A major factor in the delivery time for your agent's messages is whether the user you are attempting to reach has a data connection at the time your agent sends a message. If the user is offline, the RBM platform stores the message and attempts delivery for up to 30 days. If the message can't be delivered by then, it's removed from the system.
There are many reasons and situations where a user may not have connectivity when your agent is attempting to contact them. They could have turned off data to save money on their mobile plan, could be on an airplane without a Wi-Fi connection, or perhaps are on a subway in a tunnel. Depending on the urgency with which your messages need to arrive, your agent needs to gracefully handle offline users by revoking undelivered RBM messages and re-routing those messages through a different channel.
The following sections provide details about how to use a Google Cloud Datastore to keep track of the messages you send and deliver, how to use cron to revoke undelivered messages, and how to re-route those messages through SMS.
Keep track of sent messages
Every message that is sent by your RBM agent must include a unique message ID. To keep track of the messages your agent sends, you need to save the message ID, phone number, and timestamp for each message.
You can use a variety of technologies to store this information, including a Google Cloud Datastore. Cloud Datastore is a highly scalable NoSQL database that automatically handles sharding and replication. It's a great solution for storing non-relational data like the messages sent by an agent. Cloud Datastore depends on having an active Google App Engine instance, so you can use App Engine to host your RBM agent and configure a cron job.
There are client libraries for Cloud Datastore available in many languages. For this example, you can use Node.js and base the RBM agent code on the First Agent Node.js Sample available on the RBM Developer Website. At first, install Cloud Datastore for my Node.js project by running the following command:
npm install --save @google-cloud/datastore
In your agent source code, add a global reference to the Cloud Datastore client library.
// Imports the Google Cloud client library
const Datastore = require('@google-cloud/datastore');
// Creates a client
const datastore = new Datastore({
projectId: PROJECT_ID,
});
With the datastore object created, you can introduce a function for storing the
msisdn, message id, sent time, and delivery state for each message.
/**
* Records an entry in the Cloud Datastore to keep track of the
* messageIds sent to users and the delivery state.
*
* @property {string} msisdn The user's phone number in E.164 format.
* @property {string} messageId The unique message identifier.
* @property {boolean} delivered True if message has been delivered.
*/
function saveMessage(msisdn, messageId, delivered) {
const messageKey = datastore.key(['Message', messageId]);
const dataForMessage = {
key: messageKey,
data: {
id: messageId,
msisdn: msisdn,
lastUpdated: new Date().getTime(),
delivered: delivered
},
};
// Record that the message was sent.
datastore
.save(dataForMessage)
.then(function() {
console.log('saved message successfully');
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error('ERROR:', err);
});
}
With this function in place, you need to call this method whenever your agent
sends a message to a user. When the RBM Node.js client
library
sends RBM messages, the library supplies a response object in the callback
method that contains the messageId for the message that has been sent to the
user.
Following is an example of sending a plain text message to a user and recording the message information after successfully communicating with the RBM API.
let params = {
messageText: 'Hello, World!',
msisdn:'+12223334444',
};
// Send "Hello, World!" to the user.
rbmApiHelper.sendMessage(params,
function(response) {
// Extract the message ID from the response
let messageId = response.config.params.messageId;
// Store the sent state in the Datastore
saveMessage(phoneNumber, messageId, false);
});
After running the code, you can inspect the Datastore from the Google Cloud Console within the Datastore Entities view.
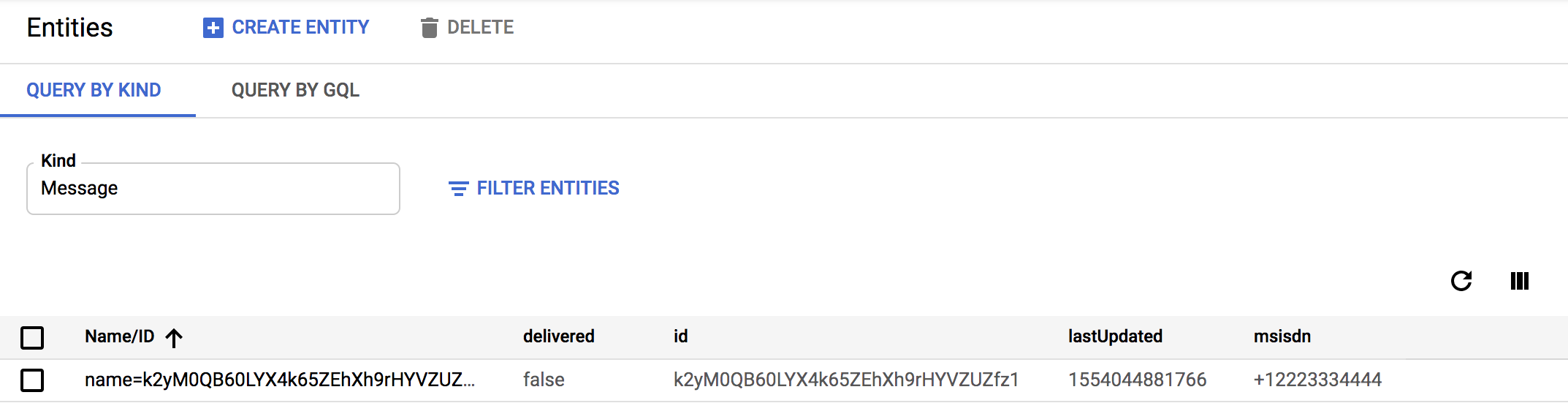
Update the delivery state of messages
Now that your agent stores sent message requests in the Datastore, update the delivery status once the message is successfully delivered to the user's device.
Users' devices send DELIVERED, READ, and IS_TYPING events to RBM agents
over Cloud Pub/Sub. In the handler for Pub/Sub, check for delivered events
and update the Datastore setting for the delivered flag to true.
/**
* Uses the event received by the Pub/Sub subscription to send a
* response to the client's device.
* @param {object} userEvent The JSON object of a message
* received by the subscription.
*/
function handleMessage(userEvent) {
if (userEvent.senderPhoneNumber != undefined) {
let msisdn = userEvent.senderPhoneNumber;
let messageId = userEvent.messageId;
let eventType = userEvent.eventType;
if(eventType === 'DELIVERED') {
saveMessage(msisdn, messageId, true);
}
// TODO: Process message and create RBM response
}
}
The agent saves outgoing messages to the Datastore and updates the data when it receives a delivery notification. In the next section, see how to set up a cron job on Google's App Engine to run every 10 minutes to monitor undelivered messages.
Cron on Google's App Engine
You can use cron jobs to schedule tasks at different intervals. In Google's App Engine, a cron job is configured with a description, a URL, and an interval.
In Node.js apps, you configure these in a cron.yaml file, which you can deploy
to App Engine using the Google Cloud SDK.
Read about other language configuration setups in Scheduling jobs with
cron.yaml.
Because the cron task needs a URL, you need to add a URL endpoint to the express app router to be called by cron. This webhook is responsible for querying the Datastore for old messages, deleting them from the RBM platform, and sending them to the user over SMS.
router.get('/expireMessages', function(req, res, next) {
// TOOD: Query the Datastore for undelivered messages,
// remove them from the RBM platform, and send them over SMS
res.status(200).send();
});
Following is the cron.yaml file configuration to execute this endpoint every 10 minutes.
cron:
- description: "Processing expired RBM messages"
url: /expireMessages
schedule: every 10 mins
To deploy the cron tasks to App Engine, run the following command:
gcloud app deploy cron.yaml
After deployment, App engine automatically configures the cron task, and the task is viewable under App Engine > Cron jobs.
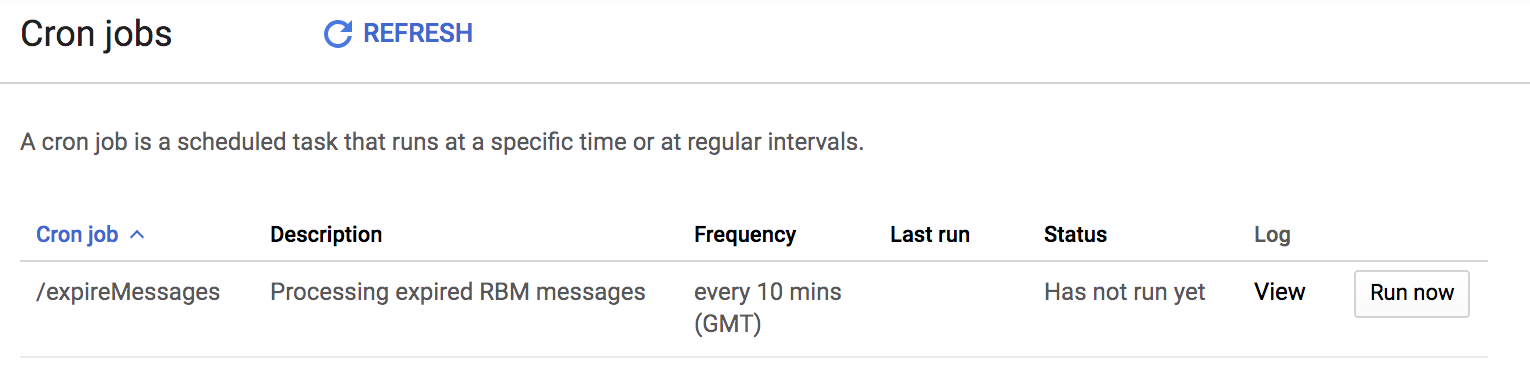
Query the Datastore for undelivered messages
In the webhook for the cron job you set up in the prior section, you need to add
logic to look up all sent messages that have a delivered state equal to false
and that have a lastUpdated time older than a predefined timeout that makes
sense for our use case. In this example, expire messages older than an hour.
In order to support a composite query like this, the Datastore needs to have a
composite index containing both the delivered and lastUpdated properties. To
do this, you can create a file in your project called index.yaml with the
following information:
indexes:
- kind: Message
properties:
- name: delivered
direction: asc
- name: lastUpdated
direction: desc
Similar to deploying the cron job you defined previously, use the Google Cloud SDK to deploy the composite index you defined with the following command:
gcloud datastore create-indexes index.yaml
After deployment, App engine automatically configures the index, and the index is shown under Datastore > Indexes.
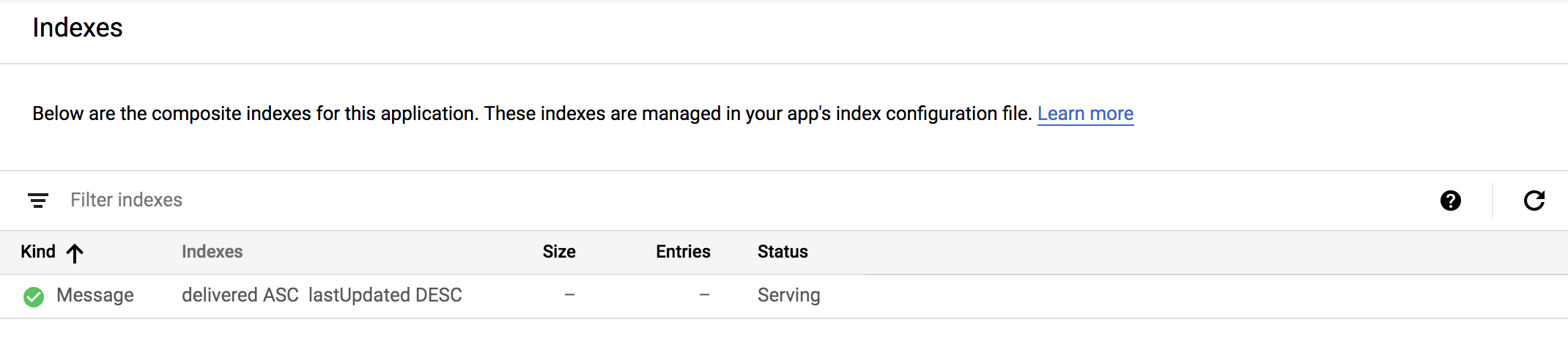
With the index defined, you can go back to the webhook you created for the cron job and complete the message expiration logic:
router.get('/expireMessages', function(req, res, next) {
// Milliseconds in an hour
const TIMEOUT = 3600000;
// Threshold is current time minus one hour
const OLD_MESSAGE_THRESHOLD = new Date().getTime() - TIMEOUT;
// Create a query to find old undelivered messages
const query = datastore
.createQuery('Message')
.filter('delivered', '=', false)
.filter('lastUpdated', '<', OLD_MESSAGE_THRESHOLD);
// Execute the query
datastore.runQuery(query).then((results) => {
for(var i = 0; i < results[0].length; i++) {
let msisdn = results[0][i].msisdn;
let messageId = results[0][i].id;
// Stop the message from being sent
rbmApiHelper.revokeMessage(msisdn, messageId);
// Remove the message from the Datastore
datastore.delete(results[0][i][datastore.KEY]);
// TODO: Send the user the message as SMS
}
});
res.status(200).send();
});
RBM does not natively support SMS fallback, so you will need to implement the logic to send your undelivered messages over SMS.
Wrap-up and summary
To handle offline users, you can build revocation logic for undelivered RBM messages. The amount of time you use before expiring the message depends on how time-sensitive the information you transmitting is. With time-sensitive information, a recommended timeout is less than two hours.
This example uses a Cloud Datastore and Google App Engine to manage the storage, query, and revocation process, but any storage mechanism for keeping track of your sent and delivered messages should work.
Good luck, and happy coding!