Logowanie przez Google w Asystencie to najprostsza i najłatwiejsza metoda dla użytkownika zarówno użytkownikom, jak i deweloperom. Twoja akcja podczas rozmowy mogą poprosić o dostęp do Twojego profilu Google użytkownika, w tym imię i nazwisko, adres e-mail i zdjęcie profilowe użytkownika.
Informacje profilowe mogą być używane do personalizowania usług w akcji. Jeśli masz aplikacje na innych platformach i używają one Logowania przez Google, Możesz też znaleźć i połączyć istniejące konto użytkownika, utworzyć nowe i ustanowienie kanału bezpośredniej komunikacji z użytkownikiem.
Aby połączyć konta z użyciem Logowania przez Google, musisz poprosić użytkownika o zgodę aby uzyskać dostęp do swojego profilu Google. Następnie używasz tych informacji do celów np. jego adres e-mail, aby zidentyfikować użytkownika w swoim systemie.
Wdrażanie łączenia konta Logowania przez Google
Wykonaj czynności opisane w sekcjach poniżej, aby dodać połączenie z kontem Logowania przez Google do Akcja.
Konfigurowanie projektu
Aby skonfigurować projekt do korzystania z funkcji łączenia kont za pomocą Logowania przez Google, wykonaj te czynności:
- Otwórz konsolę Actions i wybierz projekt.
- Kliknij kartę Programowanie i wybierz Łączenie kont.
- Włącz przełącznik obok opcji Łączenie kont.
- W sekcji Tworzenie konta wybierz Tak.
W sekcji Typ połączenia wybierz Logowanie przez Google.
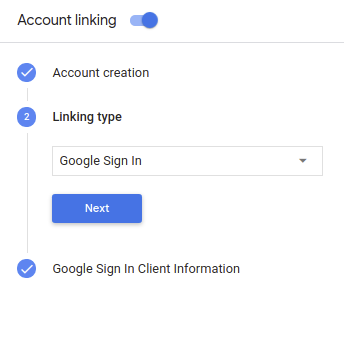
Otwórz Informacje o kliencie i zanotuj wartość identyfikatora klienta nadanego przez Google dla Twoich działań.
Kliknij Zapisz.
Rozpoczynanie procesu uwierzytelniania
Użyj intencji Asystenta logowania się na konto. aby rozpocząć proces uwierzytelniania.
Gdy użytkownik zezwoli użytkownikowi na dostęp do jego profilu Google, otrzymasz token tożsamości Google, który zawiera informacje z profilu Google użytkownika w każdym kolejnym do Twojego działania.
Aby uzyskać dostęp do informacji o profilu użytkownika, musisz najpierw zweryfikować i zdekodować token wykonując te czynności:
- Użyj biblioteki dekodowania JWT w swoim języku, aby zdekodować i użyj kluczy publicznych Google (dostępnych w JWK). lub PEM), aby zweryfikować podpis tokena.
- Sprawdź, czy wydawca tokena (pole
issw zdekodowanym tokenie) to https://accounts.google.com i że odbiorcy (poleaudw zdekodowanym tokenie) to wartość Identyfikator klienta wystawiony przez Google dla Działań, który jest przypisany do Twojego projektu w konsoli Actions on Google.
Oto przykład zdekodowanego tokena:
{ "sub": 1234567890, // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The token's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Client ID assigned to your Actions project "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the token's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the token's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "locale": "en_US" }
Jeśli używasz biblioteki klienta Actions on Google w środowisku Node.js lub biblioteki klienta Java, zajmuje się weryfikacją i dekodowaniem tokena za Ciebie, a Ty masz dostęp do jak widać w poniższych fragmentach kodu. Zwróć uwagę, że poniższy plik JSON opisuje żądanie webhooka odpowiednio do pakietów SDK Dialogflow i Actions SDK.
Te fragmenty kodu do logowania używają Dialogflow:
const {dialogflow, SignIn} = require('actions-on-google'); const app = dialogflow({ // REPLACE THE PLACEHOLDER WITH THE CLIENT_ID OF YOUR ACTIONS PROJECT clientId: CLIENT_ID, }); // Intent that starts the account linking flow. app.intent('Start Signin', (conv) => { conv.ask(new SignIn('To get your account details')); }); // Create a Dialogflow intent with the `actions_intent_SIGN_IN` event. app.intent('Get Signin', (conv, params, signin) => { if (signin.status === 'OK') { const payload = conv.user.profile.payload; conv.ask(`I got your account details, ${payload.name}. What do you want to do next?`); } else { conv.ask(`I won't be able to save your data, but what do you want to do next?`); } });
private String clientId = "<your_client_id>"; @ForIntent("Start Signin") public ActionResponse text(ActionRequest request) { ResponseBuilder rb = getResponseBuilder(request); return rb.add(new SignIn().setContext("To get your account details")).build(); } @ForIntent("actions.intent.SIGN_IN") public ActionResponse getSignInStatus(ActionRequest request) { ResponseBuilder responseBuilder = getResponseBuilder(request); if (request.isSignInGranted()) { GoogleIdToken.Payload profile = getUserProfile(request.getUser().getIdToken()); responseBuilder.add( "I got your account details, " + profile.get("given_name") + ". What do you want to do next?"); } else { responseBuilder.add("I won't be able to save your data, but what do you want to do next?"); } return responseBuilder.build(); } private GoogleIdToken.Payload getUserProfile(String idToken) { GoogleIdToken.Payload profile = null; try { profile = decodeIdToken(idToken); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("error decoding idtoken"); LOGGER.error(e.toString()); } return profile; } private GoogleIdToken.Payload decodeIdToken(String idTokenString) throws GeneralSecurityException, IOException { HttpTransport transport = GoogleNetHttpTransport.newTrustedTransport(); JacksonFactory jsonFactory = JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance(); GoogleIdTokenVerifier verifier = new GoogleIdTokenVerifier.Builder(transport, jsonFactory) // Specify the CLIENT_ID of the app that accesses the backend: .setAudience(Collections.singletonList(clientId)) .build(); GoogleIdToken idToken = verifier.verify(idTokenString); return idToken.getPayload(); }
{ "responseId": "", "queryResult": { "queryText": "", "action": "", "parameters": {}, "allRequiredParamsPresent": true, "fulfillmentText": "", "fulfillmentMessages": [], "outputContexts": [], "intent": { "name": "Get Signin", "displayName": "Get Signin" }, "intentDetectionConfidence": 1, "diagnosticInfo": {}, "languageCode": "" }, "originalDetectIntentRequest": { "source": "google", "version": "2", "payload": { "isInSandbox": true, "surface": { "capabilities": [ { "name": "actions.capability.SCREEN_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.AUDIO_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.MEDIA_RESPONSE_AUDIO" }, { "name": "actions.capability.WEB_BROWSER" } ] }, "inputs": [ { "rawInputs": [], "intent": "", "arguments": [ { "name": "SIGN_IN", "extension": { "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.actions.v2.SignInValue", "status": "OK" } } ] } ], "user": { "idToken": "peJaCGci..." }, "conversation": {}, "availableSurfaces": [ { "capabilities": [ { "name": "actions.capability.SCREEN_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.AUDIO_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.MEDIA_RESPONSE_AUDIO" }, { "name": "actions.capability.WEB_BROWSER" } ] } ] } }, "session": "" }
Te fragmenty kodu do logowania używają pakietu SDK Actions:
const {actionssdk, SignIn} = require('actions-on-google'); const app = actionssdk({ // REPLACE THE PLACEHOLDER WITH THE CLIENT_ID OF YOUR ACTIONS PROJECT clientId: CLIENT_ID, }); // Intent that starts the account linking flow. app.intent('actions.intent.TEXT', (conv) => { conv.ask(new SignIn('To get your account details')); }); // Create an Actions SDK intent with the `actions_intent_SIGN_IN` event. app.intent('actions.intent.SIGN_IN', (conv, params, signin) => { if (signin.status === 'OK') { const payload = conv.user.profile.payload; conv.ask(`I got your account details, ${payload.name}. What do you want to do next?`); } else { conv.ask(`I won't be able to save your data, but what do you want to do next?`); } });
private String clientId = "<your_client_id>"; @ForIntent("actions.intent.TEXT") public ActionResponse text(ActionRequest request) { ResponseBuilder rb = getResponseBuilder(request); return rb.add(new SignIn().setContext("To get your account details")).build(); } @ForIntent("actions.intent.SIGN_IN") public ActionResponse getSignInStatus(ActionRequest request) { ResponseBuilder responseBuilder = getResponseBuilder(request); if (request.isSignInGranted()) { GoogleIdToken.Payload profile = getUserProfile(request.getUser().getIdToken()); responseBuilder.add( "I got your account details, " + profile.get("given_name") + ". What do you want to do next?"); } else { responseBuilder.add("I won't be able to save your data, but what do you want to do next?"); } return responseBuilder.build(); } private GoogleIdToken.Payload getUserProfile(String idToken) { GoogleIdToken.Payload profile = null; try { profile = decodeIdToken(idToken); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("error decoding idtoken"); LOGGER.error(e.toString()); } return profile; } private GoogleIdToken.Payload decodeIdToken(String idTokenString) throws GeneralSecurityException, IOException { HttpTransport transport = GoogleNetHttpTransport.newTrustedTransport(); JacksonFactory jsonFactory = JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance(); GoogleIdTokenVerifier verifier = new GoogleIdTokenVerifier.Builder(transport, jsonFactory) // Specify the CLIENT_ID of the app that accesses the backend: .setAudience(Collections.singletonList(this.clientId)) .build(); GoogleIdToken idToken = verifier.verify(idTokenString); return idToken.getPayload(); }
{ "user": { "idToken": "peJaCGci..." }, "device": {}, "surface": { "capabilities": [ { "name": "actions.capability.SCREEN_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.AUDIO_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.MEDIA_RESPONSE_AUDIO" }, { "name": "actions.capability.WEB_BROWSER" } ] }, "conversation": {}, "inputs": [ { "rawInputs": [], "intent": "actions.intent.SIGN_IN", "arguments": [ { "name": "SIGN_IN", "extension": { "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.actions.v2.SignInValue", "status": "OK" } } ] } ], "availableSurfaces": [ { "capabilities": [ { "name": "actions.capability.SCREEN_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.AUDIO_OUTPUT" }, { "name": "actions.capability.MEDIA_RESPONSE_AUDIO" }, { "name": "actions.capability.WEB_BROWSER" } ] } ] }
Obsługa żądań dostępu do danych
Aby obsłużyć żądanie dostępu do danych, sprawdź, czy użytkownik potwierdził to za pomocą identyfikatora Google token znajduje się już w bazie danych. Następujący fragment kodu pokazuje: przykład sprawdzenia, czy konto użytkownika istnieje już w bazie danych Firestore.
const admin = require('firebase-admin'); const functions = require('firebase-functions'); admin.initializeApp(); const auth = admin.auth(); const db = admin.firestore(); // Save the user in the Firestore DB after successful signin app.intent('Get Sign In', async (conv, params, signin) => { if (signin.status !== 'OK') { return conv.close(`Let's try again next time.`); } const color = conv.data[Fields.COLOR]; const {email} = conv.user; if (!conv.data.uid && email) { try { conv.data.uid = (await auth.getUserByEmail(email)).uid; } catch (e) { if (e.code !== 'auth/user-not-found') { throw e; } // If the user is not found, create a new Firebase auth user // using the email obtained from the Google Assistant conv.data.uid = (await auth.createUser({email})).uid; } } if (conv.data.uid) { conv.user.ref = db.collection('users').doc(conv.data.uid); } conv.close(`I saved ${color} as your favorite color for next time.`); }); // Retrieve the user's favorite color if an account exists, ask if it doesn't. app.intent('Default Welcome Intent', async (conv) => { const {payload} = conv.user.profile; const name = payload ? ` ${payload.given_name}` : ''; conv.ask(`Hi${name}!`); // conv.user.ref contains the id of the record for the user in a Firestore DB if (conv.user.ref) { const doc = await conv.user.ref.get(); if (doc.exists) { const color = doc.data()[Fields.COLOR]; return conv.ask(`Your favorite color was ${color}. ` + 'Tell me a color to update it.'); } } conv.ask(`What's your favorite color?`); });
private class FirestoreManager { private final Firestore db; private final DocumentReference userDocRef; private final String uid; public FirestoreManager(String databaseUrl, String email) throws IOException, FirebaseAuthException { if (FirebaseApp.getApps().isEmpty()) { // Use the application default credentials (works on GCP based hosting). FirebaseOptions options = new FirebaseOptions.Builder() .setCredentials(GoogleCredentials.getApplicationDefault()) .setDatabaseUrl(databaseUrl) .build(); FirebaseApp.initializeApp(options); } this.db = FirestoreClient.getFirestore(); UserRecord userRecord; try { userRecord = FirebaseAuth.getInstance().getUserByEmail(email); } catch (FirebaseAuthException e) { if (e.getErrorCode() == FIREBASE_USER_NOT_FOUND_ERROR) { UserRecord.CreateRequest createRequest = new UserRecord.CreateRequest().setEmail(email); userRecord = FirebaseAuth.getInstance().createUser(createRequest); } else { throw e; } } uid = userRecord.getUid(); userDocRef = db.collection(FIRESTORE_USERS_PATH).document(uid); } public String readUserColor() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ApiFuture<DocumentSnapshot> future = userDocRef.get(); // future.get() blocks on response DocumentSnapshot document = future.get(); if (document.exists()) { return document.get(COLOR_KEY).toString(); } else { return ""; } } public Timestamp writeUserColor(String color) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Map<String, Object> docData = new HashMap<>(); docData.put(COLOR_KEY, color); ApiFuture<WriteResult> future = userDocRef.set(docData); // future.get() blocks on response return future.get().getUpdateTime(); } } @ForIntent("Get Sign In") public ActionResponse getSignIn(ActionRequest request) { LOGGER.info("Get sign in intent start."); ResponseBuilder responseBuilder = getResponseBuilder(request); if (request.isSignInGranted()) { String color = request.getConversationData().get(COLOR_KEY).toString(); GoogleIdToken.Payload profile = getUserProfile(request.getUser().getIdToken()); try { FirestoreManager firestoreManager = new FirestoreManager(DATABASE_URL, profile.getEmail()); saveColor(firestoreManager, color); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error(e.toString()); } responseBuilder .add("I saved " + color + " as your favorite color for next time.") .endConversation(); } else { responseBuilder.add("Let's try again next time"); } LOGGER.info("Get sign in intent end."); return responseBuilder.build(); } private void saveColor(FirestoreManager firestoreManager, String color) { try { Timestamp updateTime = firestoreManager.writeUserColor(color); LOGGER.info(String.format("Update time: %s", updateTime.toString())); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error(e.toString()); } }

