站点链接搜索框 (WebSite) 结构化数据
站点链接搜索框为用户提供了一种快捷方式,让他们可以立即在搜索结果页上搜索您的网站或应用。搜索框具有实时建议和其他功能。
当您的网站显示为搜索结果时,Google 搜索可以自动提供一个将搜索范围限定到您网站的搜索框,而不需要您执行任何其他操作来实现这一点。此搜索框由 Google 搜索提供支持。不过,您可以添加 WebSite 结构化数据,以明确提供信息,让 Google 进一步了解您的网站。
如果 Google 搜索已经为您的网站提供了站点链接搜索框,您可以通过添加 WebSite 结构化数据来控制站点链接搜索框的某些方面。
如何实现站点链接搜索框
如需让您的网站符合在 Google 搜索结果中显示搜索框的条件,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在您的网站或 Android 应用上安装有效的搜索引擎。
当用户进行站点链接搜索查询时,会转到您网站或应用的搜索结果页,因此您需要一个正常运行的搜索引擎来为此功能提供支持。
- 网站:在您的网站上设置搜索引擎。相应功能会使用在您的结构化数据中指定的语法将用户的查询转发到您的目标。您的搜索引擎必须支持 UTF-8 编码的查询。
- 应用:请参阅 Android 开发者网站上的搜索概览,了解如何为应用实现搜索引擎。您的 Android 应用必须支持来自搜索结果的
ACTION_VIEWintent,并在标记的potentialAction.target属性中指定相应的数据 URI。
- 在您网站的首页上实现
WebSite结构化数据元素。应用必须具有关联的网站才能启用此功能,即使该网站只有一个网页。下面是一些附加指南:- 只将此标记添加到首页,而不要将其添加到其他任何网页。
- 如果您已经为网站名称功能实现
WebSite结构化数据,请务必将网站名称属性嵌套在同一节点中。也就是说,请尽可能避免在首页上额外创建WebSite结构化数据块。 - 始终为网站指定一个
SearchAction,如果支持应用搜索,还可以再指定一个。您必须为网站指定SearchAction,即使应用是您的首选搜索目标也是如此;这样可确保当用户未通过 Android 手机进行搜索或未安装您的 Android 应用时,搜索结果会定向到您的网站。 - 根据您使用的格式,了解在网页上的什么位置插入结构化数据。
- 遵循指南。
- 使用富媒体搜索结果测试验证您的代码。
- 验证搜索引擎实现情况,方法是从您的结构化数据复制
WebSite.potentialAction.target网址,将{search_term_string}替换为测试查询,然后在网络浏览器中访问该网址。例如,如果您的网站是 example.com,您要测试查询内容“kittens”,那么您可以访问https://www.example.com/search/?q=kittens。 - 对网域首页的所有变体使用
rel="canonical"link 元素,从而为首页设置首选规范网址。这有助于 Google 搜索为您的标记选择正确的网址。您的服务器必须支持 UTF-8 字符编码。 - 对于应用,请启用正确的 intent 过滤器以支持您在标记的应用目标中指定的网址。有关如何为 Google 搜索网址创建 intent 过滤器的示例,请参阅适用于 Android 的 Firebase App Indexing。
- 部署一些包含结构化数据的网页,然后使用网址检查工具测试 Google 对网页的反应。请确保您的网页可供 Google 访问,不会因 robots.txt 文件、
noindex标记或登录要求而阻止 Google 访问。如果网页看起来没有问题,您可以请求 Google 重新抓取您的网址。 - 为了让 Google 随时了解日后发生的更改,我们建议您提交站点地图。Search Console Sitemap API 可以帮助您自动执行此操作。
示例
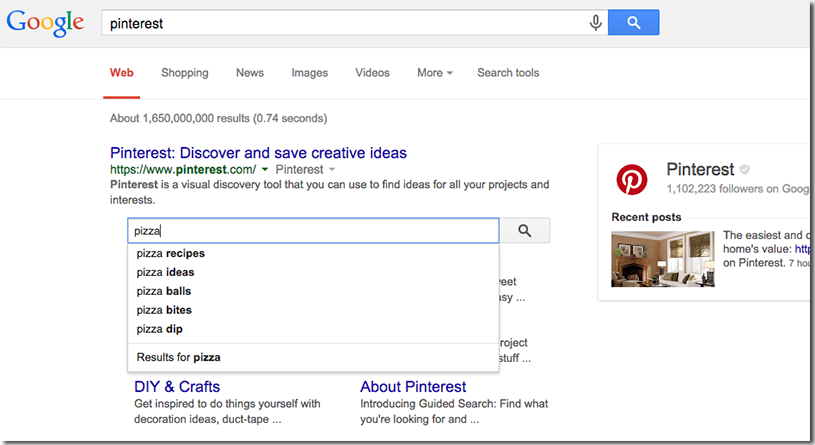
以下示例显示了在 Google 上搜索“Pinterest”时所得到的搜索结果,返回了 Pinterest 网站的站点链接搜索框:
下面是一些使用网站的自定义搜索引擎来实现站点链接搜索框的示例标记:
下面是一个 JSON-LD 格式的示例:
<html>
<head>
<title>The title of the page</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "WebSite",
"url": "https://www.example.com/",
"potentialAction": {
"@type": "SearchAction",
"target": {
"@type": "EntryPoint",
"urlTemplate": "https://query.example.com/search?q={search_term_string}"
},
"query-input": "required name=search_term_string"
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
下面是一个微数据格式的示例:
<div itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/WebSite">
<meta itemprop="url" content="https://www.example.com/"/>
<form itemprop="potentialAction" itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/SearchAction">
<meta itemprop="target" content="https://query.example.com/search?q={search_term_string}"/>
<input itemprop="query-input" type="text" name="search_term_string" required/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
</div>
下面是一个 JSON-LD 格式的网站和应用示例:
<html>
<head>
<title>The title of the page</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "WebSite",
"url": "https://www.example.com/",
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SearchAction",
"target": {
"@type": "EntryPoint",
"urlTemplate": "https://query.example.com/search?q={search_term_string}"
},
"query-input": "required name=search_term_string"
},{
"@type": "SearchAction",
"target": {
"@type": "EntryPoint",
"urlTemplate": "android-app://com.example/https/query.example.com/search/?q={search_term_string}"
},
"query-input": "required name=search_term_string"
}]
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
指南
为了使您的网站能够显示为富媒体搜索结果,您必须遵循以下指南。
阻止出现站点链接搜索框
即使您的网站不包含此处所述的结构化数据,Google 搜索也可以选择向其添加站点链接搜索框。不过,您可以通过向您的首页添加以下 meta 标记来阻止此行为:
<meta name="google" content="nositelinkssearchbox">
结构化数据类型定义
如需让您的内容符合显示站点链接搜索框的条件,请添加必要属性。
经过修改的 WebSite 类型
Google 搜索对网站和应用搜索框都使用经过修改的 WebSite 结构化数据类型。schema.org 上提供了 WebSite 的完整定义,不过 Google 搜索与此标准稍有不同。Google 支持的属性如下:
| 必需属性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
potentialAction
|
一个或两个 SearchAction 对象的数组 此对象描述了作为查询发送目标的 URI 以及发送的请求所用的语法。您必须实现可以接收请求的网页或 intent 处理程序,并对提交的字符串执行适当的搜索。如果用户没有使用 Android 应用(或者在使用 Android 应用,但未指定 Android intent 目标),则搜索框会将查询的网站版本发送到指定的位置;如果用户在使用 Android 设备并指定了 Android intent URI,则搜索框会发送该 intent。 您必须创建网站
网站示例 以下示例会向
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SearchAction",
"target": {
"@type": "EntryPoint",
"urlTemplate": "https://query.example.com/search?q={search_term_string}"
},
"query-input": "required name=search_term_string"
}]
应用示例 以下示例会向
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SearchAction",
"target": {
"@type": "EntryPoint",
"urlTemplate": "android-app://com.example/https/query.example.com/search/?q={search_term_string}"
},
"query-input": "required name=search_term_string"
}]
|
||||
potentialAction.query-input
|
使用字面量字符串
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SearchAction",
"target": {
"@type": "EntryPoint",
"urlTemplate": "https://query.example.com/search?q={search-term}"
},
"query-input": "required name=search-term"
}]
|
||||
potentialAction.target
|
具有
例如: https://query.example.com/search?q={search_term_string}
|
||||
url
|
指定要搜索的网站的网址。请将其设为您网站的规范首页。例如: |
||||
使用 Search Console 监控富媒体搜索结果
Search Console 是一款工具,可帮助您监控网页在 Google 搜索结果中的显示效果。即使没有注册 Search Console,您的网页也可能会显示在 Google 搜索结果中,但注册 Search Console 能够帮助您了解 Google 如何查看您的网站并做出相应的改进。建议您在以下情况下查看 Search Console:
首次部署结构化数据后
等 Google 将网页编入索引后,请在相关的富媒体搜索结果状态报告中查看是否存在问题。 理想情况下,有效项目数量会增加,而无效项目数量不会增加。如果您发现结构化数据存在问题,请执行以下操作:
发布新模板或更新代码后
如果对网站进行重大更改,请监控结构化数据无效项目的增幅。- 如果您发现无效项目增多了,可能是因为您推出的某个新模板无法正常工作,或者您的网站以一种新的错误方式与现有模板交互。
- 如果您发现有效项目减少了(但无效项目的增加情况并不对应),可能是因为您的网页中未再嵌入结构化数据。请通过网址检查工具了解导致此问题的原因。
定期分析流量时
请使用效果报告分析您的 Google 搜索流量。数据将显示您的网页在 Google 搜索结果中显示为富媒体搜索结果的频率、用户点击该网页的频率以及网页在搜索结果中的平均排名。您还可以使用 Search Console API 自动提取这些结果。问题排查
如果您在实施或调试结构化数据时遇到问题,请查看下面列出的一些实用资源。
- 如果您使用了内容管理系统 (CMS) 或其他人负责管理您的网站,请向其寻求帮助。请务必向其转发列明问题细节的任何 Search Console 消息。
- Google 不能保证使用结构化数据的功能一定会显示在搜索结果中。如需查看导致 Google 无法将您的内容显示为富媒体搜索结果的各种常见原因,请参阅结构化数据常规指南。
- 您的结构化数据可能存在错误。请参阅结构化数据错误列表。
- 如果您的网页受到结构化数据手动操作的影响,其中的结构化数据将会被忽略(但该网页仍可能会出现在 Google 搜索结果中)。如需修正结构化数据问题,请使用“人工处置措施”报告。
- 再次查看相关指南,确认您的内容是否未遵循指南。问题可能是因为出现垃圾内容或使用垃圾标记导致的。不过,问题可能不是语法问题,因此富媒体搜索结果测试无法识别这些问题。
- 针对富媒体搜索结果缺失/富媒体搜索结果总数下降进行问题排查。
- 请等待一段时间,以便 Google 重新抓取您的网页并重新将其编入索引。请注意,网页发布后,Google 可能需要几天时间才会找到和抓取该网页。有关抓取和索引编制的常见问题,请参阅 Google 搜索抓取和索引编制常见问题解答。
- 在 Google 搜索中心论坛中发帖提问。
