(tabId) {
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const tab = doc.getTab(tabId);
const documentTab = tab.asDocumentTab();
// Build a range that encompasses all tables within the specified
// tab.
const rangeBuilder = documentTab.newRange();
const tables = documentTab.getBody().getTables();
for (let i = 0; i < tables.length; i++) {
rangeBuilder.addElement(tables[i]);
}
// Set the document's selection to the tables within the specified
// tab. Note that this actually switches the user's active tab as
// well.
doc.setSelection(rangeBuilder.build());
}
ตั้งค่าแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่หรือที่เลือก
ตัวอย่างโค้ดบางส่วนต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีเปลี่ยนแท็บที่ใช้งานอยู่ของผู้ใช้ ตัวเลือกนี้มีผลกับสคริปต์ที่เชื่อมโยงเท่านั้น
/** * Changes the user's selected tab to the tab immediately following * the currently selected one. Handles child tabs. * *Only changes the selection if there is a tab following the * currently selected one. */ function selectNextTab() { const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); const activeTab = doc.getActiveTab(); // Find the index of the currently active tab. let activeTabIndex = -1; for (let i = 0; i < allTabs.length; i++) { if (allTabs[i].getId() === activeTab.getId()) { activeTabIndex = i; } } // Update the user's selected tab if there is a valid next tab. const nextTabIndex = activeTabIndex + 1; if (nextTabIndex < allTabs.length) { doc.setActiveTab(allTabs[nextTabIndex].getId()); } }
