Page Summary
-
Python's built-in string class, "str," offers many features for working with text.
-
Strings in Python are immutable, meaning new strings are created when modifications are needed.
-
Characters and substrings can be accessed using zero-based indexing and the handy slice syntax.
-
Python provides string methods for common operations like changing case, removing whitespace, and searching.
-
String formatting, including f-strings and the older % operator, allows for controlled output of string and variable values.
-
Python supports both unicode and byte strings, with methods to convert between them.
-
Conditional logic in Python uses indentation and a colon to define code blocks, not curly braces.
Python has a built-in string class named "str" with many handy features (there is an older module named "string" which you should not use). String literals can be enclosed by either double or single quotes, although single quotes are more commonly used. Backslash escapes work the usual way within both single and double quoted literals -- e.g. \n \' \". A double quoted string literal can contain single quotes without any fuss (e.g. "I didn't do it") and likewise single quoted string can contain double quotes. A string literal can span multiple lines, but there must be a backslash \ at the end of each line to escape the newline. String literals inside triple quotes, """ or ''', can span multiple lines of text.
Python strings are "immutable" which means they cannot be changed after they are created (Java strings also use this immutable style). Since strings can't be changed, we construct *new* strings as we go to represent computed values. So for example the expression ('hello' + 'there') takes in the 2 strings 'hello' and 'there' and builds a new string 'hellothere'.
Characters in a string can be accessed using the standard [ ] syntax, and like Java and C++, Python uses zero-based indexing, so if s is 'hello' s[1] is 'e'. If the index is out of bounds for the string, Python raises an error. The Python style (unlike Perl) is to halt if it can't tell what to do, rather than just make up a default value. The handy "slice" syntax (below) also works to extract any substring from a string. The len(string) function returns the length of a string. The [ ] syntax and the len() function actually work on any sequence type -- strings, lists, etc.. Python tries to make its operations work consistently across different types. Python newbie gotcha: don't use "len" as a variable name to avoid blocking out the len() function. The '+' operator can concatenate two strings. Notice in the code below that variables are not pre-declared -- just assign to them and go.
s = 'hi' print(s[1]) ## i print(len(s)) ## 2 print(s + ' there') ## hi there
Unlike Java, the '+' does not automatically convert numbers or other types to string form. The str() function converts values to a string form so they can be combined with other strings.
pi = 3.14 ##text = 'The value of pi is ' + pi ## NO, does not work text = 'The value of pi is ' + str(pi) ## yes
For numbers, the standard operators, +, /, * work in the usual way. There is no ++ operator, but +=, -=, etc. work. If you want integer division, use 2 slashes -- e.g. 6 // 5 is 1
The "print" function normally prints out one or more python items followed by a newline. A "raw" string literal is prefixed by an 'r' and passes all the chars through without special treatment of backslashes, so r'x\nx' evaluates to the length-4 string 'x\nx'. "print" can take several arguments to change how it prints things out (see python.org print function definition) like setting "end" to "" to no longer print a newline after it finishes printing out all of the items.
raw = r'this\t\n and that' # this\t\n and that print(raw) multi = """It was the best of times. It was the worst of times.""" # It was the best of times. # It was the worst of times. print(multi)
String Methods
Here are some of the most common string methods. A method is like a function, but it runs "on" an object. If the variable s is a string, then the code s.lower() runs the lower() method on that string object and returns the result (this idea of a method running on an object is one of the basic ideas that make up Object Oriented Programming, OOP). Here are some of the most common string methods:
- s.lower(), s.upper() -- returns the lowercase or uppercase version of the string
- s.strip() -- returns a string with whitespace removed from the start and end
- s.isalpha()/s.isdigit()/s.isspace()... -- tests if all the string chars are in the various character classes
- s.startswith('other'), s.endswith('other') -- tests if the string starts or ends with the given other string
- s.find('other') -- searches for the given other string (not a regular expression) within s, and returns the first index where it begins or -1 if not found
- s.replace('old', 'new') -- returns a string where all occurrences of 'old' have been replaced by 'new'
- s.split('delim') -- returns a list of substrings separated by the given delimiter. The delimiter is not a regular expression, it's just text. 'aaa,bbb,ccc'.split(',') -> ['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']. As a convenient special case s.split() (with no arguments) splits on all whitespace chars.
- s.join(list) -- opposite of split(), joins the elements in the given list together using the string as the delimiter. e.g. '---'.join(['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']) -> aaa---bbb---ccc
A google search for "python str" should lead you to the official python.org string methods which lists all the str methods.
Python does not have a separate character type. Instead an expression like s[8] returns a string-length-1 containing the character. With that string-length-1, the operators ==, <=, ... all work as you would expect, so mostly you don't need to know that Python does not have a separate scalar "char" type.
String Slices
The "slice" syntax is a handy way to refer to sub-parts of sequences -- typically strings and lists. The slice s[start:end] is the elements beginning at start and extending up to but not including end. Suppose we have s = "Hello"
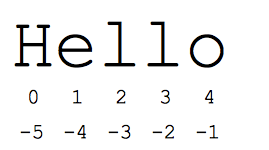
- s[1:4] is 'ell' -- chars starting at index 1 and extending up to but not including index 4
- s[1:] is 'ello' -- omitting either index defaults to the start or end of the string
- s[:] is 'Hello' -- omitting both always gives us a copy of the whole thing (this is the pythonic way to copy a sequence like a string or list)
- s[1:100] is 'ello' -- an index that is too big is truncated down to the string length
The standard zero-based index numbers give easy access to chars near the start of the string. As an alternative, Python uses negative numbers to give easy access to the chars at the end of the string: s[-1] is the last char 'o', s[-2] is 'l' the next-to-last char, and so on. Negative index numbers count back from the end of the string:
- s[-1] is 'o' -- last char (1st from the end)
- s[-4] is 'e' -- 4th from the end
- s[:-3] is 'He' -- going up to but not including the last 3 chars.
- s[-3:] is 'llo' -- starting with the 3rd char from the end and extending to the end of the string.
It is a neat truism of slices that for any index n, s[:n] + s[n:] == s. This works even for n negative or out of bounds. Or put another way s[:n] and s[n:] always partition the string into two string parts, conserving all the characters. As we'll see in the list section later, slices work with lists too.
String formatting
One neat thing python can do is automatically convert objects into a string suitable for printing. Two built-in ways to do this are formatted string literals, also called "f-strings", and invoking str.format().
Formatted string literals
You'll often see formatted string literals used in situations like:
value = 2.791514 print(f'approximate value = {value:.2f}') # approximate value = 2.79 car = {'tires':4, 'doors':2} print(f'car = {car}') # car = {'tires': 4, 'doors': 2}
A formatted literal string is prefixed with 'f' (like the 'r' prefix used for raw strings). Any text outside of curly braces '{}' is printed out directly. Expressions contained in '{}' are are printed out using the format specification described in the format spec. There are lots of neat things you can do with the formatting including truncation and conversion to scientific notation and left/right/center alignment.
f-strings are very useful when you'd like to print out a table of objects and would like the columns representing different object attributes to be aligned like
address_book = [{'name':'N.X.', 'addr':'15 Jones St', 'bonus': 70}, {'name':'J.P.', 'addr':'1005 5th St', 'bonus': 400}, {'name':'A.A.', 'addr':'200001 Bdwy', 'bonus': 5},] for person in address_book: print(f'{person["name"]:8} || {person["addr"]:20} || {person["bonus"]:>5}') # N.X. || 15 Jones St || 70 # J.P. || 1005 5th St || 400 # A.A. || 200001 Bdwy || 5
String %
Python also has an older printf()-like facility to put together a string. The % operator takes a printf-type format string on the left (%d int, %s string, %f/%g floating point), and the matching values in a tuple on the right (a tuple is made of values separated by commas, typically grouped inside parentheses):
# % operator text = "%d little pigs come out, or I'll %s, and I'll %s, and I'll blow your %s down." % (3, 'huff', 'puff', 'house')
The above line is kind of long -- suppose you want to break it into separate lines. You cannot just split the line after the '%' as you might in other languages, since by default Python treats each line as a separate statement (on the plus side, this is why we don't need to type semi-colons on each line). To fix this, enclose the whole expression in an outer set of parenthesis -- then the expression is allowed to span multiple lines. This code-across-lines technique works with the various grouping constructs detailed below: ( ), [ ], { }.
# Add parentheses to make the long line work: text = ( "%d little pigs come out, or I'll %s, and I'll %s, and I'll blow your %s down." % (3, 'huff', 'puff', 'house'))
That's better, but the line is still a little long. Python lets you cut a line up into chunks, which it will then automatically concatenate. So, to make this line even shorter, we can do this:
# Split the line into chunks, which are concatenated automatically by Python text = ( "%d little pigs come out, " "or I'll %s, and I'll %s, " "and I'll blow your %s down." % (3, 'huff', 'puff', 'house'))
Strings (Unicode vs bytes)
Regular Python strings are unicode.
Python also supports strings composed of plain bytes (denoted by the prefix 'b' in front of a string literal) like:
> byte_string = b'A byte string' > byte_string b'A byte string'
A unicode string is a different type of object from a byte string but various libraries such as regular expressions work correctly if passed either type of string.
To convert a regular Python string to bytes, call the encode() method on the string. Going the other direction, the byte string decode() method converts encoded plain bytes to a unicode string:
> ustring = 'A unicode \u018e string \xf1' > b = ustring.encode('utf-8') > b b'A unicode \xc6\x8e string \xc3\xb1' ## bytes of utf-8 encoding. Note the b-prefix. > t = b.decode('utf-8') ## Convert bytes back to a unicode string > t == ustring ## It's the same as the original, yay!True
In the file-reading section, there's an example that shows how to open a text file with some encoding and read out unicode strings.
If Statement
Python does not use { } to enclose blocks of code for if/loops/function etc.. Instead, Python uses the colon (:) and indentation/whitespace to group statements. The boolean test for an if does not need to be in parenthesis (big difference from C++/Java), and it can have *elif* and *else* clauses (mnemonic: the word "elif" is the same length as the word "else").
Any value can be used as an if-test. The "zero" values all count as false: None, 0, empty string, empty list, empty dictionary. There is also a Boolean type with two values: True and False (converted to an int, these are 1 and 0). Python has the usual comparison operations: ==, !=, <, <=, >, >=. Unlike Java and C, == is overloaded to work correctly with strings. The boolean operators are the spelled out words *and*, *or*, *not* (Python does not use the C-style && || !). Here's what the code might look like for a health app providing drink recommendations throughout the day -- notice how each block of then/else statements starts with a : and the statements are grouped by their indentation:
if time_hour >= 0 and time_hour <= 24: print('Suggesting a drink option...') if mood == 'sleepy' and time_hour < 10: print('coffee') elif mood == 'thirsty' or time_hour < 2: print('lemonade') else: print('water')
I find that omitting the ":" is my most common syntax mistake when typing in the above sort of code, probably since that's an additional thing to type vs. my C++/Java habits. Also, don't put the boolean test in parentheses -- that's a C/Java habit. If the code is short, you can put the code on the same line after ":", like this (this applies to functions, loops, etc. also), although some people feel it's more readable to space things out on separate lines.
if time_hour < 10: print('coffee') else: print('water')
Exercise: string1.py
To practice the material in this section, try the string1.py exercise in the Basic Exercises.