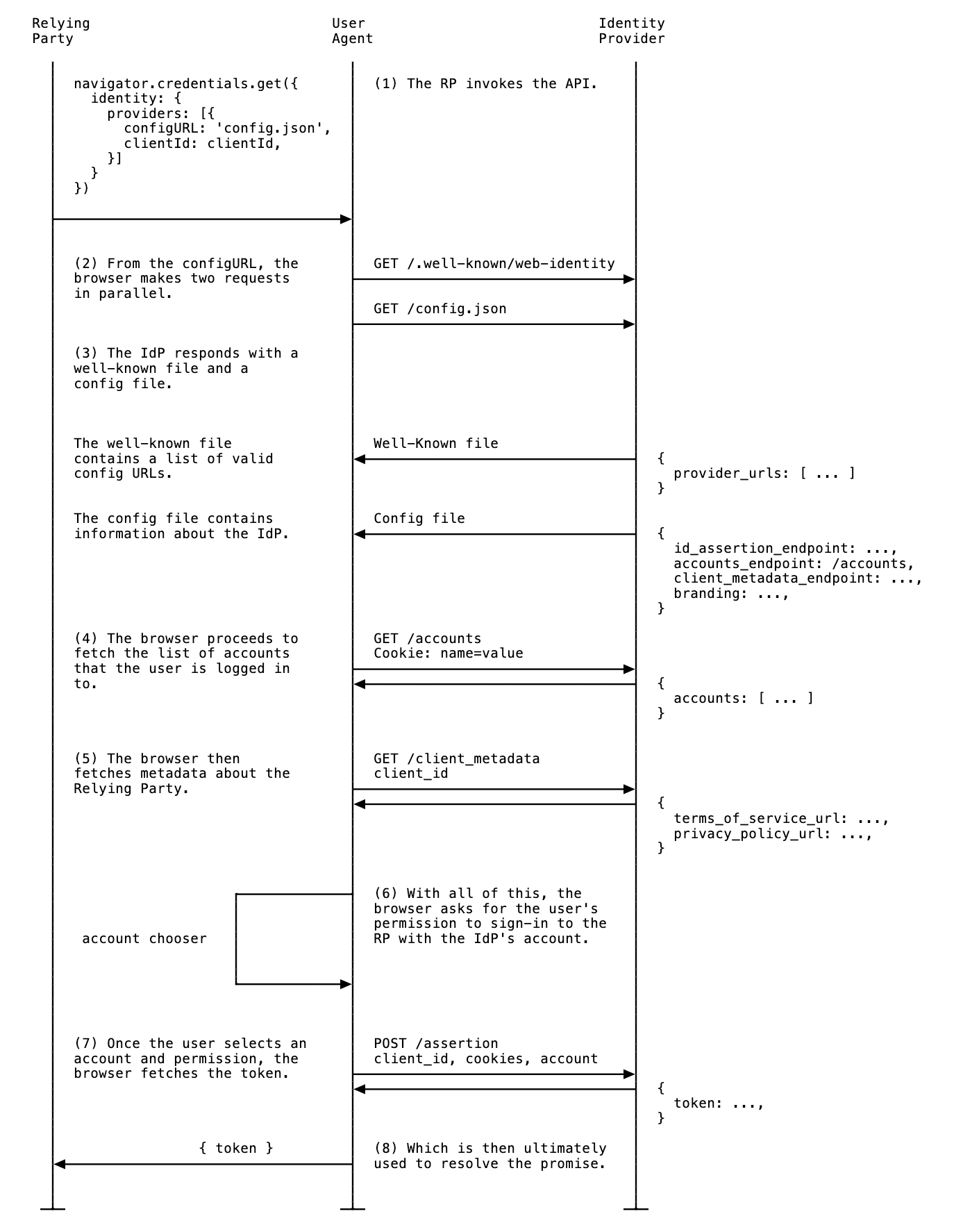
FedCM 实现包括针对身份提供方 (IdP) 和依赖方 (RP) 的几个核心步骤。请参阅文档,了解如何在 RP 端实现 FedCM。
IdPs 必须完成以下步骤才能实现 FedCM:
创建 well-known 文件
为防止跟踪器滥用 API,必须从 IdP 的 eTLD+1 的 /.well-known/web-identity 中提供 well-known 文件。
知名文件可以包含以下属性:
| 属性 | 必需 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
provider_urls
|
必填 | IdP 配置文件路径的数组。如果指定了 accounts_endpoint 和 login_url,则会被忽略(但仍是必需的)。 |
accounts_endpoint
|
推荐,需要 login_url |
账号端点的网址。这样,您就可以支持多个配置,前提是每个配置文件都使用相同的 login_url 和 accounts_endpoint 网址。注意:Chrome 132 开始支持此参数。 |
login_url
|
推荐,需要 accounts_endpoint |
用户登录 IdP 的登录页网址。这样,您就可以支持多个配置,前提是每个配置文件都使用相同的 login_url 和 accounts_endpoint。注意:Chrome 132 及更高版本支持此参数。 |
例如,如果 IdP 端点在 https://accounts.idp.example/ 下提供,则必须在 https://idp.example/.well-known/web-identity 下提供 well-known 文件以及 IdP 配置文件。以下是众所周知的文件内容示例:
{
"provider_urls": ["https://accounts.idp.example/config.json"]
}
IdP 可以通过在 well-known 文件中指定 accounts_endpoint 和 login_url 来容纳多个 IdP 配置文件。
在以下情况下,此功能非常有用:
- IdP 需要支持多个不同的测试和生产配置。
- IdP 需要支持每个区域的不同配置(例如
eu-idp.example和us-idp.example)。
如需支持多种配置(例如,区分测试环境和生产环境),IdP 必须指定 accounts_endpoint 和 login_url:
{
// This property is required, but will be ignored when IdP supports
// multiple configs (when `accounts_endpoint` and `login_url` are
// specified), as long as `accounts_endpoint` and `login_url` in
// that config file match those in the well-known file.
"provider_urls": [ "https://idp.example/fedcm.json" ],
// Specify accounts_endpoint and login_url properties to support
// multiple config files.
// Note: The accounts_endpoint and login_url must be identical
// across all config files. Otherwise,
// the configurations won't be supported.
"accounts_endpoint": "https://idp.example/accounts",
"login_url": "https://idp.example/login"
}
创建 IdP 配置文件和端点
IdP 配置文件为浏览器提供了必需端点的列表。IdP 必须托管一个或多个配置文件以及所需的端点和网址。所有 JSON 响应都必须使用 application/json content-type 提供。
配置文件的网址由向在 RP 上执行的 navigator.credentials.get() 调用提供的值决定。
const credential = await navigator.credentials.get({
identity: {
context: 'signup',
providers: [{
configURL: 'https://accounts.idp.example/config.json',
clientId: '********',
nonce: '******'
}]
}
});
const { token } = credential;
RP 会将配置文件的网址传递给 FedCM API 调用,以便用户登录:
// Executed on RP's side:
const credential = await navigator.credentials.get({
identity: {
context: 'signup',
providers: [{
// To allow users to sign in with an IdP using FedCM, RP specifies the IdP's config file URL:
configURL: 'https://accounts.idp.example/fedcm.json',
clientId: '********',
});
const { token } = credential;
浏览器将使用不含 Origin 标头或 Referer 标头的 GET 请求提取配置文件。请求不含 Cookie,也不遵循重定向。这样做可以有效防止 IdP 了解是谁发出了请求以及哪个 RP 正在尝试连接。例如:
GET /config.json HTTP/1.1
Host: accounts.idp.example
Accept: application/json
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentity
IdP 必须实现一个会以 JSON 响应的配置端点。JSON 包含以下属性:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
accounts_endpoint(必需) |
账号端点的网址。 |
accounts.include (可选)
|
自定义账号标签字符串,用于确定使用此配置文件时应返回哪些账号,例如: "accounts": {"include": "developer"}。
IdP 可以按如下方式实现自定义账号标签:
例如,IdP 会实现指定了 "accounts": {"include": "developer"} 的 "https://idp.example/developer-config.json" 配置文件。IdP 还会使用账号端点中的 labels 参数将部分账号标记为 "developer" 标签。当 RP 调用 navigator.credentials.get() 并指定 "https://idp.example/developer-config.json" 配置文件时,系统只会返回具有 "developer" 标签的账号。注意:Chrome 132 开始支持自定义账号标签。 |
client_metadata_endpoint(可选) |
客户端元数据端点的网址。 |
id_assertion_endpoint(必需) |
ID 断言端点的网址。 |
disconnect(可选) |
断开连接端点的网址。 |
login_url(必需) |
用户登录 IdP 的登录页网址。 |
branding(可选) |
包含各种品牌选项的对象。 |
branding.background_color(可选) |
用于设置“继续以...身份操作”按钮背景颜色的品牌化选项。使用相关的 CSS 语法,即 hex-color、hsl()、rgb() 或 named-color。 |
branding.color(可选) |
用于设置“继续以...身份操作”按钮文本颜色的品牌选项。使用相关的 CSS 语法,即 hex-color、hsl()、rgb() 或 named-color。 |
branding.icons(可选) |
图标对象的数组。这些图标会显示在登录对话框中。图标对象有两个参数:
|
modes |
包含有关 FedCM 界面在不同模式下显示方式的规范的对象:
|
modes.active
|
包含允许在特定模式下自定义 FedCM 行为的属性的对象。modes.active 和 modes.passive 都可以包含以下参数:
注意:Chrome 132 及更高版本支持“使用其他账号”功能和活跃模式。 |
modes.passive
|
以下是身份提供程序的响应正文示例:
{
"accounts_endpoint": "/accounts.example",
"client_metadata_endpoint": "/client_metadata.example",
"id_assertion_endpoint": "/assertion.example",
"disconnect_endpoint": "/disconnect.example",
"login_url": "/login",
// When RPs use this config file, only those accounts will be
//returned that include `developer` label in the accounts endpoint.
"accounts": {"include": "developer"},
"modes": {
"active": {
"supports_use_other_account": true,
}
},
"branding": {
"background_color": "green",
"color": "#FFEEAA",
"icons": [{
"url": "https://idp.example/icon.ico",
"size": 25
}]
}
}
浏览器提取配置文件后,会向 IdP 端点发送后续请求:
使用其他账号
如果 IdP 支持多个账号或替换现有账号,用户可以切换到与其当前登录的账号不同的账号。
如需允许用户选择其他账号,IdP 必须在配置文件中指定此功能:
{
"accounts_endpoint" : "/accounts.example",
"modes": {
"active": {
// Allow the user to choose other account (false by default)
"supports_use_other_account": true
}
// "passive" mode can be configured separately
}
}
账号端点
IdP 的账号端点会返回用户在 IdP 中登录的账号列表。如果 IdP 支持多个账号,此端点将返回所有已登录的账号。
浏览器发送包含 SameSite=None 的 Cookie 的 GET 请求,但不包含 client_id 参数、Origin 标头或 Referer 标头。这可有效防止 IdP 了解用户尝试登录哪个 RP。例如:
GET /accounts.example HTTP/1.1
Host: accounts.idp.example
Accept: application/json
Cookie: 0x23223
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentity
收到请求后,服务器应:
- 验证请求是否包含
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentityHTTP 标头。 - 将会话 Cookie 与已登录账号的 ID 进行匹配。
- 响应并提供账号列表。
浏览器预期 JSON 响应包含 accounts 属性,其中包含具有以下属性的账号信息数组:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
id(必需) |
用户的唯一 ID。 |
name(必需) |
用户的名字和姓氏。 |
email(必需) |
用户的电子邮件地址。 |
given_name(可选) |
用户的名字。 |
picture(可选) |
用户头像图片的网址。 |
approved_clients(可选) |
用户已注册的 RP 客户端 ID 的数组。 |
login_hints(可选) |
一个数组,其中包含 IdP 支持的用于指定账号的所有可能的过滤条件类型。RP 可以使用 loginHint 属性调用 navigator.credentials.get(),以有选择地显示指定的账号。 |
domain_hints(可选) |
账号关联的所有网域的数组。RP 可以使用 domainHint 属性调用 navigator.credentials.get() 来过滤账号。 |
labels(可选)
|
与账号关联的自定义账号标签的字符串数组。 IdP 可以按如下方式实现自定义账号标签:
例如,IdP 会实现指定了 "accounts": {"include": "developer"} 的 https://idp.example/developer-config.json 配置文件。IdP 还会使用 账号端点中的 labels 参数将部分账号标记为 "developer" 标签。当 RP 调用 navigator.credentials.get() 并指定 https://idp.example/developer-config.json 配置文件时,系统只会返回具有 "developer" 标签的账号。自定义账号标签与登录提示和域名提示不同,它们由 IdP 服务器完全维护,RP 仅指定要使用的配置文件。 注意:Chrome 132 开始支持自定义账号标签。 |
响应正文示例:
{
"accounts": [{
"id": "1234",
"given_name": "John",
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john_doe@idp.example",
"picture": "https://idp.example/profile/123",
// Ids of those RPs where this account can be used
"approved_clients": ["123", "456", "789"],
// This account has 'login_hints`. When an RP calls `navigator.credentials.get()`
// with a `loginHint` value specified, for example, `exampleHint`, only those
// accounts will be shown to the user whose 'login_hints' array contains the `exampleHint`.
"login_hints": ["demo1", "exampleHint"],
// This account is labelled. IdP can implement a specific config file for a
// label, for example, `https://idp.example/developer-config.json`. Like that
// RPs can filter out accounts by calling `navigator.credentials.get()` with
// `https://idp.example/developer-config.json` config file.
"labels": ["hr", "developer"]
}, {
"id": "5678",
"given_name": "Johnny",
"name": "Johnny",
"email": "johnny@idp.example",
"picture": "https://idp.example/profile/456",
"approved_clients": ["abc", "def", "ghi"],
"login_hints": ["demo2"],
"domain_hints": ["@domain.example"]
}]
}
如果用户未登录,请响应 HTTP 401(未经授权)。
返回的账号列表将由浏览器使用,RP 无法使用。
ID 断言端点
IdP 的 ID 断言端点会为其已登录的用户返回断言。当用户使用 navigator.credentials.get() 调用登录 RP 网站时,浏览器会向此端点发送包含 SameSite=None 和内容类型为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 的 Cookie 的 POST 请求,其中包含以下信息:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
client_id(必需) |
RP 的客户端标识符。 |
account_id(必需) |
登录用户的唯一 ID。 |
disclosure_text_shown |
结果为 "true" 或 "false" 字符串(而非布尔值)。在以下情况下,结果为 "false":
|
is_auto_selected |
如果对 RP 执行了自动重新身份验证,is_auto_selected 表示 "true"。否则为 "false"。这有助于支持更多与安全相关的功能。例如,有些用户可能更倾向于更高级别的安全性,这需要在身份验证过程中明确由用户参与。如果 IdP 收到没有此类中介的令牌请求,则可以以其他方式处理该请求。例如,返回一个错误代码,以便 RP 可以使用 mediation: required 再次调用 FedCM API。 |
fields(可选)
|
字符串数组,用于指定 RP 需要 IdP 与其分享的用户信息(“name”“email”“picture”)。 浏览器将发送 fields、disclosure_text_shown 和 disclosure_shown_for,在 POST 请求中列出指定字段,如以下示例所示。注意:Chrome 132 开始支持“Fields”参数。 |
params(可选)
|
允许指定其他自定义键值参数的任何有效 JSON 对象,例如:
params 值将序列化为 JSON,然后进行百分比编码。注意:Chrome 132 及更高版本支持 Parameters API。 |
HTTP 标头示例:
POST /assertion.example HTTP/1.1
Host: accounts.idp.example
Origin: https://rp.example/
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Cookie: 0x23223
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentity
// disclosure_text_shown is set to 'false', as the 'name' field value is missing in 'fields' array
// params value is serialized to JSON and then percent-encoded.
account_id=123&client_id=client1234&disclosure_text_shown=false&is_auto_selected=true¶ms=%22%7B%5C%22nonce%5C%22%3A%5C%22nonce-value%5C%22%7D%22.%0D%0A4&disclosure_text_shown=true&fields=email,picture&disclosure_shown_for=email,picture
收到请求后,服务器应:
- 使用 CORS(跨源资源共享)响应请求。
- 验证请求是否包含
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentityHTTP 标头。 - 将
Origin标头与client_id确定的 RP 源进行匹配。如果不匹配,请拒绝。 - 将
account_id与已登录账号的 ID 进行匹配。如果不一致,则拒绝。 - 使用令牌进行响应。如果请求被拒绝,请返回错误响应。
IdP 可以决定如何发放令牌。通常,该令牌使用账号 ID、客户端 ID、签发者来源和 Nonce 等信息进行签名,以便 RP 能够验证令牌是否真实。
浏览器希望 JSON 响应包含以下属性:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
token |
令牌是包含与身份验证相关的声明的字符串。 |
continue_on |
用于启用多步登录流程的重定向网址。 |
浏览器会将返回的令牌传递给 RP,以便 RP 验证身份验证。
{
// IdP can respond with a token to authenticate the user
"token": "***********"
}
“继续操作”功能
IdP 可以在 ID 断言端点响应中提供重定向网址,以启用多步登录流程。当 IdP 需要请求更多信息或权限时,此功能非常有用,例如:
- 访问用户服务器端资源的权限。
- 验证联系信息是否是最新的。
- 家长控制。
身份断言端点可以返回一个 continue_on 属性,其中包含指向身份断言端点的绝对路径或相对路径。
{
// In the id_assertion_endpoint, instead of returning a typical
// "token" response, the IdP decides that it needs the user to
// continue on a popup window:
"continue_on": "https://idp.example/continue_on_url"
}
如果响应包含 continue_on 参数,系统会打开一个新的弹出式窗口,并将用户定向到指定的路径。用户与 continue_on 页面互动后,IdP 应调用 IdentityProvider.resolve(),并将令牌作为参数传递,以便解析原始 navigator.credentials.get() 调用的 promise:
document.getElementById('example-button').addEventListener('click', async () => {
let accessToken = await fetch('/generate_access_token.cgi');
// Closes the window and resolves the promise (that is still hanging
// in the relying party's renderer) with the value that is passed.
IdentityProvider.resolve(accessToken);
});
然后,浏览器会自动关闭弹出式窗口,并将令牌返回给 API 调用方。父窗口 (RP) 和弹出式窗口 (IdP) 之间的唯一通信方式是一次性 IdentityProvider.resolve() 调用。
如果用户拒绝请求,IdP 可以通过调用 IdentityProvider.close() 关闭窗口。
IdentityProvider.close();
Continuation API 需要用户明确互动(点击)才能正常运行。Continuation API 与不同中介模式的配合使用方式如下:
- 在被动模式下:
mediation: 'optional'(默认):Continuation API 仅适用于用户手势,例如点击页面或 FedCM 界面上的按钮。如果在没有用户手势的情况下触发自动重新身份验证,系统不会打开弹出式窗口,并且会拒绝该 promise。mediation: 'required':始终要求用户互动,因此 Continuation API 始终有效。
- 在活动模式下:
- 始终需要用户激活。Continuation API 是兼容的。
如果用户出于某种原因更改了弹出式窗口中的账号(例如,IdP 提供了“使用其他账号”功能,或者在委托情况下),resolve 调用会接受一个可选的第二个参数,允许执行以下操作:
IdentityProvider.resolve(token, {accountId: '1234');
返回错误响应
id_assertion_endpoint 还可以返回“错误”响应,其中包含两个可选字段:
code:IdP 可以从 OAuth 2.0 指定的错误列表中选择一个已知错误(invalid_request、unauthorized_client、access_denied、server_error和temporarily_unavailable),也可以使用任何任意字符串。如果是后者,Chrome 会使用通用错误消息呈现错误界面,并将代码传递给 RP。url:用于标识包含错误信息的人类可读网页,以向用户提供有关错误的更多信息。此字段对用户很有用,因为浏览器无法在内置界面中提供丰富的错误消息。例如:后续步骤的链接或客户服务联系信息。如果用户想要详细了解错误以及如何修正,可以通过浏览器界面访问提供的页面,了解更多详情。网址必须与 IdPconfigURL位于同一网站上。
// id_assertion_endpoint response
{
"error" : {
"code": "access_denied",
"url" : "https://idp.example/error?type=access_denied"
}
}
自定义账号标签
借助自定义账号标签,IdP 可以为用户账号添加标签注释,RP 可以选择仅提取具有特定标签的账号,方法是为该特定标签指定 configURL。当 RP 需要按特定条件滤除账号时,此方法会很有用,例如,仅显示角色专用账号,例如 "developer" 或 "hr"。
您也可以使用网域提示和登录提示功能进行类似的过滤,只需在 navigator.credentials.get() 调用中指定这些功能即可。不过,自定义账号标签可以通过指定配置文件来过滤用户,这在使用多个 config网址 时特别有用。自定义账号标签也不同,因为它们是从 IdP 服务器提供的,而不是从 RP 提供的,例如登录或网域提示。
假设某个 IdP 想要区分 "developer" 账号和 "hr" 账号。为此,IdP 需要分别为 "developer" 和 "hr" 支持两个 config网址:
- 开发者配置文件
https://idp.example/developer/fedcm.json具有"developer"标签,企业配置文件https://idp.example/hr/fedcm.json具有"hr"标签,如下所示:
// The developer config file at `https://idp.example/developer/fedcm.json`
{
"accounts_endpoint": "https://idp.example/accounts",
"client_metadata_endpoint": "/client_metadata",
"login_url": "https://idp.example/login",
"id_assertion_endpoint": "/assertion",
"accounts": {
// Account label
"include": "developer"
}
}
// The hr config file at `https://idp.example/hr/fedcm.json`
{
"accounts_endpoint": "https://idp.example/accounts",
"client_metadata_endpoint": "/client_metadata",
"login_url": "https://idp.example/login",
"id_assertion_endpoint": "/assertion",
"accounts": {
// Account label
"include": "hr"
}
}
- 采用这种设置时,well-known 文件应包含
accounts_endpoint和login_url,以允许多个 config网址:
{
"provider_urls": [ "https://idp.example/fedcm.json" ],
"accounts_endpoint": "https://idp.example/accounts",
"login_url": "https://idp.example/login"
}
- 常见 IdP accounts 端点(在此示例中为
https://idp.example/accounts)会返回一个账号列表,其中包含每个账号对应的labels属性,该属性在数组中包含分配的标签:
{
"accounts": [{
"id": "123",
"given_name": "John",
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john_doe@idp.example",
"picture": "https://idp.example/profile/123",
"labels": ["developer"]
}], [{
"id": "4567",
"given_name": "Jane",
"name": "Jane Doe",
"email": "jane_doe@idp.example",
"picture": "https://idp.example/profile/4567",
"labels": ["hr"]
}]
}
当 RP 想要允许 "hr" 用户登录时,可以在 navigator.credentials.get() 调用中指定 config网址 https://idp.example/hr/fedcm.json:
let { token } = await navigator.credentials.get({
identity: {
providers: [{
clientId: '1234',
nonce: '234234',
configURL: 'https://idp.example/hr/fedcm.json',
},
}
});
因此,用户只能使用账号 ID 4567 登录。
浏览器会静默隐藏 123 的账号 ID,以免向用户提供此网站上的 IdP 不支持的账号。
- 标签是字符串。如果
labels数组或include字段包含非字符串内容,则系统会忽略该内容。 - 如果未在
configURL中指定任何标签,FedCM 账号选择器中将显示所有账号。 - 如果未为账号指定任何标签,则只有在
configURL也未指定标签的情况下,该账号才会显示在账号选择器中。 - 如果在被动模式下没有任何账号与请求的标签匹配(类似于网域提示功能),FedCM 对话框会显示登录提示,以便用户登录 IdP 账号。对于活动模式,系统会直接打开登录弹出式窗口。
断开端点
通过调用 IdentityCredential.disconnect(),浏览器会向此断开连接端点发送包含 SameSite=None 和内容类型为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 的跨源 POST 请求,其中包含以下信息:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
account_hint |
IdP 账号的提示。 |
client_id |
RP 的客户端标识符。 |
POST /disconnect.example HTTP/1.1
Host: idp.example
Origin: rp.example
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Cookie: 0x123
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentity
account_hint=account456&client_id=rp123
收到请求后,服务器应:
- 使用 CORS(跨源资源共享)响应请求。
- 验证请求是否包含
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentityHTTP 标头。 - 将
Origin标头与client_id确定的 RP 源进行匹配。如果不匹配,请拒绝。 - 将
account_hint与已登录账号的 ID 进行匹配。 - 解除用户账号与 RP 的关联。
- 以 JSON 格式向浏览器响应已识别的用户账号信息。
响应 JSON 载荷示例如下:
{
"account_id": "account456"
}
相反,如果 IdP 希望浏览器断开与 RP 关联的所有账号,请传递与任何账号 ID 都不匹配的字符串,例如 "*"。
客户端元数据端点
IdP 的客户端元数据端点会返回依赖方的元数据,例如 RP 的隐私权政策、服务条款和徽标图标。RP 应提前向 IdP 提供指向其隐私权政策和服务条款的链接。如果用户尚未在 RP 上使用 IdP 注册,系统会在登录对话框中显示这些链接。
浏览器使用不含 Cookie 的 client_id
navigator.credentials.get 发送 GET 请求。例如:
GET /client_metadata.example?client_id=1234 HTTP/1.1
Host: accounts.idp.example
Origin: https://rp.example/
Accept: application/json
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentity
收到请求后,服务器应:
- 确定
client_id的 RP。 - 使用客户端元数据进行响应。
客户端元数据端点的属性包括:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
privacy_policy_url(可选) |
RP 隐私权政策网址。 |
terms_of_service_url(可选) |
RP 服务条款网址。 |
icons(可选) |
对象数组,例如 [{ "url": "https://rp.example/rp-icon.ico", "size": 40}] |
浏览器会要求从该端点返回 JSON 响应:
{
"privacy_policy_url": "https://rp.example/privacy_policy.html",
"terms_of_service_url": "https://rp.example/terms_of_service.html",
"icons": [{
"url": "https://rp.example/rp-icon.ico",
"size": 40
}]
}
返回的客户端元数据将由浏览器使用,而不会提供给 RP。
登录网址
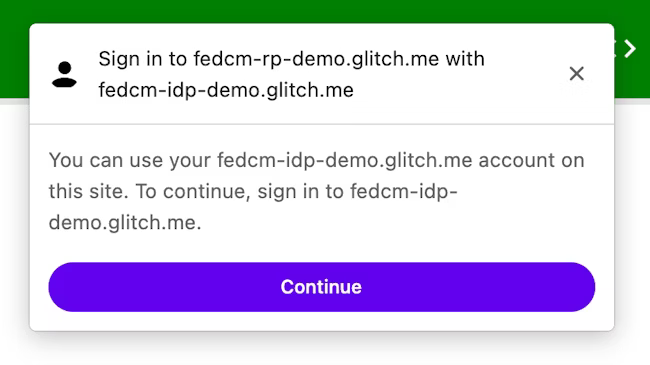
此端点用于让用户登录 IdP。
使用 Login Status API 时,IdP 必须向浏览器告知用户的登录状态。不过,状态可能会不同步,例如在会话过期时。在这种情况下,浏览器可以动态允许用户通过使用 idp 配置文件的 login_url 指定的登录页面网址登录 IdP。
FedCM 对话框会显示一条提示登录的消息,如下图所示。
当用户点击 Continue 按钮时,浏览器会打开一个弹出式窗口,显示 IdP 的登录页面。
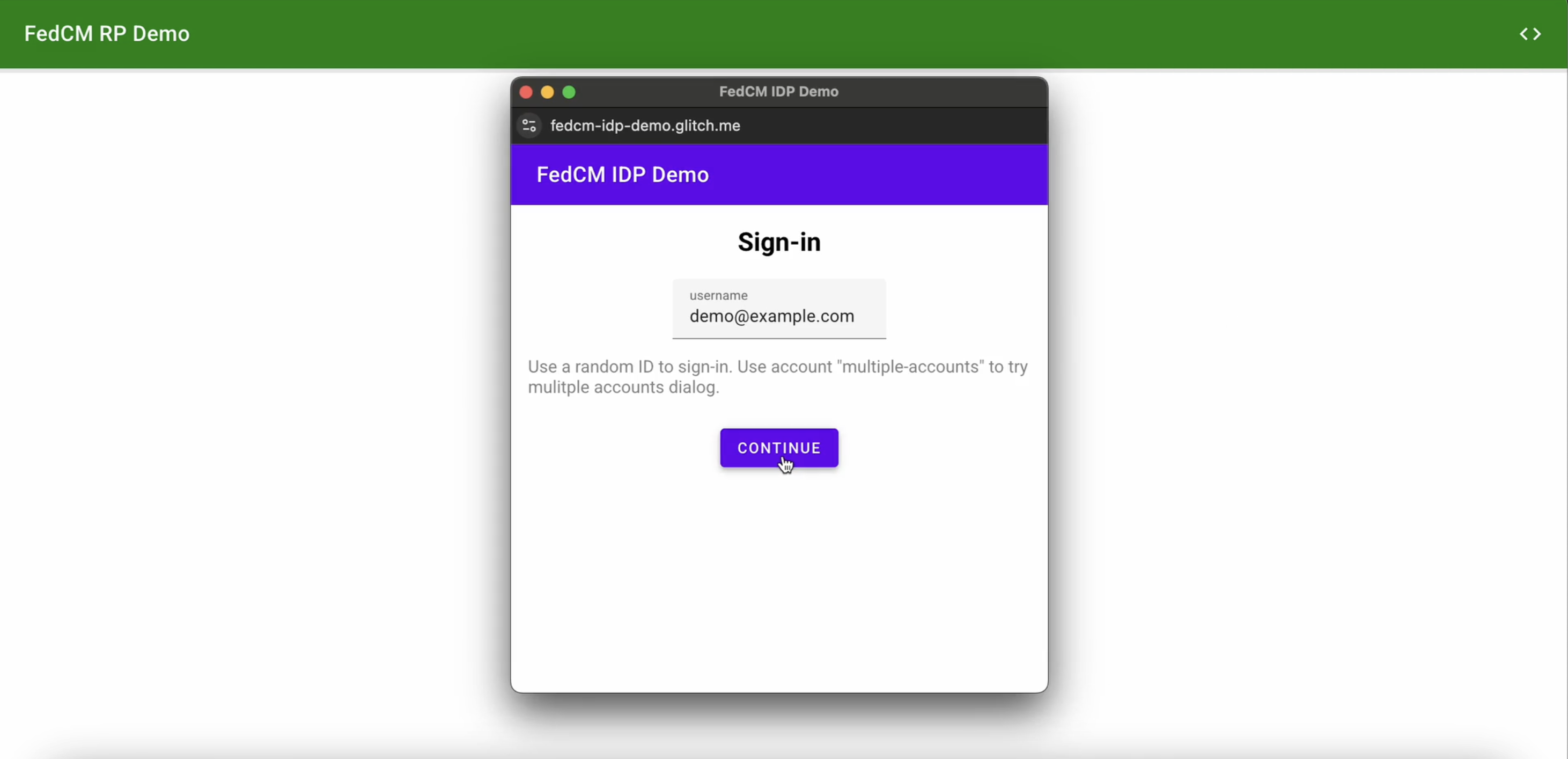
该对话框是一个包含第一方 Cookie 的常规浏览器窗口。对话框中发生的任何情况均由 IdP 决定,并且没有窗口句柄可用于向 RP 页面发出跨源通信请求。用户登录后,IdP 应:
- 发送
Set-Login: logged-in标头或调用navigator.login.setStatus("logged-in")API 以告知浏览器用户已登录。 - 调用
IdentityProvider.close()以关闭对话框。
告知浏览器用户的登录状态
Login Status API 是一种机制,可让网站(尤其是 IdP)告知浏览器用户在 IdP 上的登录状态。借助此 API,浏览器可以减少对 IDP 的不必要请求,并减少潜在的时间攻击。
当用户在 IdP 上登录或退出所有 IdP 账号时,IdP 可以通过发送 HTTP 标头或调用 JavaScript API 向浏览器发送用户的登录状态信号。对于每个 IdP(通过其配置网址进行标识),浏览器都会保留一个三态变量来表示登录状态,可能的值如下:
logged-inlogged-outunknown(默认)
| 登录状态 | 说明 |
|---|---|
logged-in |
当用户的登录状态设置为 logged-in 时,调用 FedCM 的 RP 会向 IdP 的账号端点发出请求,并在 FedCM 对话框中向用户显示可用账号。 |
logged-out |
当用户的登录状态为 logged-out 时,调用 FedCM 会静默失败,而不会向 IdP 的账号端点发出请求。 |
unknown(默认) |
在 IdP 使用 Login Status API 发送信号之前,系统会设置 unknown 状态。当状态为 unknown 时,浏览器会向 IdP 的账号端点发出请求,并根据账号端点的响应更新状态。 |
如需指示用户已登录,请在顶级导航栏中发送 Set-Login: logged-in HTTP 标头,或在 IdP 源中发送同一网站子资源请求:
Set-Login: logged-in
或者,在顶级导航栏中从 IdP 来源调用 JavaScript 方法 navigator.login.setStatus('logged-in'):
navigator.login.setStatus('logged-in')
用户的登录状态将设为 logged-in。
如需指示用户已从其所有账号退出,请在顶级导航中发送 Set-Login: logged-out HTTP 标头,或在 IdP 源中发送同一网站子资源请求:
Set-Login: logged-out
或者,您也可以在顶级导航栏中的 IdP 来源中调用 JavaScript API navigator.login.setStatus('logged-out'):
navigator.login.setStatus('logged-out')
用户的登录状态将设为 logged-out。
在 IdP 使用 Login Status API 发送信号之前,系统会设置 unknown 状态。浏览器向 IdP 的账号端点发出请求,并根据账号端点的响应更新状态:
- 如果端点返回有效账号列表,请将状态更新为
logged-in,然后打开 FedCM 对话框以显示这些账号。 - 如果端点未返回任何账号,请将状态更新为
logged-out并使 FedCM 调用失败。
允许用户通过动态登录流程登录
即使 IdP 会持续向浏览器告知用户的登录状态,但状态也可能会不同步,例如在会话过期时。当登录状态为 logged-in 时,浏览器会尝试向账号端点发送包含凭据的请求,但由于会话不再可用,服务器不会返回任何账号。在这种情况下,浏览器可以动态让用户通过弹出式窗口登录 IdP。

