ה-History API מאפשר לאפליקציה לבצע פעולות בכמות גדולה בחנות הכושר: קריאה, הזנה, עדכון ומחיקה של נתונים היסטוריים של בריאות ורווחה. תוכלו להשתמש ב-History API כדי לבצע את הפעולות הבאות:
- קריאה של נתוני בריאות וכושר שנוספו או תועדו באמצעות מכשיר אחר באפליקציות.
- ייבוא של נתוני אצווה אל Google Fit.
- עדכון הנתונים ב-Google Fit.
- מחיקה של נתונים היסטוריים שהאפליקציה איחסנה בעבר.
כדי להוסיף נתונים שמכילים מטא-נתונים של הסשן, צריך להשתמש Sessions API
קריאת נתונים
בקטעים הבאים מוסבר איך לקרוא סוגים שונים של נתונים נצברים.
לקריאת נתונים מפורטים ונצברים
כדי לקרוא נתונים היסטוריים, צריך ליצור
DataReadRequest
מכונה.
Kotlin
// Read the data that's been collected throughout the past week. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusWeeks(1) Log.i(TAG, "Range Start: $startTime") Log.i(TAG, "Range End: $endTime") val readRequest = DataReadRequest.Builder() // The data request can specify multiple data types to return, // effectively combining multiple data queries into one call. // This example demonstrates aggregating only one data type. .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) // Analogous to a "Group By" in SQL, defines how data should be // aggregated. // bucketByTime allows for a time span, whereas bucketBySession allows // bucketing by <a href="/fit/android/using-sessions">sessions</a>. .bucketByTime(1, TimeUnit.DAYS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build()
Java
// Read the data that's been collected throughout the past week. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusWeeks(1); Log.i(TAG, "Range Start: $startTime"); Log.i(TAG, "Range End: $endTime"); DataReadRequest readRequest = new DataReadRequest.Builder() // The data request can specify multiple data types to return, // effectively combining multiple data queries into one call. // This example demonstrates aggregating only one data type. .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) // Analogous to a "Group By" in SQL, defines how data should be // aggregated. // bucketByTime allows for a time span, while bucketBySession allows // bucketing by sessions. .bucketByTime(1, TimeUnit.DAYS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build();
בדוגמה הקודמת נעשה שימוש בנקודות נתונים נצברים, שבהן כל DataPoint
מייצג את מספר הצעדים שהלכת ביום. בתרחיש הספציפי הזה,
לנתונים נצברים יש שני יתרונות:
- האפליקציה וחנות הכושר ממירות כמויות קטנות יותר של נתונים.
- האפליקציה לא צריכה לצבור את הנתונים באופן ידני.
נתונים נצברים לסוגים שונים של פעילויות
האפליקציה שלך יכולה להשתמש בבקשות לנתונים כדי לאחזר סוגים שונים של נתונים.
הדוגמה הבאה מראה איך ליצור
DataReadRequest כדי לקבל קלוריות שנשרפו בכל פעילות שמבוצעת במסגרת
טווח הזמן שצוין. הנתונים שמתקבלים תואמים את הקלוריות לכל פעילות, באופן הבא:
מדווחות באפליקציית Google Fit, שבה לכל פעילות משויכת קטגוריה משלה.
של נתוני קלוריות.
Kotlin
val readRequest = DataReadRequest.Builder() .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_CALORIES_EXPENDED) .bucketByActivityType(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build()
Java
DataReadRequest readRequest = new DataReadRequest.Builder() .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_CALORIES_EXPENDED) .bucketByActivityType(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build();
אחרי שיוצרים מכונת DataReadRequest, משתמשים ב-
HistoryClient.readData()
לקריאת נתונים היסטוריים באופן אסינכרוני.
הדוגמה הבאה ממחישה איך למצוא את המכונות של DataPoint מ-
DataSet:
Kotlin
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .readData(readRequest) .addOnSuccessListener { response -> // The aggregate query puts datasets into buckets, so flatten into a // single list of datasets for (dataSet in response.buckets.flatMap { it.dataSets }) { dumpDataSet(dataSet) } } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG,"There was an error reading data from Google Fit", e) } fun dumpDataSet(dataSet: DataSet) { Log.i(TAG, "Data returned for Data type: ${dataSet.dataType.name}") for (dp in dataSet.dataPoints) { Log.i(TAG,"Data point:") Log.i(TAG,"\tType: ${dp.dataType.name}") Log.i(TAG,"\tStart: ${dp.getStartTimeString()}") Log.i(TAG,"\tEnd: ${dp.getEndTimeString()}") for (field in dp.dataType.fields) { Log.i(TAG,"\tField: ${field.name.toString()} Value: ${dp.getValue(field)}") } } } fun DataPoint.getStartTimeString() = Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getStartTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString() fun DataPoint.getEndTimeString() = Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getEndTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString()
Java
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .readData(readRequest) .addOnSuccessListener (response -> { // The aggregate query puts datasets into buckets, so convert to a // single list of datasets for (Bucket bucket : response.getBuckets()) { for (DataSet dataSet : bucket.getDataSets()) { dumpDataSet(dataSet); } } }) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error reading data from Google Fit", e)); } private void dumpDataSet(DataSet dataSet) { Log.i(TAG, "Data returned for Data type: ${dataSet.dataType.name}"); for (DataPoint dp : dataSet.getDataPoints()) { Log.i(TAG,"Data point:"); Log.i(TAG,"\tType: ${dp.dataType.name}"); Log.i(TAG,"\tStart: ${dp.getStartTimeString()}"); Log.i(TAG,"\tEnd: ${dp.getEndTimeString()}"); for (Field field : dp.getDataType().getFields()) { Log.i(TAG,"\tField: ${field.name.toString()} Value: ${dp.getValue(field)}"); } } } private String getStartTimeString() { return Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getStartTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString(); } private String getEndTimeString() { return Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getEndTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString(); }
קריאה של נתונים כוללים יומיים
Google Fit מספקת גם גישה פשוטה לנתונים
מהסוג שצוין. משתמשים ב
HistoryClient.readDailyTotal()
שיטה לאחזור סוג הנתונים שמציינים החל מחצות של
יום באזור הזמן הנוכחי של המכשיר. לדוגמה, מעבירים את
סוג נתונים אחד (TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) לשיטה הזו, כדי לאחזר את הסכום היומי
לבצע מיליון שלבים. אפשר להעביר בסוג נתונים מיידי שיש בו נתונים מצטברים
סה"כ. למידע נוסף על סוגי הנתונים הנתמכים, ראו
DataType.getAggregateType
Google Fit לא דורשת הרשאה כדי להירשם
עדכונים על TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA מהHistoryClient.readDailyTotal()
כשמתבצעת קריאה לשיטה הזו באמצעות חשבון ברירת המחדל
ציינת היקפים.
האפשרות הזו יכולה להיות שימושית אם אתם צריכים נתוני צעד כדי להשתמש בהם באזורים שבהם אתם לא יכולים
כדי להציג את חלונית ההרשאות, למשל בתצוגות שעון עם Wear OS.
המשתמשים מעדיפים לראות ספירות עקביות של צעדים באפליקציית Google Fit
אפליקציות אחרות ותצוגות שעון של Wear OS, כי זה מספק להן
עקביות ואמינה. כדי לשמור על עקביות בספירת הצעדים, כדאי להירשם אל
צעדים בפלטפורמת Google Fit מהאפליקציה או מתצוגת השעון,
מעדכנים את הספירה ב-
onExitAmbient()
לקבלת מידע נוסף על אופן השימוש בנתונים האלה בתצוגת שעון:
תכונות נוספות של תצוגת השעון
ובאפליקציה לדוגמה של Android WatchFace.
הוספת נתונים
כדי להוסיף נתונים היסטוריים, קודם צריך ליצור מכונה של DataSet:
Kotlin
// Declare that the data being inserted was collected during the past hour. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusHours(1) // Create a data source val dataSource = DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build() // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 950 new steps. val stepCountDelta = 950 val dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build() val dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build()
Java
// Declare that the data being inserted was collected during the past hour. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusHours(1); // Create a data source DataSource dataSource = new DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build(); // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 950 new steps. int stepCountDelta = 950; DataPoint dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); DataSet dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build();
אחרי שיוצרים מכונת DataSet, משתמשים ב-
HistoryClient.insertData
כדי להוסיף באופן אסינכרוני את הנתונים ההיסטוריים האלה.
Kotlin
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .insertData(dataSet) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "DataSet added successfully!") } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error adding the DataSet", e) }
Java
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .insertData(dataSet) .addOnSuccessListener (unused -> Log.i(TAG, "DataSet added successfully!")) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error adding the DataSet", e)); }
ניהול נקודות מתנגשות על הגרף
כל אחד
DataPoint
ב-DataSet של האפליקציה חייבים להיות startTime ו-endTime שמגדירים
מרווח ייחודי בתוך אותו DataSet, ללא חפיפה בין DataPoint
במקרים שונים.
אם האפליקציה שלך מנסה להוסיף DataPoint חדש שמתנגש עם
המופע DataPoint, הערך החדש 'DataPoint' נמחק. כדי להוסיף תג חדש
DataPoint שעשויה להיות חופפת לנקודות נתונים קיימות, משתמשים בפונקציה
HistoryClient.updateData
המתוארת בעדכון נתונים.
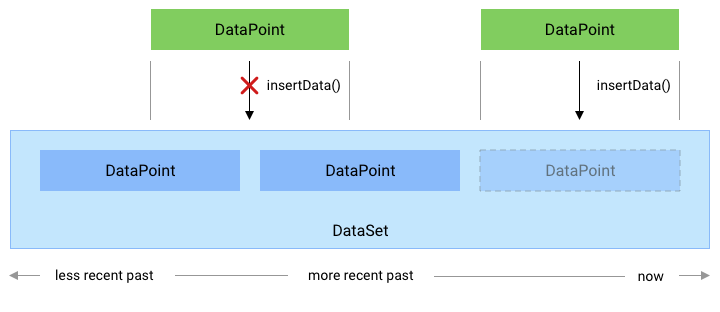
איור 1. איך השיטה insertData() מטפלת בנקודות נתונים חדשות
יש התנגשות עם DataPoint קיים.
עדכון נתונים
Google Fit מאפשרת לאפליקציה לעדכן את הנתונים ההיסטוריים של בריאות וכושר
שנוספו בעבר. כדי להוסיף נתונים היסטוריים עבור DataSet חדש, או כדי להוסיף חדש
DataPoint מופעים שלא מתנגשים עם נתונים קיימים
נקודות, יש להשתמש בשיטה HistoryApi.insertData.
כדי לעדכן נתונים היסטוריים, צריך להשתמש בשיטה HistoryClient.updateData. הזה
ה-method מוחק את כל המופעים הקיימים של DataPoint שחופפים ל-DataPoint
למכונות שנוספו באמצעות השיטה הזו.
כדי לעדכן את הנתונים ההיסטוריים של בריאות ואיכות חיים, צריך קודם ליצור DataSet
מופע:
Kotlin
// Declare that the historical data was collected during the past 50 minutes. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusMinutes(50) // Create a data source val dataSource = DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build() // Create a data set // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 1000 new steps. val stepCountDelta = 1000 val dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .build() val dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build()
Java
// Declare that the historical data was collected during the past 50 minutes. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusMinutes(50); // Create a data source DataSource dataSource = new DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build(); // Create a data set // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 1000 new steps. int stepCountDelta = 1000; DataPoint dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .build(); DataSet dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build();
לאחר מכן משתמשים ב-DataUpdateRequest.Builder() כדי ליצור בקשה חדשה לעדכון נתונים.
כדי לבצע את הבקשה, צריך להשתמש בשיטה HistoryClient.updateData:
Kotlin
val request = DataUpdateRequest.Builder() .setDataSet(dataSet) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build() Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .updateData(request) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "DataSet updated successfully!") } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error updating the DataSet", e) }
Java
DataUpdateRequest request = new DataUpdateRequest.Builder() .setDataSet(dataSet) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .updateData(request) .addOnSuccessListener(unused -> Log.i(TAG, "DataSet updated successfully!")) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error updating the DataSet", e));
מחיקת נתונים
אפליקציית Google Fit מאפשרת לאפליקציה למחוק את נתוני הבריאות ואיכות החיים ההיסטוריים שלה שנוספו בעבר.
כדי למחוק נתונים היסטוריים, משתמשים
HistoryClient.deleteData
method:
Kotlin
// Declare that this code deletes step count information that was collected // throughout the past day. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusDays(1) // Create a delete request object, providing a data type and a time interval val request = DataDeleteRequest.Builder() .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .addDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .build() // Invoke the History API with the HistoryClient object and delete request, and // then specify a callback that will check the result. Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .deleteData(request) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "Data deleted successfully!") } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error with the deletion request", e) }
Java
// Declare that this code deletes step count information that was collected // throughout the past day. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusDays(1); // Create a delete request object, providing a data type and a time interval DataDeleteRequest request = new DataDeleteRequest.Builder() .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .addDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .build(); // Invoke the History API with the HistoryClient object and delete request, and // then specify a callback that will check the result. Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .deleteData(request) .addOnSuccessListener (unused -> Log.i(TAG, "Data deleted successfully!")) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error with the deletion request", e));
אפליקציות יכולות למחוק נתונים מסשנים ספציפיים או
מחיקת כל הנתונים. מידע נוסף זמין במשאבי העזרה של ה-API
DataDeleteRequest
הרשמה לקבלת עדכוני נתונים
האפליקציה יכולה לקרוא נתוני חיישנים גולמיים בזמן אמת באמצעות הרשמה אל
SensorsClient
אם מדובר בנתונים מסוגים אחרים שנספרים בתדירות נמוכה יותר ונספרים באופן ידני, ניתן:
האפליקציה יכולה להירשם לקבלת עדכונים כשהמדידות האלה מוכנסות
במסד הנתונים של Google Fit. דוגמאות לסוגי נתונים אלה כוללות גובה,
משקולות ואימוני כושר כמו הרמת משקולות; פרטים נוספים זמינים ברשימה המלאה
של סוגי הנתונים הנתמכים.
כדי להירשם לקבלת עדכונים, השתמשו
HistoryClient.registerDataUpdateListener
קטע הקוד הבא מאפשר לאפליקציה לקבל התראה כשהמשתמש מזין קוד אימות ערך המשקל שלהם:
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(this, MyDataUpdateService::class.java) val pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getService(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT) val request = DataUpdateListenerRegistrationRequest.Builder() .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_WEIGHT) .setPendingIntent(pendingIntent) .build() Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .registerDataUpdateListener(request) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "DataUpdateListener registered") }
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyDataUpdateService.class); PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getService(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT) DataUpdateListenerRegistrationRequest request = new DataUpdateListenerRegistrationRequest.Builder() .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_WEIGHT) .setPendingIntent(pendingIntent) .build(); Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .registerDataUpdateListener(request) .addOnSuccessListener(unused -> Log.i(TAG, "DataUpdateListener registered"));
אפשר להשתמש במכשיר IntentService כדי לקבל התראות לגבי עדכונים:
Kotlin
class MyDataUpdateService : IntentService("MyDataUpdateService") { override fun onHandleIntent(intent: Intent?) { val update = DataUpdateNotification.getDataUpdateNotification(intent) // Show the time interval over which the data points were collected. // To extract specific data values, in this case the user's weight, // use DataReadRequest. update?.apply { val start = getUpdateStartTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) val end = getUpdateEndTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) Log.i(TAG, "Data Update start: $start end: $end DataType: ${dataType.name}") } } }
Java
public class MyDataUpdateService extends IntentService { public MyDataUpdateService(String name) { super("MyDataUpdateService"); } @Override protected void onHandleIntent(@Nullable Intent intent) { if (intent != null) { DataUpdateNotification update = DataUpdateNotification.getDataUpdateNotification(intent); // Show the time interval over which the data points // were collected. // To extract specific data values, in this case the user's weight, // use DataReadRequest. if (update != null) { long start = update.getUpdateStartTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); long end = update.getUpdateEndTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } Log.i(TAG, "Data Update start: $start end: $end DataType: ${dataType.name}"); } } }
צריך להצהיר על IntentService בקובץ AndroidManifest.xml.

