Dopo aver creato il fulfillment webhook, eseguine il deployment in produzione e connetti all'Azione. I passaggi seguenti mostrano come configurare il tuo ambiente per il deployment in Cloud Functions for Firebase per l'hosting in produzione. Tuttavia, puoi scegliere qualsiasi piattaforma di hosting web che supporti le richieste HTTPS per ospitare il fulfillment.
Se hai già eseguito il deployment del webhook su una piattaforma di hosting web, puoi passa a Collega il webhook all'azione. Tieni presente che l'ultimo I passaggi della procedura seguente variano a seconda che utilizzi Dialogflow o SDK Actions.
Esegui il deployment in Cloud Functions for Firebase
- Scarica e installa Node.js.
Configura e inizializza l'interfaccia a riga di comando di Firebase. Se il comando seguente ha esito negativo con un errore
EACCES, potresti dover modificare le autorizzazioni npm.npm install -g firebase-toolsAutentica lo strumento Firebase con il tuo Account Google:
firebase loginVai alla directory del progetto di azione e inizializza Firebase. Sarai ti viene chiesto di selezionare le funzionalità dell'interfaccia a riga di comando di Firebase da configurare per Progetto Actions. Scegli
Functionse altre funzionalità che ti potrebbero interessare. come Firestore, quindi premi Invio per confermare e continuare:cd <cloud_function_dir> firebase initAssocia lo strumento Firebase al progetto Actions selezionandolo utilizzando i tasti freccia per spostarti nell'elenco dei progetti:
Dopo aver scelto il progetto, lo strumento Firebase avvia la configurazione di Functions che ti chiede quale lingua vuoi usare. Seleziona utilizzando i tasti freccia e premi Invio per continuare.
=== Functions Setup
A functions directory will be created in your project with a Node.js package pre-configured. Functions can be deployed with firebase deploy. ? What language would you like to use to write Cloud Functions? (Use arrow keys) > JavaScript TypeScriptScegli se utilizzare ESLint per rilevare probabili bug e applicare lo stile digitando
YoN:? Do you want to use ESLint to catch probable bugs and enforce style? (Y/n)
Per ottenere le dipendenze del progetto, digita
Ynel prompt:? Do you want to install dependencies with npm now? (Y/n)
Una volta completata la configurazione, verrà visualizzato un output simile al seguente:
✔ Firebase initialization complete!
Installa la dipendenza actions-on-google:
cd <cloud_function_dir>/functions npm install actions-on-googleRecupera le dipendenze di fulfillment ed esegui il deployment della funzione di fulfillment:
npm install firebase deploy --only functionsIl deployment richiede alcuni minuti. Al termine, vedrai l'output in modo simile al seguente. Avrai bisogno dell'URL della funzione per accedere Dialogflow.
✔ Deploy complete!
Project Console: https://console.firebase.google.com/project/exampleproject-123/overview Function URL (cloudFunctionName): https://us-central1-exampleproject-123.cloudfunctions.net/cloudFunctionName
Collega il webhook all'azione
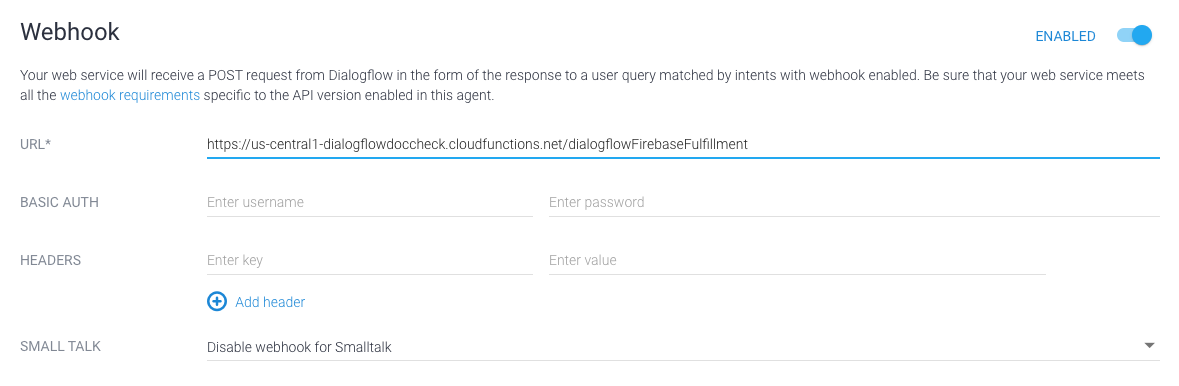
Se utilizzi Dialogflow: nella sezione Console Dialogflow, vai a Fulfillment, imposta il pulsante Webhook su ATTIVATO e sostituiscilo l'URL nel campo URL con l'URL della funzione.
Se utilizzi l'SDK Actions: crea un oggetto
all'interno dell'oggetto conversations per dichiarare il completamento nell'Azione
pacchetto:
{
"actions": [
{
"description": "Default Welcome Intent",
"name": "MAIN",
"fulfillment": {
"conversationName": "myFulfillmentFunction"
},
"intent": {
"name": "actions.intent.MAIN",
"trigger": {
"queryPatterns": [
"talk to myFulfillmentFunction"
]
}
}
}
],
"conversations": {
"myFulfillmentFunction": {
"name": "myFulfillmentFunction",
"url": "https://us-central1-myprojectname-ab123.cloudfunctions.net/cloudFunctionName"
}
},
"locale": "en"
}