ส่วนนี้อธิบาย API สำหรับตัวเข้ารหัสและตัวถอดรหัสที่รวมอยู่ในไลบรารี WebP คำอธิบาย API นี้เกี่ยวข้องกับเวอร์ชัน 1.6.0
ส่วนหัวและไลบรารี
เมื่อคุณติดตั้ง libwebp ระบบจะติดตั้งไดเรกทอรีชื่อ webp/
ในตำแหน่งทั่วไปสำหรับแพลตฟอร์มของคุณ เช่น ในแพลตฟอร์ม Unix ระบบจะคัดลอกไฟล์ส่วนหัวต่อไปนี้ไปยัง /usr/local/include/webp/
decode.h
encode.h
types.h
ไลบรารีจะอยู่ในไดเรกทอรีไลบรารีตามปกติ ไลบรารีแบบคงที่และแบบไดนามิกอยู่ใน /usr/local/lib/ บนแพลตฟอร์ม Unix
Simple Decoding API
หากต้องการเริ่มต้นใช้งาน Decoding API คุณต้องตรวจสอบว่าได้ติดตั้งไลบรารีและไฟล์ส่วนหัวตามที่อธิบายไว้ด้านบน
ใส่ส่วนหัวของ API การถอดรหัสในโค้ด C/C++ ดังนี้
#include "webp/decode.h"
int WebPGetInfo(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
ฟังก์ชันนี้จะตรวจสอบส่วนหัวของรูปภาพ WebP และดึงความกว้าง
และความสูงของรูปภาพ คุณส่งต่อพอยน์เตอร์ *width และ *height เป็น NULL ได้หากเห็นว่าไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
แอตทริบิวต์อินพุต
- เพิ่มเติม
- ตัวชี้ไปยังข้อมูลรูปภาพ WebP
- data_size
- นี่คือขนาดของบล็อกหน่วยความจำที่ชี้โดย
dataซึ่งมี ข้อมูลรูปภาพ
การคืนสินค้า
- เท็จ
- รหัสข้อผิดพลาดที่ส่งกลับในกรณีที่เกิด (ก) ข้อผิดพลาดด้านการจัดรูปแบบ
- จริง
- เมื่อสำเร็จ
*widthและ*heightจะใช้ได้เมื่อคืนสินค้าสำเร็จเท่านั้น - ความกว้าง
- ค่าจำนวนเต็ม ช่วงจะจำกัดตั้งแต่ 1 ถึง 16383
- ส่วนสูง
- ค่าจำนวนเต็ม ช่วงนี้จะต้องไม่เกิน 1 ถึง 16383
struct WebPBitstreamFeatures {
int width; // Width in pixels.
int height; // Height in pixels.
int has_alpha; // True if the bitstream contains an alpha channel.
int has_animation; // True if the bitstream is an animation.
int format; // 0 = undefined (/mixed), 1 = lossy, 2 = lossless
}
VP8StatusCode WebPGetFeatures(const uint8_t* data,
size_t data_size,
WebPBitstreamFeatures* features);
ฟังก์ชันนี้จะดึงฟีเจอร์จากบิตสตรีม ระบบจะป้อนข้อมูลที่รวบรวมจากบิตสตรีมลงในโครงสร้าง *features
แอตทริบิวต์อินพุต
- เพิ่มเติม
- ตัวชี้ไปยังข้อมูลรูปภาพ WebP
- data_size
- นี่คือขนาดของบล็อกหน่วยความจำที่ชี้โดย
dataซึ่งมี ข้อมูลรูปภาพ
การคืนสินค้า
VP8_STATUS_OK- เมื่อดึงข้อมูลฟีเจอร์สำเร็จ
VP8_STATUS_NOT_ENOUGH_DATA- เมื่อต้องการข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเพื่อดึงข้อมูลฟีเจอร์จากส่วนหัว
VP8StatusCodeค่าข้อผิดพลาดเพิ่มเติมในกรณีอื่นๆ
- ฟีเจอร์
- ตัวชี้ไปยังโครงสร้าง WebPBitstreamFeatures
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBA(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeARGB(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRA(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGB(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGR(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
ฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้จะถอดรหัสรูปภาพ WebP ที่ data ชี้อยู่
WebPDecodeRGBAจะแสดงตัวอย่างรูปภาพ RGBA ตามลำดับ[r0, g0, b0, a0, r1, g1, b1, a1, ...]WebPDecodeARGBจะแสดงตัวอย่างรูปภาพ ARGB ตามลำดับ[a0, r0, g0, b0, a1, r1, g1, b1, ...]WebPDecodeBGRAจะแสดงตัวอย่างรูปภาพ BGRA ตามลำดับ[b0, g0, r0, a0, b1, g1, r1, a1, ...]WebPDecodeRGBจะแสดงตัวอย่างรูปภาพ RGB ตามลำดับ[r0, g0, b0, r1, g1, b1, ...]WebPDecodeBGRจะแสดงตัวอย่างรูปภาพ BGR ตามลำดับ[b0, g0, r0, b1, g1, r1, ...]
โค้ดที่เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้ต้องลบบัฟเฟอร์ข้อมูล
(uint8_t*)ที่ฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้ส่งคืนด้วย WebPFree()
แอตทริบิวต์อินพุต
- เพิ่มเติม
- ตัวชี้ไปยังข้อมูลรูปภาพ WebP
- data_size
- นี่คือขนาดของบล็อกหน่วยความจำที่ชี้โดย
dataซึ่งมี ข้อมูลรูปภาพ - ความกว้าง
- ค่าจำนวนเต็ม ปัจจุบันช่วงจะจำกัดไว้ที่ 1 ถึง 16383
- ส่วนสูง
- ค่าจำนวนเต็ม ปัจจุบันช่วงจะจำกัดไว้ที่ 1 ถึง 16383
การคืนสินค้า
- uint8_t*
- พอยน์เตอร์ไปยังตัวอย่างรูปภาพ WebP ที่ถอดรหัสแล้วในลำดับ RGBA/ARGB/BGRA/RGB/BGR เชิงเส้น ตามลำดับ
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBAInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeARGBInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRAInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
ฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้เป็นตัวแปรของฟังก์ชันข้างต้นและจะถอดรหัสรูปภาพโดยตรง
ลงในบัฟเฟอร์ที่จัดสรรไว้ล่วงหน้า output_buffer output_buffer_size ระบุพื้นที่เก็บข้อมูลสูงสุดที่ใช้ได้ในบัฟเฟอร์นี้ หากพื้นที่เก็บข้อมูลนี้ไม่เพียงพอ (หรือเกิดข้อผิดพลาด) ระบบจะแสดงผล NULL มิเช่นนั้น ระบบจะแสดงผล output_buffer เพื่อความสะดวก
พารามิเตอร์ output_stride ระบุระยะห่าง (เป็นไบต์) ระหว่าง
บรรทัดสแกน ดังนั้น output_buffer_size จึงควรมีค่าอย่างน้อย output_stride * picture - height
แอตทริบิวต์อินพุต
- เพิ่มเติม
- ตัวชี้ไปยังข้อมูลรูปภาพ WebP
- data_size
- นี่คือขนาดของบล็อกหน่วยความจำที่ชี้โดย
dataซึ่งมี ข้อมูลรูปภาพ - output_buffer_size
- ค่าจำนวนเต็ม ขนาดของบัฟเฟอร์ที่จัดสรร
- output_stride
- ค่าจำนวนเต็ม ระบุระยะห่างระหว่างเส้นสแกน
การคืนสินค้า
- output_buffer
- ตัวชี้ไปยังรูปภาพ WebP ที่ถอดรหัสแล้ว
- uint8_t*
output_bufferหากฟังก์ชันสำเร็จ หรือNULLในกรณีอื่นๆ
Advanced Decoding API
การถอดรหัส WebP รองรับ API ขั้นสูงเพื่อให้สามารถครอบตัดและปรับขนาดได้ทันที ซึ่งเป็นประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งในสภาพแวดล้อมที่มีข้อจำกัดด้านหน่วยความจำ เช่น โทรศัพท์มือถือ โดยพื้นฐานแล้ว การใช้หน่วยความจำจะปรับขนาดตามขนาดเอาต์พุต ไม่ใช่ขนาดอินพุต เมื่อผู้ใช้ต้องการเพียงตัวอย่างด่วนหรือส่วนที่ซูมเข้าของรูปภาพที่ใหญ่เกินไป นอกจากนี้ยังประหยัด CPU ได้ด้วย
การถอดรหัส WebP มี 2 รูปแบบ ได้แก่ การถอดรหัสรูปภาพแบบเต็มและการถอดรหัสแบบเพิ่มทีละส่วนผ่านบัฟเฟอร์อินพุตขนาดเล็ก ผู้ใช้สามารถระบุบัฟเฟอร์หน่วยความจำภายนอกเพื่อถอดรหัสรูปภาพได้ (ไม่บังคับ) ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้จะแสดงขั้นตอนการใช้ API การถอดรหัสขั้นสูง
ก่อนอื่นเราต้องเริ่มต้นออบเจ็กต์การกำหนดค่า
#include "webp/decode.h"
WebPDecoderConfig config;
CHECK(WebPInitDecoderConfig(&config));
// One can adjust some additional decoding options:
config.options.no_fancy_upsampling = 1;
config.options.use_scaling = 1;
config.options.scaled_width = scaledWidth();
config.options.scaled_height = scaledHeight();
// etc.
ตัวเลือกการถอดรหัสจะรวบรวมไว้ในWebPDecoderConfig
โครงสร้างดังนี้
struct WebPDecoderOptions {
int bypass_filtering; // if true, skip the in-loop filtering
int no_fancy_upsampling; // if true, use faster pointwise upsampler
int use_cropping; // if true, cropping is applied first
int crop_left, crop_top; // top-left position for cropping.
// Will be snapped to even values.
int crop_width, crop_height; // dimension of the cropping area
int use_scaling; // if true, scaling is applied afterward
int scaled_width, scaled_height; // final resolution
int use_threads; // if true, use multi-threaded decoding
int dithering_strength; // dithering strength (0=Off, 100=full)
int flip; // if true, flip output vertically
int alpha_dithering_strength; // alpha dithering strength in [0..100]
};
คุณอาจอ่านฟีเจอร์บิตสตรีมลงใน config.input
ในกรณีที่เราจำเป็นต้องทราบล่วงหน้า เช่น การทราบว่ารูปภาพมีความโปร่งใสหรือไม่ก็เป็นประโยชน์
โปรดทราบว่าการดำเนินการนี้จะ
แยกวิเคราะห์ส่วนหัวของบิตสตรีมด้วย จึงเป็นวิธีที่ดีในการตรวจสอบ
ว่าบิตสตรีมมีลักษณะเหมือน WebP ที่ถูกต้องหรือไม่
CHECK(WebPGetFeatures(data, data_size, &config.input) == VP8_STATUS_OK);
จากนั้นเราต้องตั้งค่าบัฟเฟอร์หน่วยความจำสำหรับการถอดรหัสในกรณีที่เราต้องการจัดหาบัฟเฟอร์หน่วยความจำ โดยตรงแทนที่จะพึ่งพาตัวถอดรหัสในการจัดสรร เราเพียงแค่ต้อง ระบุพอยน์เตอร์ไปยังหน่วยความจำ รวมถึงขนาดรวมของบัฟเฟอร์และ ระยะก้าวย่างของบรรทัด (ระยะห่างเป็นไบต์ระหว่างบรรทัดสแกน)
// Specify the desired output colorspace:
config.output.colorspace = MODE_BGRA;
// Have config.output point to an external buffer:
config.output.u.RGBA.rgba = (uint8_t*)memory_buffer;
config.output.u.RGBA.stride = scanline_stride;
config.output.u.RGBA.size = total_size_of_the_memory_buffer;
config.output.is_external_memory = 1;
รูปภาพพร้อมที่จะถอดรหัสแล้ว การถอดรหัสรูปภาพมี 2 รูปแบบที่เป็นไปได้ เราถอดรหัสรูปภาพได้ในครั้งเดียวโดยใช้
CHECK(WebPDecode(data, data_size, &config) == VP8_STATUS_OK);
หรือเราจะใช้วิธีการเพิ่มทีละรายการเพื่อถอดรหัสรูปภาพทีละน้อย เมื่อมีไบต์ใหม่ก็ได้
WebPIDecoder* idec = WebPINewDecoder(&config.output);
CHECK(idec != NULL);
while (additional_data_is_available) {
// ... (get additional data in some new_data[] buffer)
VP8StatusCode status = WebPIAppend(idec, new_data, new_data_size);
if (status != VP8_STATUS_OK && status != VP8_STATUS_SUSPENDED) {
break;
}
// The above call decodes the current available buffer.
// Part of the image can now be refreshed by calling
// WebPIDecGetRGB()/WebPIDecGetYUVA() etc.
}
WebPIDelete(idec); // the object doesn't own the image memory, so it can
// now be deleted. config.output memory is preserved.
ตอนนี้รูปภาพที่ถอดรหัสแล้วอยู่ใน config.output (หรือใน config.output.u.RGBA ในกรณีนี้ เนื่องจากพื้นที่สีเอาต์พุตที่ขอคือ MODE_BGRA) บันทึก แสดง หรือประมวลผลรูปภาพได้ หลังจากนั้น เราเพียงแค่ต้องเรียกคืนหน่วยความจำที่จัดสรรไว้ในออบเจ็กต์ของ Config คุณเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันนี้ได้อย่างปลอดภัยแม้ว่าหน่วยความจำจะอยู่ภายนอกและไม่ได้ จัดสรรโดย WebPDecode() ก็ตาม
WebPFreeDecBuffer(&config.output);
เมื่อใช้ API นี้ คุณยังถอดรหัสรูปภาพเป็นรูปแบบ YUV และ YUVA ได้ด้วยโดยใช้
MODE_YUV และ MODE_YUVA ตามลำดับ รูปแบบนี้เรียกอีกอย่างว่า
Y'CbCr
Simple Encoding API
ฟังก์ชันที่เรียบง่ายมากบางอย่างมีไว้สำหรับการเข้ารหัสอาร์เรย์ของตัวอย่าง RGBA
ในเลย์เอาต์ที่พบบ่อยที่สุด โดยจะประกาศในwebp/encode.h
ส่วนหัวดังนี้
size_t WebPEncodeRGB(const uint8_t* rgb, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeBGR(const uint8_t* bgr, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeRGBA(const uint8_t* rgba, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeBGRA(const uint8_t* bgra, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
ปัจจัยด้านคุณภาพ quality_factor มีค่าตั้งแต่ 0 ถึง 100 และ
ควบคุมการสูญเสียและคุณภาพระหว่างการบีบอัด ค่า 0 หมายถึงคุณภาพต่ำและขนาดเอาต์พุตเล็ก ส่วนค่า 100 หมายถึงคุณภาพสูงสุดและขนาดเอาต์พุตใหญ่ที่สุด
เมื่อสำเร็จ ระบบจะวางไบต์ที่บีบอัดไว้ใน*output
พอยน์เตอร์ และแสดงผลขนาดเป็นไบต์ (หากไม่สำเร็จ ระบบจะแสดงผลเป็น 0) ผู้เรียกใช้ต้องเรียกใช้ WebPFree() ใน *output
พอยน์เตอร์เพื่อเรียกคืนหน่วยความจำ
อาร์เรย์อินพุตควรเป็นอาร์เรย์ไบต์ที่แพ็กแล้ว (1 ไบต์ต่อช่องสัญญาณ ตามที่ชื่อฟังก์ชันระบุ) stride สอดคล้องกับ
จำนวนไบต์ที่ต้องใช้ในการข้ามจากแถวหนึ่งไปยังแถวถัดไป เช่น
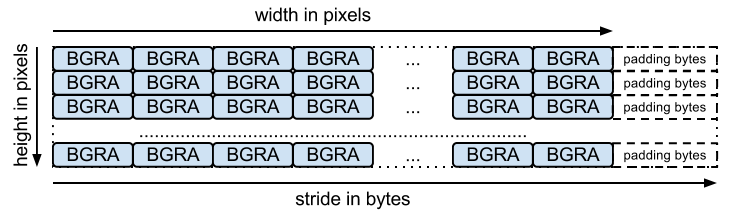
เลย์เอาต์ BGRA คือ
มีฟังก์ชันที่เทียบเท่าสำหรับการเข้ารหัสแบบไม่สูญเสียข้อมูล โดยมีลายเซ็นดังนี้
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessRGB(const uint8_t* rgb, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessBGR(const uint8_t* bgr, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessRGBA(const uint8_t* rgba, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessBGRA(const uint8_t* bgra, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
โปรดทราบว่าฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้จะใช้การตั้งค่าเริ่มต้นของไลบรารี
เช่นเดียวกับเวอร์ชันแบบมีการสูญเสีย สำหรับแบบไม่สูญเสียข้อมูล หมายความว่าปิดใช้ "ตรงกัน" ระบบจะแก้ไขค่า RGB ในพื้นที่โปร่งใสโดยสมบูรณ์ (นั่นคือ พื้นที่ที่มีค่าอัลฟ่าเท่ากับ 0) เพื่อปรับปรุงการบีบอัด หากต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหานี้ ให้ใช้ WebPEncode() และตั้งค่า
WebPConfig::exact เป็น 1
Advanced Encoding API
โดยเบื้องหลังแล้ว ตัวเข้ารหัสมาพร้อมกับพารามิเตอร์การเข้ารหัสขั้นสูงมากมาย
ซึ่งอาจมีประโยชน์ในการปรับสมดุลระหว่างประสิทธิภาพการบีบอัดกับเวลาในการประมวลผลให้ดียิ่งขึ้น
พารามิเตอร์เหล่านี้จะรวบรวมไว้ในโครงสร้าง WebPConfig
ฟิลด์ที่ใช้มากที่สุดของโครงสร้างนี้ ได้แก่
struct WebPConfig {
int lossless; // Lossless encoding (0=lossy(default), 1=lossless).
float quality; // between 0 and 100. For lossy, 0 gives the smallest
// size and 100 the largest. For lossless, this
// parameter is the amount of effort put into the
// compression: 0 is the fastest but gives larger
// files compared to the slowest, but best, 100.
int method; // quality/speed trade-off (0=fast, 6=slower-better)
WebPImageHint image_hint; // Hint for image type (lossless only for now).
// Parameters related to lossy compression only:
int target_size; // if non-zero, set the desired target size in bytes.
// Takes precedence over the 'compression' parameter.
float target_PSNR; // if non-zero, specifies the minimal distortion to
// try to achieve. Takes precedence over target_size.
int segments; // maximum number of segments to use, in [1..4]
int sns_strength; // Spatial Noise Shaping. 0=off, 100=maximum.
int filter_strength; // range: [0 = off .. 100 = strongest]
int filter_sharpness; // range: [0 = off .. 7 = least sharp]
int filter_type; // filtering type: 0 = simple, 1 = strong (only used
// if filter_strength > 0 or autofilter > 0)
int autofilter; // Auto adjust filter's strength [0 = off, 1 = on]
int alpha_compression; // Algorithm for encoding the alpha plane (0 = none,
// 1 = compressed with WebP lossless). Default is 1.
int alpha_filtering; // Predictive filtering method for alpha plane.
// 0: none, 1: fast, 2: best. Default if 1.
int alpha_quality; // Between 0 (smallest size) and 100 (lossless).
// Default is 100.
int pass; // number of entropy-analysis passes (in [1..10]).
int show_compressed; // if true, export the compressed picture back.
// In-loop filtering is not applied.
int preprocessing; // preprocessing filter (0=none, 1=segment-smooth)
int partitions; // log2(number of token partitions) in [0..3]
// Default is set to 0 for easier progressive decoding.
int partition_limit; // quality degradation allowed to fit the 512k limit on
// prediction modes coding (0: no degradation,
// 100: maximum possible degradation).
int use_sharp_yuv; // if needed, use sharp (and slow) RGB->YUV conversion
};
โปรดทราบว่าพารามิเตอร์ส่วนใหญ่เหล่านี้สามารถเข้าถึงได้เพื่อทำการทดสอบ
โดยใช้cwebpเครื่องมือบรรทัดคำสั่ง
ควรห่อหุ้มตัวอย่างอินพุตไว้ในโครงสร้าง WebPPicture
โครงสร้างนี้สามารถจัดเก็บตัวอย่างอินพุตในรูปแบบ RGBA หรือ YUVA ก็ได้ ขึ้นอยู่กับค่าของแฟล็ก use_argb
โครงสร้างจะจัดระเบียบดังนี้
struct WebPPicture {
int use_argb; // To select between ARGB and YUVA input.
// YUV input, recommended for lossy compression.
// Used if use_argb = 0.
WebPEncCSP colorspace; // colorspace: should be YUVA420 or YUV420 for now (=Y'CbCr).
int width, height; // dimensions (less or equal to WEBP_MAX_DIMENSION)
uint8_t *y, *u, *v; // pointers to luma/chroma planes.
int y_stride, uv_stride; // luma/chroma strides.
uint8_t* a; // pointer to the alpha plane
int a_stride; // stride of the alpha plane
// Alternate ARGB input, recommended for lossless compression.
// Used if use_argb = 1.
uint32_t* argb; // Pointer to argb (32 bit) plane.
int argb_stride; // This is stride in pixels units, not bytes.
// Byte-emission hook, to store compressed bytes as they are ready.
WebPWriterFunction writer; // can be NULL
void* custom_ptr; // can be used by the writer.
// Error code for the latest error encountered during encoding
WebPEncodingError error_code;
};
โครงสร้างนี้ยังมีฟังก์ชันในการปล่อยไบต์ที่บีบอัดเมื่อพร้อมใช้งานด้วย
ดูตัวอย่างที่มีเครื่องมือเขียนในหน่วยความจำได้ที่ด้านล่าง
ผู้เขียนคนอื่นๆ สามารถจัดเก็บข้อมูลลงในไฟล์ได้โดยตรง (ดูตัวอย่างได้ที่
examples/cwebp.c)
ขั้นตอนทั่วไปสำหรับการเข้ารหัสโดยใช้ API ขั้นสูงมีลักษณะดังนี้
ก่อนอื่น เราต้องตั้งค่าการเข้ารหัสที่มี พารามิเตอร์การบีบอัด โปรดทราบว่าคุณสามารถใช้การกำหนดค่าเดียวกัน เพื่อบีบอัดรูปภาพต่างๆ หลายรูปในภายหลังได้
#include "webp/encode.h"
WebPConfig config;
if (!WebPConfigPreset(&config, WEBP_PRESET_PHOTO, quality_factor)) return 0; // version error
// Add additional tuning:
config.sns_strength = 90;
config.filter_sharpness = 6;
config.alpha_quality = 90;
config_error = WebPValidateConfig(&config); // will verify parameter ranges (always a good habit)
จากนั้นต้องอ้างอิงตัวอย่างอินพุตใน WebPPicture โดยการอ้างอิงหรือคัดลอก ตัวอย่างการจัดสรรบัฟเฟอร์สำหรับเก็บตัวอย่างมีดังนี้
แต่คุณสามารถตั้งค่า "มุมมอง" ให้กับอาร์เรย์ตัวอย่างที่จัดสรรแล้วได้อย่างง่ายดาย
ดูฟังก์ชัน WebPPictureView()
// Setup the input data, allocating a picture of width x height dimension
WebPPicture pic;
if (!WebPPictureInit(&pic)) return 0; // version error
pic.width = width;
pic.height = height;
if (!WebPPictureAlloc(&pic)) return 0; // memory error
// At this point, 'pic' has been initialized as a container, and can receive the YUVA or RGBA samples.
// Alternatively, one could use ready-made import functions like WebPPictureImportRGBA(), which will take
// care of memory allocation. In any case, past this point, one will have to call WebPPictureFree(&pic)
// to reclaim allocated memory.
หากต้องการส่งไบต์ที่บีบอัด ระบบจะเรียกใช้ Hook ทุกครั้งที่มีไบต์ใหม่
ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างง่ายๆ ที่มีการประกาศ memory-writer ใน
webp/encode.h การเริ่มต้นนี้อาจจำเป็นสำหรับ
แต่ละรูปภาพเพื่อบีบอัด
// Set up a byte-writing method (write-to-memory, in this case):
WebPMemoryWriter writer;
WebPMemoryWriterInit(&writer);
pic.writer = WebPMemoryWrite;
pic.custom_ptr = &writer;
ตอนนี้เราพร้อมที่จะบีบอัดตัวอย่างอินพุต (และปล่อยหน่วยความจำหลังจากนั้น) แล้ว
int ok = WebPEncode(&config, &pic);
WebPPictureFree(&pic); // Always free the memory associated with the input.
if (!ok) {
printf("Encoding error: %d\n", pic.error_code);
} else {
printf("Output size: %d\n", writer.size);
}
หากต้องการใช้ API และโครงสร้างขั้นสูงเพิ่มเติม เราขอแนะนำให้ดูเอกสารประกอบที่มีอยู่ในส่วนหัว webp/encode.h
การอ่านโค้ดตัวอย่าง examples/cwebp.c อาจมีประโยชน์
ในการค้นหาพารามิเตอร์ที่ใช้ไม่บ่อย
