概览
基于 OAuth 的 Google 登录简化关联会在 OAuth 关联的基础上添加 Google 登录。这样可以为 Google 用户提供流畅的关联体验,还支持账号创建,让用户可以使用其 Google 账号在您的服务中创建新账号。
如需使用 OAuth 和 Google 登录功能执行账号关联,请按照以下常规步骤操作:
- 首先,请用户同意访问其 Google 个人资料。
- 使用其个人资料中的信息检查用户账号是否存在。
- 对于现有用户,请关联账号。
- 如果您在身份验证系统中找不到与 Google 用户匹配的用户,请验证从 Google 收到的 ID 令牌。然后,您可以根据 ID 令牌中包含的个人资料信息创建用户。
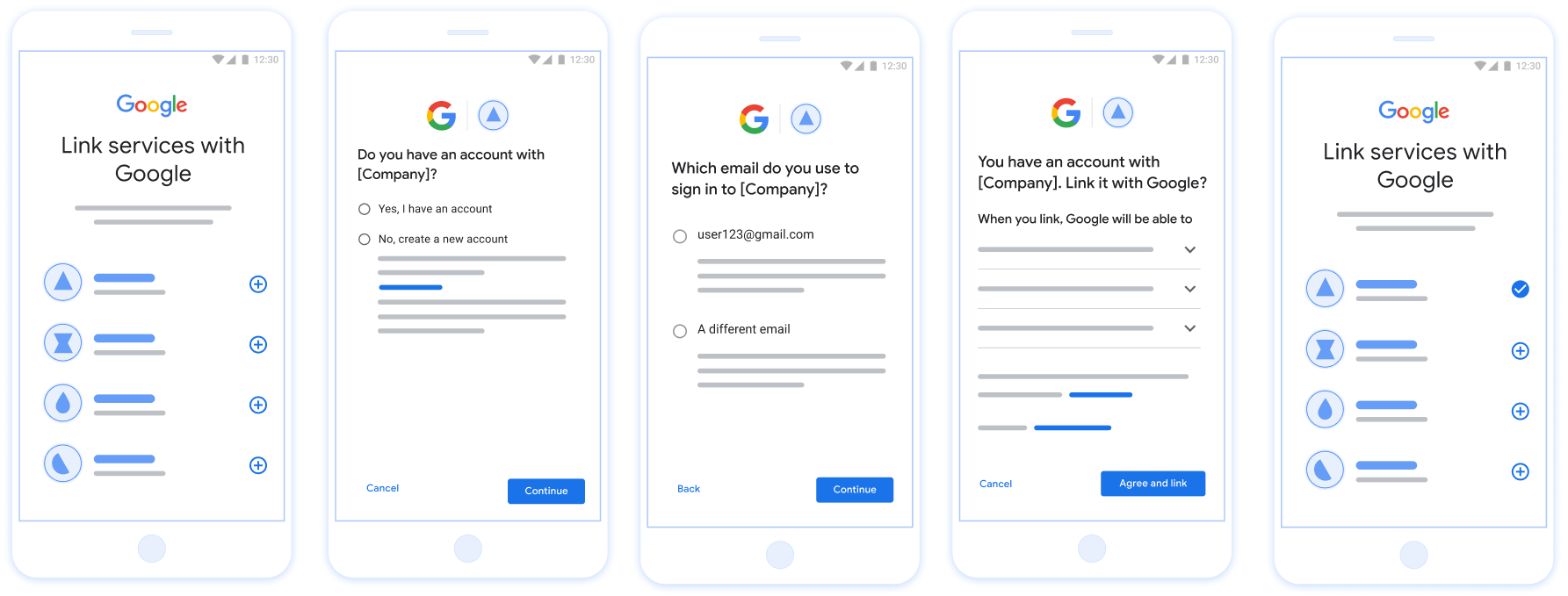
图 1. 在用户手机上使用精简关联功能进行账号关联
简化关联的要求
- 实现基本 Web OAuth 关联流程。您的服务必须支持符合 OAuth 2.0 标准的授权和令牌交换端点。
- 您的令牌交换端点必须支持 JSON Web 令牌 (JWT) 断言,并实现
check、create和getintent。
实现 OAuth 服务器
您的令牌交换端点必须支持 check、create、get intent。下图显示了通过账号关联流程完成的步骤,并指明了调用不同 intent 的时间:
- 用户是否在您的身份验证系统中拥有账号?(用户通过选择“是”或“否”来决定)
- 是:用户是否使用与其 Google 账号关联的电子邮件地址登录您的平台?(用户通过选择“是”或“否”来决定)
- 是:用户在您的身份验证系统中是否有匹配的账号?(系统会调用
check intent进行确认)- 是:系统会调用
get intent,如果 get intent 返回成功,则关联账号。 - 否:创建新账号?(用户通过选择“是”或“否”来决定)
- 是:如果 create intent 返回成功,系统会调用
create intent并关联账号。 - 否:系统会触发 Web OAuth 流程,将用户定向到其浏览器,并向用户提供使用其他电子邮件地址关联的选项。
- 是:如果 create intent 返回成功,系统会调用
- 是:系统会调用
- 否:系统会触发 Web OAuth 流程,将用户定向到其浏览器,并为用户提供使用其他电子邮件地址关联的选项。
- 是:用户在您的身份验证系统中是否有匹配的账号?(系统会调用
- 否:用户在您的身份验证系统中是否有匹配的账号?(系统会调用
check intent进行确认)- 是:如果 get intent 返回成功,系统会调用
get intent并关联账号。 - 否:如果 create intent 成功返回,系统会调用
create intent并关联账号。
- 是:如果 get intent 返回成功,系统会调用
- 是:用户是否使用与其 Google 账号关联的电子邮件地址登录您的平台?(用户通过选择“是”或“否”来决定)
检查现有用户账号(检查 intent)
在用户同意访问其 Google 个人资料后,Google 会发送 请求,其中包含 Google 用户身份的已签名断言。通过 断言包含的信息包括用户的 Google 账号 ID、 姓名和电子邮件地址为您的 Google Cloud 控制台配置的令牌交换端点 项目处理该请求。
如果您的身份验证中已有相应的 Google 账号
系统时,您的令牌交换端点会返回 account_found=true。如果
Google 账号与现有用户不匹配,您的令牌交换端点
返回“HTTP 404 Not Found”错误以及 account_found=false。
请求的格式如下:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=check&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
您的令牌交换端点必须能够处理以下参数:
| 令牌端点参数 | |
|---|---|
intent |
对于这些请求,此参数的值为
check。 |
grant_type |
所交换的令牌的类型。对于这类请求
参数的值为 urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer。 |
assertion |
一个 JSON Web 令牌 (JWT),提供 Google 用户身份。JWT 包含的信息包括用户 Google 账号 ID、姓名和电子邮件地址。 |
client_id |
您分配给 Google 的客户 ID。 |
client_secret |
您分配给 Google 的客户端密钥。 |
如需响应 check intent 请求,您的令牌交换端点必须执行以下步骤:
- 验证和解码 JWT 断言。
- 检查您的身份验证系统中是否已存在该 Google 账号。
验证和解码 JWT 断言
您可以使用 适用于您所用语言的 JWT 解码库。使用 Google 的公钥,在 JWK 或 PEM 格式,用于验证 令牌的签名。
解码后,JWT 断言如以下示例所示:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
除了验证令牌的签名之外,还要验证断言的
颁发者(iss 字段)为 https://accounts.google.com,
(aud 字段)是分配给您的客户端 ID,并且令牌未过期
(exp 字段)。
使用 email、email_verified 和 hd 字段,您可以确定
Google 负责托管电子邮件地址,并对其具有权威性。如果 Google
权威性 - 用户当前被认定为合法账号所有者
您可以跳过密码或其他验证方法。否则,这些方法
可用于在关联之前验证账号。
Google 具有权威性的情形:
email的后缀为@gmail.com,这是一个 Gmail 账号。email_verified为 true 且hd已设置,这是 G Suite 账号。
用户无需使用 Gmail 或 G Suite 即可注册 Google 账号。时间
email 不包含 @gmail.com 后缀,且 hd 不存在 Google 不
建议使用权威凭据和密码或其他验证方法进行验证
用户。email_verified 可能为 true,因为 Google 最初验证了
创建 Google 账号后,该用户会获得第三方的所有权,
后,电子邮件账号可能已更改。
检查您的身份验证系统中是否已存在该 Google 账号
请检查以下任一条件是否成立:
- Google 账号 ID(可在断言的
sub字段中找到)位于您的用户中 数据库。 - 断言中的电子邮件地址与用户数据库中的用户匹配。
如果满足上述任一条件,则表明用户已注册。在这种情况下 返回如下所示的响应:
HTTP/1.1 200 Success
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"true",
}
如果 Google 账号 ID 和
断言与您的数据库中的用户匹配,该用户尚未注册。在
在这种情况下,您的令牌交换端点需要返回 HTTP 404 错误
指定 "account_found": "false",如以下示例所示:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"false",
}
处理自动链接(获取 intent)
在用户同意访问其 Google 个人资料后,Google 会发送 请求,其中包含 Google 用户身份的已签名断言。通过 断言包含的信息包括用户的 Google 账号 ID、 姓名和电子邮件地址为您的 Google Cloud 控制台配置的令牌交换端点 项目处理该请求。
如果您的身份验证中已有相应的 Google 账号
系统,您的令牌交换端点将为用户返回一个令牌。如果
Google 账号与现有用户不匹配,您的令牌交换端点
返回 linking_error 错误和可选的 login_hint。
请求的格式如下:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=get&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
您的令牌交换端点必须能够处理以下参数:
| 令牌端点参数 | |
|---|---|
intent |
对于这些请求,此参数的值为 get。 |
grant_type |
所交换的令牌的类型。对于这类请求
参数的值为 urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer。 |
assertion |
一个 JSON Web 令牌 (JWT),提供 Google 用户身份。JWT 包含的信息包括用户 Google 账号 ID、姓名和电子邮件地址。 |
scope |
可选:您已将 Google 配置为向其请求访问权限的任何范围 用户。 |
client_id |
您分配给 Google 的客户 ID。 |
client_secret |
您分配给 Google 的客户端密钥。 |
如需响应 get intent 请求,您的令牌交换端点必须执行以下步骤:
- 验证和解码 JWT 断言。
- 检查您的身份验证系统中是否已存在该 Google 账号。
验证和解码 JWT 断言
您可以使用 适用于您所用语言的 JWT 解码库。使用 Google 的公钥,在 JWK 或 PEM 格式,用于验证 令牌的签名。
解码后,JWT 断言如以下示例所示:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
除了验证令牌的签名之外,还要验证断言的
颁发者(iss 字段)为 https://accounts.google.com,
(aud 字段)是分配给您的客户端 ID,并且令牌未过期
(exp 字段)。
使用 email、email_verified 和 hd 字段,您可以确定
Google 负责托管电子邮件地址,并对其具有权威性。如果 Google
权威性 - 用户当前被认定为合法账号所有者
您可以跳过密码或其他验证方法。否则,这些方法
可用于在关联之前验证账号。
Google 具有权威性的情形:
email的后缀为@gmail.com,这是一个 Gmail 账号。email_verified为 true 且hd已设置,这是 G Suite 账号。
用户无需使用 Gmail 或 G Suite 即可注册 Google 账号。时间
email 不包含 @gmail.com 后缀,且 hd 不存在 Google 不
建议使用权威凭据和密码或其他验证方法进行验证
用户。email_verified 可能为 true,因为 Google 最初验证了
创建 Google 账号后,该用户会获得第三方的所有权,
后,电子邮件账号可能已更改。
检查您的身份验证系统中是否已存在该 Google 账号
请检查以下任一条件是否成立:
- Google 账号 ID(可在断言的
sub字段中找到)位于您的用户中 数据库。 - 断言中的电子邮件地址与用户数据库中的用户匹配。
如果找到了用户的账号,请发出访问令牌,并在 HTTPS 响应正文的 JSON 对象中返回相应值,如以下示例所示:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
在某些情况下,基于 ID 令牌的账号关联可能会失败。如果
因为任何原因,您的令牌交换端点都需要以 HTTP 响应
指定 error=linking_error 的 401 错误,如以下示例所示:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
当 Google 收到包含 linking_error 的 401 错误响应时,会发送
使用 login_hint 作为参数将用户发送到您的授权端点。通过
用户在浏览器中使用 OAuth 关联流程完成账号关联。
通过 Google 登录功能处理账号创建(创建 intent)
当用户需要在您的服务中创建账号时,Google 会发出请求
发送到指定 intent=create 的令牌交换端点。
请求的格式如下:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded response_type=token&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&scope=SCOPES&intent=create&assertion=JWT&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
您的令牌交换端点必须能够处理以下参数:
| 令牌端点参数 | |
|---|---|
intent |
对于这些请求,此参数的值为 create。 |
grant_type |
所交换的令牌的类型。对于这类请求
参数的值为 urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer。 |
assertion |
一个 JSON Web 令牌 (JWT),提供 Google 用户身份。JWT 包含的信息包括用户 Google 账号 ID、姓名和电子邮件地址。 |
client_id |
您分配给 Google 的客户 ID。 |
client_secret |
您分配给 Google 的客户端密钥。 |
assertion 参数中的 JWT 包含用户的 Google 账号 ID。
姓名和电子邮件地址,可用于在 Gmail 中创建新账号
服务。
如需响应 create intent 请求,您的令牌交换端点必须执行以下步骤:
- 验证和解码 JWT 断言。
- 验证用户信息并创建新账号。
验证和解码 JWT 断言
您可以使用 适用于您所用语言的 JWT 解码库。使用 Google 的公钥,在 JWK 或 PEM 格式,用于验证 令牌的签名。
解码后,JWT 断言如以下示例所示:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
除了验证令牌的签名之外,还要验证断言的
颁发者(iss 字段)为 https://accounts.google.com,
(aud 字段)是分配给您的客户端 ID,并且令牌未过期
(exp 字段)。
使用 email、email_verified 和 hd 字段,您可以确定
Google 负责托管电子邮件地址,并对其具有权威性。如果 Google
权威性 - 用户当前被认定为合法账号所有者
您可以跳过密码或其他验证方法。否则,这些方法
可用于在关联之前验证账号。
Google 具有权威性的情形:
email的后缀为@gmail.com,这是一个 Gmail 账号。email_verified为 true 且hd已设置,这是 G Suite 账号。
用户无需使用 Gmail 或 G Suite 即可注册 Google 账号。时间
email 不包含 @gmail.com 后缀,且 hd 不存在 Google 不
建议使用权威凭据和密码或其他验证方法进行验证
用户。email_verified 可能为 true,因为 Google 最初验证了
创建 Google 账号后,该用户会获得第三方的所有权,
后,电子邮件账号可能已更改。
验证用户信息并创建新账号
请检查以下任一条件是否成立:
- Google 账号 ID(可在断言的
sub字段中找到)位于您的用户中 数据库。 - 断言中的电子邮件地址与用户数据库中的用户匹配。
如果满足上述任一条件,请提示用户关联其现有账号
与其 Google 账号关联。为此,请使用 HTTP 401 错误响应请求
该参数指定 error=linking_error 并将用户的电子邮件地址作为
login_hint。以下是示例响应:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
当 Google 收到包含 linking_error 的 401 错误响应时,会发送
使用 login_hint 作为参数将用户发送到您的授权端点。通过
用户在浏览器中使用 OAuth 关联流程完成账号关联。
如果以上两个条件都不满足,请使用相应信息创建一个新的用户账号 。新账号通常不会设置密码。时间是 建议您将 Google 登录功能添加到其他平台,以便用户 使用 Google 账号登录。或者 可以通过电子邮件向用户发送链接,启动密码恢复流程,以允许 用户设置密码,以便在其他平台上登录。
创建完成后,发出一个访问令牌 和刷新令牌 并在 HTTPS 响应的正文,如以下示例所示:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
获取您的 Google API 客户端 ID
您需要在账号关联注册流程中提供 Google API 客户端 ID。
使用您在完成 OAuth 关联步骤时创建的项目获取 API 客户端 ID。为此,请完成以下步骤:
创建或选择一个 Google API 项目。
如果您的项目没有 Web 应用类型的客户端 ID,请点击创建客户端以创建一个。请务必在已获授权的 JavaScript 来源框中添加您网站的域名。执行本地测试或开发时,您必须将
http://localhost和http://localhost:<port_number>添加到已获授权的 JavaScript 来源字段。
验证您的实现
您可以使用 OAuth 2.0 Playground 工具验证您的实现。
在该工具中,执行以下步骤:
- 点击配置 以打开 OAuth 2.0 配置窗口。
- 在 OAuth flow 字段中,选择 Client-side(客户端)。
- 在 OAuth 端点字段中,选择自定义。
- 在相应字段中指定您的 OAuth 2.0 端点和您分配给 Google 的客户端 ID。
- 在第 1 步部分,不要选择任何 Google 范围。请将此字段留空或输入对服务器有效的范围(如果您不使用 OAuth 范围,则可以输入任意字符串)。完成后,点击授权 API。
- 在 Step 2 和 Step 3 部分中,完成 OAuth 2.0 流程,并验证每个步骤是否按预期运行。
您可以使用 Google 账号关联演示版工具验证您的实现。
在该工具中,执行以下步骤:
- 点击使用 Google 账号登录按钮。
- 选择您要关联的账号。
- 输入服务 ID。
- (可选)输入您要请求访问权限的一个或多个范围。
- 点击开始演示。
- 当系统提示时,请确认您同意或拒绝关联请求。
- 确认您已被重定向到您的平台。
