借助 Google Docs API,您可以访问文档中任何标签页的内容。
什么是标签页?
Google 文档具有一个名为标签页的组织层。在 Google 文档中,用户可以在单个文档中创建多个标签页,类似于 Google 表格中目前的标签页。每个标签页都有自己的标题和 ID(附加在网址中)。标签页还可以有子标签页,即嵌套在另一个标签页下的标签页。
对文档资源中表示文档内容的方式进行了结构性更改
过去,文档没有标签页的概念,因此 Document 资源通过以下字段直接包含所有文本内容:
document.bodydocument.headersdocument.footersdocument.footnotesdocument.documentStyledocument.suggestedDocumentStyleChangesdocument.namedStylesdocument.suggestedNamedStylesChangesdocument.listsdocument.namedRangesdocument.inlineObjectsdocument.positionedObjects
由于添加了标签页的额外结构层次,这些字段在语义上不再表示文档中所有标签页的文本内容。基于文本的内容现在以不同的层级表示。您可以使用 document.tabs 访问 Google 文档中的标签页属性和内容,该属性是一个 Tab 对象列表,每个对象都包含上述所有文本内容字段。后面的部分会简要介绍一下;标签页 JSON 表示法也会提供更详细的信息。
访问标签页属性
使用 tab.tabProperties 访问标签页属性,其中包括标签页的 ID、标题和位置等信息。
访问标签页中的文本内容
标签页中的实际文档内容会作为 tab.documentTab 公开。
可以使用 tab.documentTab 访问上述所有文本内容字段。例如,您应该使用 document.tabs[indexOfTab].documentTab.body,而不是 document.body。
标签页层次结构
在 API 中,子标签页表示为 Tab 上的 tab.childTabs 字段。如需访问文档中的所有标签页,需要遍历子标签页的“树”。例如,假设某个文档包含如下所示的标签页层次结构:
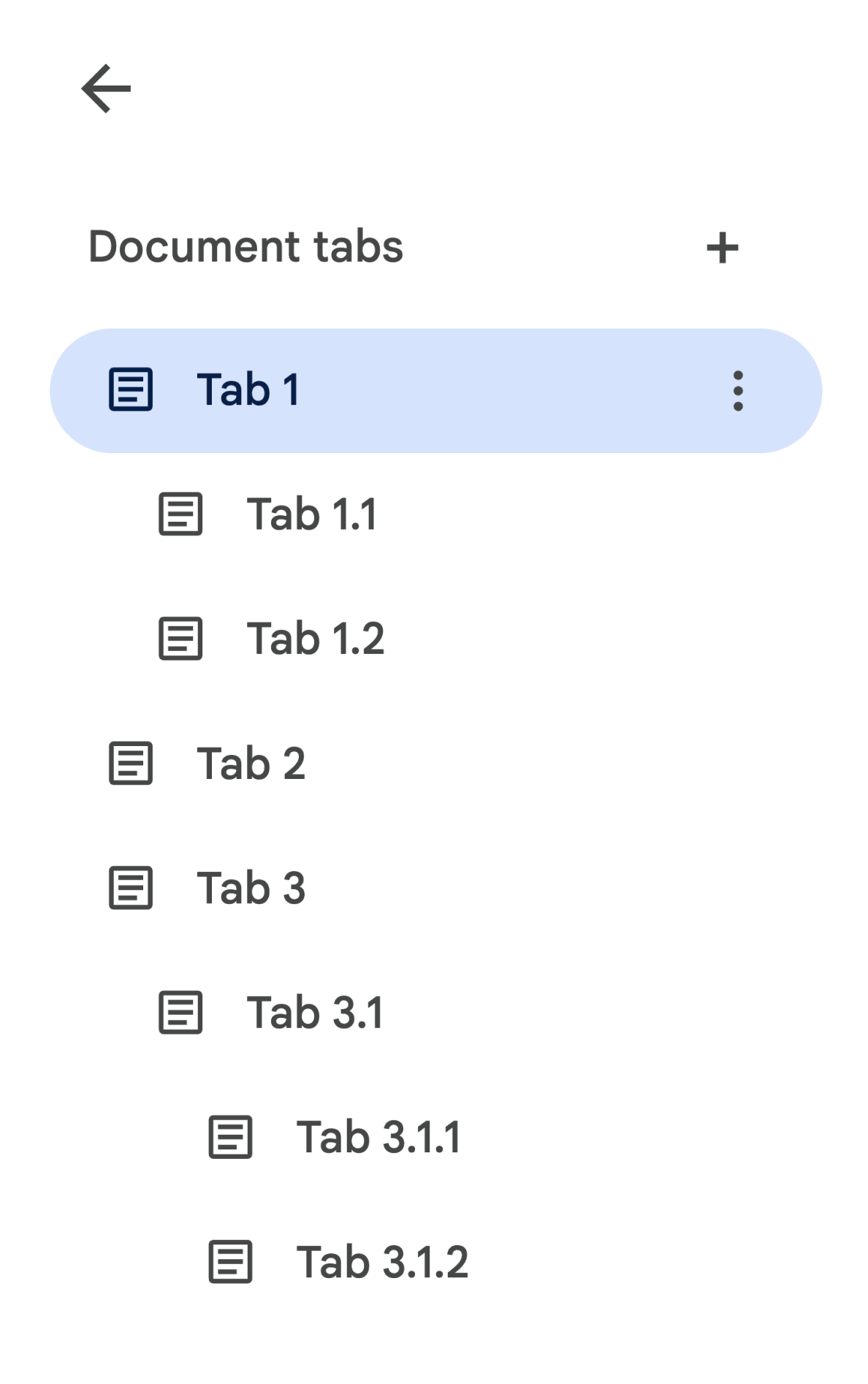
如需从 Tab 3.1.2 中检索 Body,您需要访问 document.tabs[2].childTabs[0].childTabs[1].documentTab.body。请参阅后一部分中的示例代码块,其中提供了用于遍历文档中所有标签页的示例代码。
方法变更
随着标签页的推出,每种文档方法都发生了一些变化,可能需要您更新代码。
documents.get
默认情况下,系统不会返回所有标签页内容。开发者应更新其代码,以访问所有标签页。documents.get 方法公开了一个 includeTabsContent 参数,用于配置是否在响应中提供所有标签页的内容。
- 如果
includeTabsContent设置为true,documents.get方法将返回一个Document资源,其中填充了document.tabs字段。document上的所有文本字段(例如document.body)都将留空。 - 如果未提供
includeTabsContent,则Document资源(例如document.body)中的文本字段将仅填充第一个标签页中的内容。document.tabs字段将为空,并且不会返回其他标签页中的内容。
documents.create
documents.create 方法会返回一个 Document 资源,表示已创建的空文档。返回的 Document 资源将填充文档文本内容字段和 document.tabs 中的空白文档内容。
document.batchUpdate
每个 Request 都包含一种指定要应用更新的标签页的方法。默认情况下,如果未指定标签页,Request 在大多数情况下将应用于文档中的第一个标签页。ReplaceAllTextRequest、DeleteNamedRangeRequest 和 ReplaceNamedRangeContentRequest 是三个特殊请求,默认情况下会应用于所有标签页。
如需了解具体情况,请参阅 Request 的文档。
内部链接的更改
用户可以在文档中创建指向标签页、书签和标题的内部链接。
随着标签页功能的推出,Link 资源中的 link.bookmarkId 和 link.headingId 字段不再表示文档中特定标签页内的书签或标题。
开发者应更新其代码,以便在读取和写入操作中使用 link.bookmark 和 link.heading。它们使用 BookmarkLink 和 HeadingLink 对象公开内部链接,每个对象都包含相应书签或标题的 ID 以及它所在的标签页的 ID。此外,link.tabId 还公开了指向标签页的内部链接。
documents.get 响应的链接内容也会因 includeTabsContent 参数而异:
- 如果
includeTabsContent设置为true,则所有内部链接都将显示为link.bookmark和link.heading。旧版字段将不再使用。 - 如果未提供
includeTabsContent,那么在包含单个标签页的文档中,指向该标签页内书签或标题的任何内部链接仍会显示为link.bookmarkId和link.headingId。在包含多个标签页的文档中,内部链接将显示为link.bookmark和link.heading。
在 document.batchUpdate 中,如果使用某个旧版字段创建内部链接,则书签或标题将被视为来自 Request 中指定的标签页 ID。如果未指定标签页,则系统会认为数据来自文档中的第一个标签页。
链接 JSON 表示法提供了更详细的信息。
标签页的常见使用模式
以下代码示例介绍了与标签页互动的各种方式。
读取文档中所有标签页的标签页内容
之前在标签页功能推出之前执行此操作的现有代码可以通过以下方式迁移为支持标签页:将 includeTabsContent 参数设置为 true,遍历标签页树层次结构,并调用 Tab 和 DocumentTab 的 getter 方法,而不是 Document。以下部分代码示例基于从文档中提取文本中的代码段。该示例展示了如何打印文档中每个标签页的所有文本内容。此标签页遍历代码可适用于许多其他不关心标签页实际结构的用例。
Java
/** Prints all text contents from all tabs in the document. */ static void printAllText(Docs service, String documentId) throws IOException { // Fetch the document with all of the tabs populated, including any nested // child tabs. Document doc = service.documents().get(documentId).setIncludeTabsContent(true).execute(); List<Tab> allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); // Print the content from each tab in the document. for (Tab tab: allTabs) { // Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab. DocumentTab documentTab = tab.getDocumentTab(); System.out.println( readStructuralElements(documentTab.getBody().getContent())); } } /** * Returns a flat list of all tabs in the document in the order they would * appear in the UI (top-down ordering). Includes all child tabs. */ private List<Tab> getAllTabs(Document doc) { List<Tab> allTabs = new ArrayList<>(); // Iterate over all tabs and recursively add any child tabs to generate a // flat list of Tabs. for (Tab tab: doc.getTabs()) { addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs); } return allTabs; } /** * Adds the provided tab to the list of all tabs, and recurses through and * adds all child tabs. */ private void addCurrentAndChildTabs(Tab tab, List<Tab> allTabs) { allTabs.add(tab); for (Tab tab: tab.getChildTabs()) { addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs); } } /** * Recurses through a list of Structural Elements to read a document's text * where text may be in nested elements. * * <p>For a code sample, see * <a href="https://developers.google.com/workspace/docs/api/samples/extract-text">Extract * the text from a document</a>. */ private static String readStructuralElements(List<StructuralElement> elements) { ... }
从文档的第一个标签页读取标签页内容
这类似于阅读所有标签页。
Java
/** Prints all text contents from the first tab in the document. */ static void printAllText(Docs service, String documentId) throws IOException { // Fetch the document with all of the tabs populated, including any nested // child tabs. Document doc = service.documents().get(documentId).setIncludeTabsContent(true).execute(); List<Tab> allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); // Print the content from the first tab in the document. Tab firstTab = allTabs.get(0); // Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab. DocumentTab documentTab = firstTab.getDocumentTab(); System.out.println( readStructuralElements(documentTab.getBody().getContent())); }
发出更新第一个标签页的请求
以下部分代码示例展示了如何在 Request 中定位特定标签页。
此代码基于插入、删除和移动文本指南中的示例。
Java
/** Inserts text into the first tab of the document. */ static void insertTextInFirstTab(Docs service, String documentId) throws IOException { // Get the first tab's ID. Document doc = service.documents().get(documentId).setIncludeTabsContent(true).execute(); Tab firstTab = doc.getTabs().get(0); String tabId = firstTab.getTabProperties().getTabId(); List<Request>requests = new ArrayList<>(); requests.add(new Request().setInsertText( new InsertTextRequest().setText(text).setLocation(new Location() // Set the tab ID. .setTabId(tabId) .setIndex(25)))); BatchUpdateDocumentRequest body = new BatchUpdateDocumentRequest().setRequests(requests); BatchUpdateDocumentResponse response = docsService.documents().batchUpdate(DOCUMENT_ID, body).execute(); }