Übersicht
Bei der optimierten OAuth-basierten Google Log-in-Verknüpfung wird Google Log-in zusätzlich zur OAuth-Verknüpfung verwendet. So können Google-Nutzer Konten nahtlos verknüpfen und Konten erstellen, um mit ihrem Google-Konto ein neues Konto in Ihrem Dienst zu erstellen.
So verknüpfen Sie Konten mit OAuth und Google Sign-In:
- Bitten Sie den Nutzer zuerst, seine Einwilligung zum Zugriff auf sein Google-Profil zu erteilen.
- Prüfe anhand der Informationen in seinem Profil, ob das Nutzerkonto vorhanden ist.
- Verknüpfen Sie die Konten für bestehende Nutzer.
- Wenn Sie in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem keinen entsprechenden Nutzer finden, validieren Sie das von Google empfangene ID-Token. Sie können dann einen Nutzer basierend auf den Profilinformationen im ID-Token erstellen.
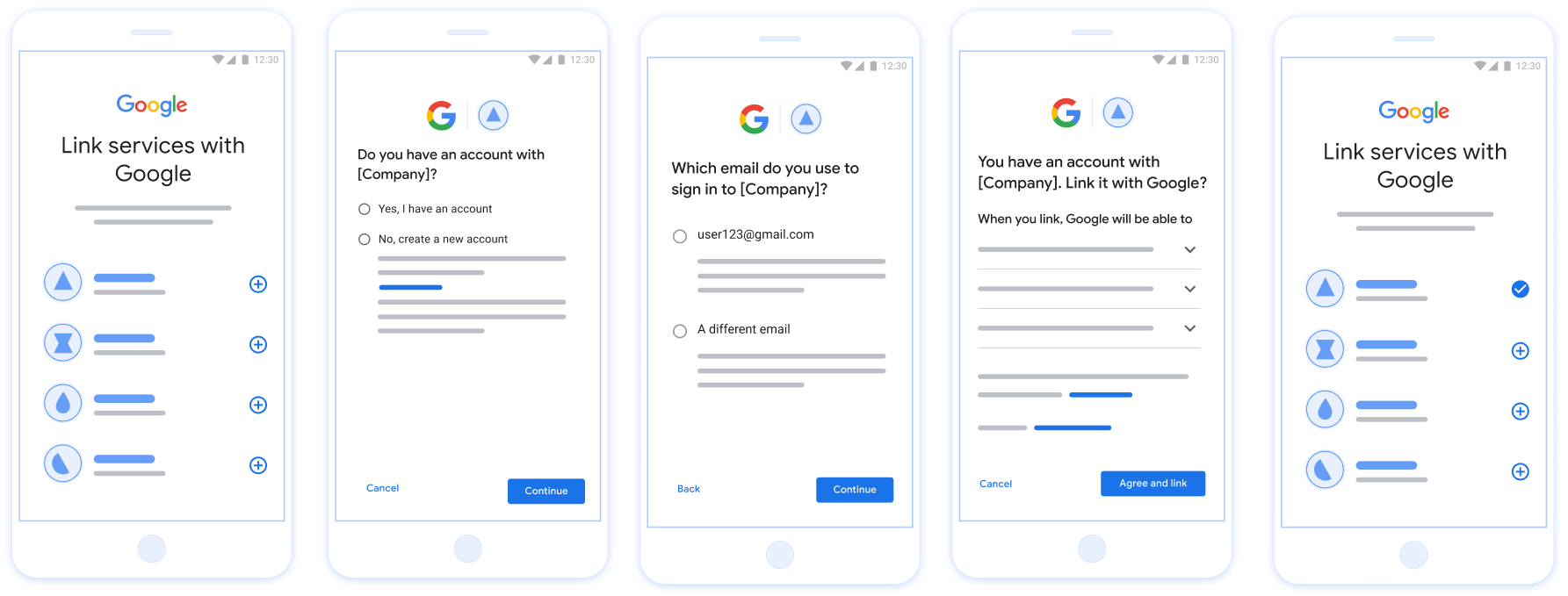
Abbildung 1. Kontoverknüpfung auf dem Smartphone eines Nutzers mit optimierter Verknüpfung
Anforderungen für die vereinfachte Verknüpfung
- Implementiere den grundlegenden OAuth-Verknüpfungsvorgang für das Web. Ihr Dienst muss OAuth 2.0-konforme Autorisierungs- und Token-Austauschendpunkte unterstützen.
- Der Token-Austausch-Endpunkt muss JSON Web Token (JWT)-Behauptungen unterstützen und die Intents
check,createundgetimplementieren.
OAuth-Server implementieren
Der Token-Austauschendpunkt muss die Intents check, create und get unterstützen. Unten sind die Schritte zu sehen, die während des Kontoverknüpfungsvorgangs ausgeführt werden, und es wird angegeben, wann die verschiedenen Intents aufgerufen werden:
- Hat der Nutzer ein Konto in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem? (Nutzer wählt JA oder NEIN aus)
- JA : Verwendet der Nutzer die mit seinem Google-Konto verknüpfte E-Mail-Adresse, um sich auf Ihrer Plattform anzumelden? (Nutzer wählt JA oder NEIN aus)
- JA : Hat der Nutzer ein übereinstimmendes Konto in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem? (
check intentwird zur Bestätigung aufgerufen)- JA :
get intentwird aufgerufen und das Konto wird verknüpft, wenn „get intent“ erfolgreich zurückgegeben wird. - NEIN : Neues Konto erstellen? (Nutzer wählt JA oder NEIN aus)
- JA :
create intentwird aufgerufen und das Konto wird verknüpft, wenn „create intent“ erfolgreich zurückgegeben wird. - NEIN : Der Web-OAuth-Vorgang wird ausgelöst, der Nutzer wird zu seinem Browser weitergeleitet und hat die Möglichkeit, eine andere E-Mail-Adresse zu verknüpfen.
- JA :
- JA :
- NEIN : Der OAuth-Webablauf wird ausgelöst, der Nutzer wird zu seinem Browser weitergeleitet und hat die Möglichkeit, eine andere E-Mail-Adresse zu verknüpfen.
- JA : Hat der Nutzer ein übereinstimmendes Konto in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem? (
- NEIN : Hat der Nutzer ein übereinstimmendes Konto in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem? (
check intentwird zur Bestätigung aufgerufen)- JA :
get intentwird aufgerufen und das Konto wird verknüpft, wenn „get intent“ erfolgreich zurückgegeben wird. - NEIN :
create intentwird aufgerufen und das Konto wird verknüpft, wenn „create intent“ erfolgreich zurückgegeben wird.
- JA :
- JA : Verwendet der Nutzer die mit seinem Google-Konto verknüpfte E-Mail-Adresse, um sich auf Ihrer Plattform anzumelden? (Nutzer wählt JA oder NEIN aus)
Nach einem vorhandenen Nutzerkonto suchen (Intent überprüfen)
Nachdem der Nutzer seine Einwilligung für den Zugriff auf sein Google-Profil erteilt hat, sendet Google eine -Anfrage, die eine signierte Bestätigung der Identität des Google-Nutzers enthält. Die Assertion enthält Informationen wie die Google-Konto-ID, Name und E-Mail-Adresse. Der Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt, der für Ihr diese Anfrage verarbeitet.
Wenn das entsprechende Google-Konto bereits in Ihrer Authentifizierung vorhanden ist
reagiert, antwortet der Endpunkt des Tokenaustauschs mit account_found=true. Wenn die
Das Google-Konto stimmt mit keinem vorhandenen Nutzer überein, Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch
gibt den Fehler „HTTP 404 Not Found“ mit account_found=false zurück.
Die Anfrage hat das folgende Format:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=check&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Der Endpunkt des Tokenaustauschs muss die folgenden Parameter verarbeiten können:
| Parameter für Tokenendpunkt | |
|---|---|
intent |
Bei diesen Anfragen lautet der Wert dieses Parameters
check |
grant_type |
Der Tokentyp, der ausgetauscht wird. Bei diesen Anfragen
den Wert urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer hat. |
assertion |
Ein JSON Web Token (JWT), das eine signierte Assertion der Google der Identität des Nutzers. Das JWT enthält Informationen wie die ID, Name und E-Mail-Adresse des Google-Kontos |
client_id |
Die Client-ID, die Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
client_secret |
Der Clientschlüssel, den Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch muss die folgenden Schritte ausführen, um auf die Intent-Anfragen check zu antworten:
- Validieren und decodieren Sie die JWT-Assertion.
- Prüfen Sie, ob das Google-Konto bereits in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem vorhanden ist.
JWT-Assertion validieren und decodieren
Sie können die JWT-Assertion mit einem JWT-Decodierungsbibliothek für Ihre Sprache. Verwenden Sie Die öffentlichen Schlüssel von Google, verfügbar in JWK oder PEM-Formate, zur Überprüfung die Signatur des Tokens.
Nach der Decodierung sieht die JWT-Assertion so aus:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
Neben der Verifizierung der Tokensignatur müssen Sie auch prüfen, ob die
Aussteller (Feld iss) ist https://accounts.google.com, die Zielgruppe
(Feld aud) enthält Ihre zugewiesene Client-ID und das Token, das nicht abgelaufen ist.
(Feld exp).
Mit den Feldern email, email_verified und hd können Sie festlegen,
Google hostet eine E-Mail-Adresse und ist für sie maßgeblich. In Fällen, in denen Google
autoritativer Nutzer, der derzeit als rechtmäßiger Kontoinhaber bekannt ist
und Sie können das Passwort oder andere Methoden zur Identitätsbestätigung überspringen. Andernfalls werden diese Methoden
kann vor der Verknüpfung zur Bestätigung des Kontos verwendet werden.
Fälle, in denen Google als vertrauenswürdig eingestuft wird:
emailhat das Suffix@gmail.com. Dies ist ein Gmail-Konto.email_verifiedist „true“ undhdist festgelegt. Dies ist ein G Suite-Konto.
Nutzer können sich für ein Google-Konto registrieren, ohne Gmail oder die G Suite zu verwenden. Wann?
email enthält kein @gmail.com-Suffix und hd fehlt. Google ist kein
werden zur Bestätigung der Identität empfohlen,
Nutzenden. email_verified kann auch „true“ sein, da Google das
Nutzer beim Erstellen des Google-Kontos, aber die Inhaberschaft des Drittanbieters
Ihr E-Mail-Konto hat sich in der Zwischenzeit möglicherweise geändert.
Prüfen, ob das Google-Konto bereits in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem vorhanden ist
Prüfen Sie, ob eine der folgenden Bedingungen erfüllt ist:
- Die Google-Konto-ID, die Sie im Feld
subder Assertion finden, gehört Ihrem Nutzer Datenbank. - Die E-Mail-Adresse in der Assertion stimmt mit einem Nutzer in Ihrer Nutzerdatenbank überein.
Wenn eine der Bedingungen erfüllt ist, hat sich der Nutzer bereits registriert. In diesem Fall eine Antwort wie die folgende zurückgeben:
HTTP/1.1 200 Success
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"true",
}
Wenn weder die Google-Konto-ID noch die E-Mail-Adresse im
Assertion mit einem Nutzer in Ihrer Datenbank übereinstimmt, hat sich dieser Nutzer noch nicht registriert. In
muss der Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt mit dem HTTP-Fehler 404
der "account_found": "false" angibt, wie im folgenden Beispiel:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"false",
}
Automatische Verknüpfung (get-Intent)
Nachdem der Nutzer seine Einwilligung für den Zugriff auf sein Google-Profil erteilt hat, sendet Google eine -Anfrage, die eine signierte Bestätigung der Identität des Google-Nutzers enthält. Die Assertion enthält Informationen wie die Google-Konto-ID, Name und E-Mail-Adresse. Der Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt, der für Ihr diese Anfrage verarbeitet.
Wenn das entsprechende Google-Konto bereits in Ihrer Authentifizierung vorhanden ist
System gibt Ihr Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt ein Token für den Nutzer zurück. Wenn die
Google-Konto stimmt mit keinem vorhandenen Nutzer überein, Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch
gibt einen linking_error-Fehler und optional login_hint zurück.
Die Anfrage hat das folgende Format:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=get&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Der Endpunkt des Tokenaustauschs muss die folgenden Parameter verarbeiten können:
| Parameter für Tokenendpunkt | |
|---|---|
intent |
Bei diesen Anfragen lautet der Wert des Parameters get. |
grant_type |
Der Tokentyp, der ausgetauscht wird. Bei diesen Anfragen
den Wert urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer hat. |
assertion |
Ein JSON Web Token (JWT), das eine signierte Assertion der Google der Identität des Nutzers. Das JWT enthält Informationen wie die ID, Name und E-Mail-Adresse des Google-Kontos |
scope |
Optional: Alle Bereiche, die Sie in Google so konfiguriert haben, dass sie von Ihnen angefordert werden Nutzenden. |
client_id |
Die Client-ID, die Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
client_secret |
Der Clientschlüssel, den Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch muss die folgenden Schritte ausführen, um auf die Intent-Anfragen get zu antworten:
- Validieren und decodieren Sie die JWT-Assertion.
- Prüfen Sie, ob das Google-Konto bereits in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem vorhanden ist.
JWT-Assertion validieren und decodieren
Sie können die JWT-Assertion mit einem JWT-Decodierungsbibliothek für Ihre Sprache. Verwenden Sie Die öffentlichen Schlüssel von Google, verfügbar in JWK oder PEM-Formate, zur Überprüfung die Signatur des Tokens.
Nach der Decodierung sieht die JWT-Assertion so aus:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
Neben der Verifizierung der Tokensignatur müssen Sie auch prüfen, ob die
Aussteller (Feld iss) ist https://accounts.google.com, die Zielgruppe
(Feld aud) enthält Ihre zugewiesene Client-ID und das Token, das nicht abgelaufen ist.
(Feld exp).
Mit den Feldern email, email_verified und hd können Sie festlegen,
Google hostet eine E-Mail-Adresse und ist für sie maßgeblich. In Fällen, in denen Google
autoritativer Nutzer, der derzeit als rechtmäßiger Kontoinhaber bekannt ist
und Sie können das Passwort oder andere Methoden zur Identitätsbestätigung überspringen. Andernfalls werden diese Methoden
kann vor der Verknüpfung zur Bestätigung des Kontos verwendet werden.
Fälle, in denen Google als vertrauenswürdig eingestuft wird:
emailhat das Suffix@gmail.com. Dies ist ein Gmail-Konto.email_verifiedist „true“ undhdist festgelegt. Dies ist ein G Suite-Konto.
Nutzer können sich für ein Google-Konto registrieren, ohne Gmail oder die G Suite zu verwenden. Wann?
email enthält kein @gmail.com-Suffix und hd fehlt. Google ist kein
werden zur Bestätigung der Identität empfohlen,
Nutzenden. email_verified kann auch „true“ sein, da Google das
Nutzer beim Erstellen des Google-Kontos, aber die Inhaberschaft des Drittanbieters
Ihr E-Mail-Konto hat sich in der Zwischenzeit möglicherweise geändert.
Prüfen, ob das Google-Konto bereits in Ihrem Authentifizierungssystem vorhanden ist
Prüfen Sie, ob eine der folgenden Bedingungen erfüllt ist:
- Die Google-Konto-ID, die Sie im Feld
subder Assertion finden, gehört Ihrem Nutzer Datenbank. - Die E-Mail-Adresse in der Assertion stimmt mit einem Nutzer in Ihrer Nutzerdatenbank überein.
Wenn für den Nutzer ein Konto gefunden wird, geben Sie ein Zugriffstoken aus und geben Sie die Werte wie im folgenden Beispiel in einem JSON-Objekt im Text Ihrer HTTPS-Antwort zurück:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
In einigen Fällen schlägt die auf dem ID-Token basierende Kontoverknüpfung für den Nutzer möglicherweise fehl. Wenn es
aus irgendeinem Grund tut, muss Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch mit einem HTTP-Statuscode
401-Fehler, der error=linking_error angibt, wie im folgenden Beispiel gezeigt:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Wenn Google eine 401-Fehlerantwort mit linking_error erhält, sendet Google
den Nutzer zu Ihrem Autorisierungsendpunkt mit login_hint als Parameter. Die
Der Nutzer schließt die Kontoverknüpfung mithilfe des OAuth-Verknüpfungsvorgangs in seinem Browser ab.
Kontoerstellung über Google Log-in durchführen (Create-Intent)
Wenn ein Nutzer ein Konto bei Ihrem Dienst erstellen muss, stellt Google eine Anfrage
zu Ihrem Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt, der intent=create angibt.
Die Anfrage hat das folgende Format:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded response_type=token&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&scope=SCOPES&intent=create&assertion=JWT&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Der Endpunkt des Tokenaustauschs muss die folgenden Parameter verarbeiten können:
| Parameter für Tokenendpunkt | |
|---|---|
intent |
Bei diesen Anfragen lautet der Wert des Parameters create. |
grant_type |
Der Tokentyp, der ausgetauscht wird. Bei diesen Anfragen
den Wert urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer hat. |
assertion |
Ein JSON Web Token (JWT), das eine signierte Assertion der Google der Identität des Nutzers. Das JWT enthält Informationen wie die ID, Name und E-Mail-Adresse des Google-Kontos |
client_id |
Die Client-ID, die Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
client_secret |
Der Clientschlüssel, den Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
Das JWT im Parameter assertion enthält die Google-Konto-ID des Nutzers,
und die E-Mail-Adresse, mit der Sie ein neues Konto auf Ihrem
.
Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch muss die folgenden Schritte ausführen, um auf die Intent-Anfragen create zu antworten:
- Validieren und decodieren Sie die JWT-Assertion.
- Validieren Sie die Nutzerinformationen und erstellen Sie ein neues Konto.
JWT-Assertion validieren und decodieren
Sie können die JWT-Assertion mit einem JWT-Decodierungsbibliothek für Ihre Sprache. Verwenden Sie Die öffentlichen Schlüssel von Google, verfügbar in JWK oder PEM-Formate, zur Überprüfung die Signatur des Tokens.
Nach der Decodierung sieht die JWT-Assertion so aus:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
Neben der Verifizierung der Tokensignatur müssen Sie auch prüfen, ob die
Aussteller (Feld iss) ist https://accounts.google.com, die Zielgruppe
(Feld aud) enthält Ihre zugewiesene Client-ID und das Token, das nicht abgelaufen ist.
(Feld exp).
Mit den Feldern email, email_verified und hd können Sie festlegen,
Google hostet eine E-Mail-Adresse und ist für sie maßgeblich. In Fällen, in denen Google
autoritativer Nutzer, der derzeit als rechtmäßiger Kontoinhaber bekannt ist
und Sie können das Passwort oder andere Methoden zur Identitätsbestätigung überspringen. Andernfalls werden diese Methoden
kann vor der Verknüpfung zur Bestätigung des Kontos verwendet werden.
Fälle, in denen Google als vertrauenswürdig eingestuft wird:
emailhat das Suffix@gmail.com. Dies ist ein Gmail-Konto.email_verifiedist „true“ undhdist festgelegt. Dies ist ein G Suite-Konto.
Nutzer können sich für ein Google-Konto registrieren, ohne Gmail oder die G Suite zu verwenden. Wann?
email enthält kein @gmail.com-Suffix und hd fehlt. Google ist kein
werden zur Bestätigung der Identität empfohlen,
Nutzenden. email_verified kann auch „true“ sein, da Google das
Nutzer beim Erstellen des Google-Kontos, aber die Inhaberschaft des Drittanbieters
Ihr E-Mail-Konto hat sich in der Zwischenzeit möglicherweise geändert.
Nutzerinformationen validieren und neues Konto erstellen
Prüfen Sie, ob eine der folgenden Bedingungen erfüllt ist:
- Die Google-Konto-ID, die Sie im Feld
subder Assertion finden, gehört Ihrem Nutzer Datenbank. - Die E-Mail-Adresse in der Assertion stimmt mit einem Nutzer in Ihrer Nutzerdatenbank überein.
Wenn eine der Bedingungen zutrifft, fordern Sie den Nutzer auf, sein vorhandenes Konto zu verknüpfen.
mit ihrem Google-Konto. Antworten Sie dazu mit einem HTTP 401-Fehler auf die Anfrage.
der error=linking_error angibt und die E-Mail-Adresse des Nutzers als
login_hint. Hier ist eine Beispielantwort:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Wenn Google eine 401-Fehlerantwort mit linking_error erhält, sendet Google
den Nutzer zu Ihrem Autorisierungsendpunkt mit login_hint als Parameter. Die
Der Nutzer schließt die Kontoverknüpfung mithilfe des OAuth-Verknüpfungsvorgangs in seinem Browser ab.
Wenn keine der beiden Bedingungen zutrifft, erstellen Sie ein neues Nutzerkonto mit den entsprechenden Informationen. die im JWT bereitgestellt werden. Für neue Konten wird normalerweise kein Passwort festgelegt. Es ist empfohlen, Google Log-in auf anderen Plattformen hinzuzufügen, damit Nutzer in allen Oberflächen Ihrer App bei Google anmelden. Alternativ können Sie kann dem Nutzer per E-Mail einen Link senden, mit dem die Passwortwiederherstellung gestartet wird. , um ein Passwort für die Anmeldung auf anderen Plattformen festzulegen.
Wenn die Erstellung abgeschlossen ist, geben Sie ein Zugriffstoken aus und aktualisieren Sie das Token und geben die Werte in einem JSON-Objekt in den Text Ihrer HTTPS-Antwort ein, wie im folgenden Beispiel:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google API-Client-ID abrufen
Sie müssen Ihre Google API-Client-ID während der Registrierung für die Kontoverknüpfung angeben.
So rufen Sie Ihre API-Client-ID mit dem Projekt ab, das Sie bei der OAuth-Verknüpfung erstellt haben. Führen Sie dazu folgende Schritte aus:
Erstellen oder wählen Sie ein Google APIs-Projekt aus.
Wenn Ihr Projekt keine Client-ID für den Webanwendungstyp hat, klicken Sie auf Client erstellen, um eine zu erstellen. Geben Sie im Feld Autorisierte JavaScript-Quellen die Domain Ihrer Website an. Wenn Sie lokale Tests oder die Entwicklung durchführen, müssen Sie dem Feld Autorisierte JavaScript-Quellen sowohl
http://localhostals auchhttp://localhost:<port_number>hinzufügen.
Implementierung validieren
Sie können Ihre Implementierung mit dem Tool OAuth 2.0 Playground validieren.
Führen Sie im Tool die folgenden Schritte aus:
- Klicken Sie auf Konfiguration , um das Fenster für die OAuth 2.0-Konfiguration zu öffnen.
- Wählen Sie im Feld OAuth-Ablauf die Option Clientseitig aus.
- Wählen Sie im Feld OAuth-Endpunkte die Option Benutzerdefiniert aus.
- Geben Sie in den entsprechenden Feldern Ihren OAuth 2.0-Endpunkt und die Client-ID an, die Sie Google zugewiesen haben.
- Wählen Sie im Abschnitt Schritt 1 keine Google-Bereiche aus. Lassen Sie dieses Feld stattdessen leer oder geben Sie einen für Ihren Server gültigen Bereich ein (oder einen beliebigen String, wenn Sie keine OAuth-Bereiche verwenden). Wenn Sie fertig sind, klicken Sie auf APIs autorisieren.
- Führen Sie in den Abschnitten Schritt 2 und Schritt 3 den OAuth 2.0-Ablauf durch und prüfen Sie, ob jeder Schritt wie vorgesehen funktioniert.
Sie können Ihre Implementierung mit der Demo zur Google-Kontoverknüpfung prüfen.
Führen Sie im Tool die folgenden Schritte aus:
- Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche Über Google anmelden.
- Wählen Sie das Konto aus, das Sie verknüpfen möchten.
- Geben Sie die Service-ID ein.
- Optional können Sie einen oder mehrere Bereiche angeben, für die Sie Zugriff anfordern möchten.
- Klicken Sie auf Demo starten.
- Bestätigen Sie bei Aufforderung, dass Sie der Verknüpfungsanfrage zustimmen oder sie ablehnen können.
- Prüfen Sie, ob Sie zu Ihrer Plattform weitergeleitet werden.
