概览
借助精细权限,消费者可以更精细地控制自己选择与每个应用分享的账号数据。精细权限可提供更高的控制权、透明度和安全性,因此对用户和开发者都有好处。本指南将帮助您了解成功更新应用以处理精细权限所需的更改和步骤。
什么是精细权限?
假设您开发了一款可提高办公效率的应用,该应用同时请求电子邮件和日历范围。您的用户可能只想将您的应用用于 Google 日历,而不想用于 Gmail。借助精细的 OAuth 权限,用户可以选择仅授予 Google 日历权限,而不授予 Gmail 权限。 通过让用户授予对特定数据的访问权限,可以最大限度地减少数据泄露,增强信任,并让用户能够以隐私保护为先的原则来控制自己的数字生活。请务必设计应用以处理此类情况。
请求了多个非登录范围时
登录范围和非登录范围
对于同时请求登录范围和非登录范围的应用,用户首先会看到登录范围(email、profile 和 openid)的同意页面。在用户同意分享其基本身份信息(姓名、电子邮件地址和个人资料照片)后,用户会看到非登录范围的精细权限同意屏幕。在这种情况下,应用必须检查用户授予的范围,而不能假设用户授予了所有请求的范围。在以下示例中,Web 应用请求了所有三个登录范围和一个 Google 云端硬盘非登录范围。用户同意登录范围后,系统会向用户显示 Google 云端硬盘权限的精细权限同意屏幕:
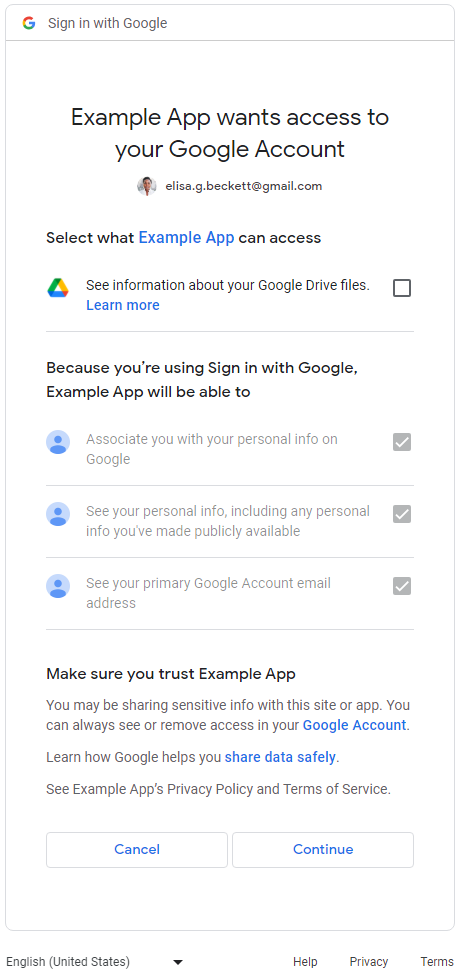
多个非登录范围
当应用请求多个非登录范围时,系统会向用户显示精细权限同意屏幕。用户可以选择要批准哪些权限以与应用分享。以下是请求访问用户的 Gmail 邮件和 Google 日历数据的精细权限同意屏幕示例:
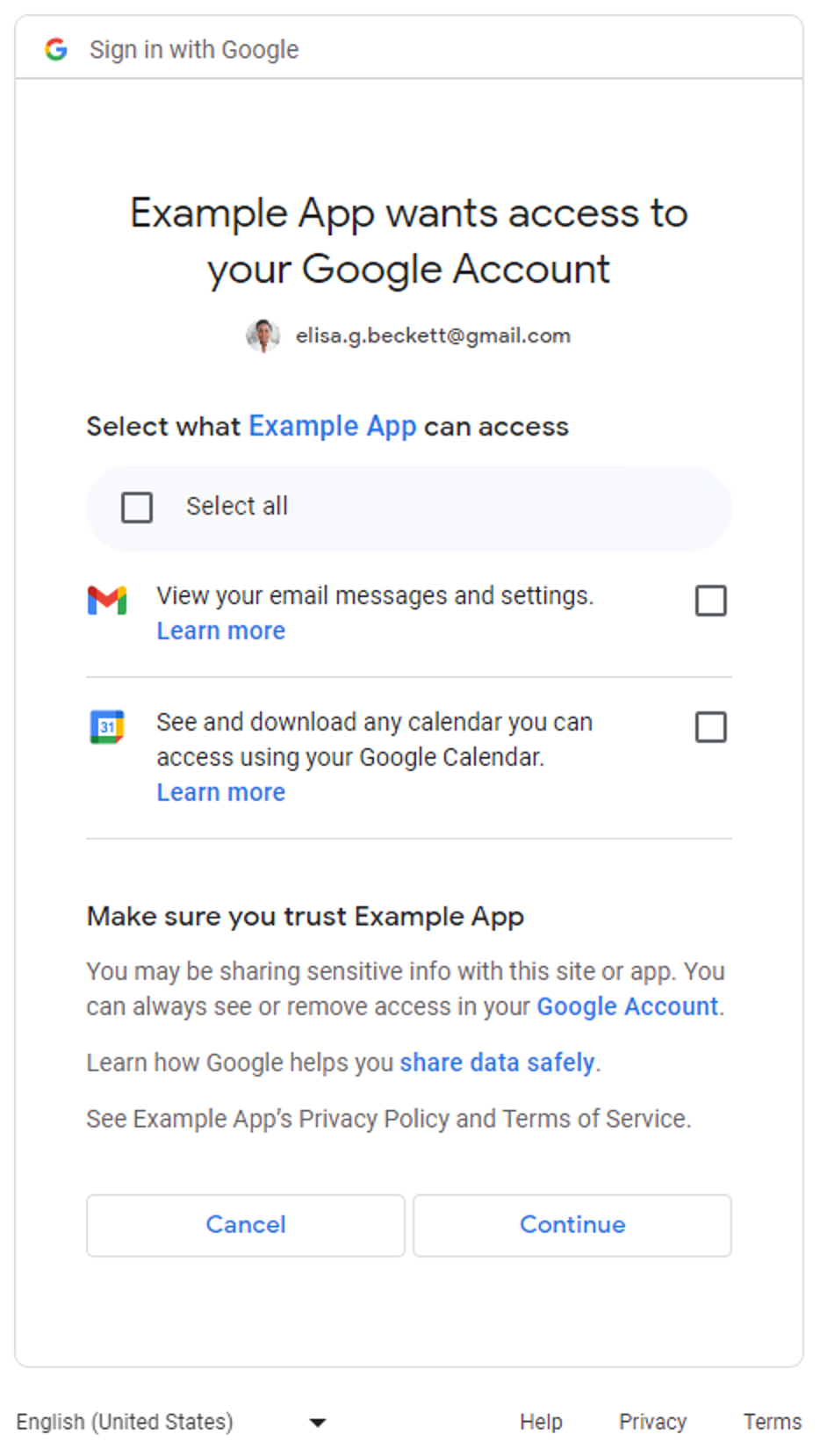
对于仅请求登录范围(email、profile 和 openid)的应用,细化权限同意屏幕不适用。用户可以批准或拒绝整个登录请求。换句话说,如果应用仅请求登录范围(一个、两个或全部三个),则细化权限同意屏幕不适用。
对于仅请求一项非登录范围的应用,细化权限同意屏幕不适用。换句话说,用户要么批准整个请求,要么拒绝整个请求,并且同意屏幕中没有复选框。下表总结了何时显示精细权限同意屏幕。
| 登录范围的数量 | 非登录范围的数量 | 精细权限同意页面 |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 0 | 不适用 |
| 1-3 | 1+ | 适用 |
| 0 | 1 | 不适用 |
| 0 | 2+ | 适用 |
确定您的应用是否会受到影响
全面检查应用中所有使用 Google OAuth 2.0 授权端点来请求权限的部分。请注意请求多个范围的范围,因为它们会激活向用户显示的精细权限同意屏幕。在这种情况下,请确保您的代码可以处理用户仅授权部分范围的情况。
如何确定您的应用是否使用了多个范围
检查应用代码或出站网络调用,以确定应用发出的 Google OAuth 2.0 授权请求是否会导致系统显示精细权限请求页面。
检查应用代码
检查应用代码中调用 Google OAuth 授权端点以向用户请求权限的部分。如果您使用某个 Google API 客户端库,通常可以在客户端初始化步骤中找到应用请求的范围。以下部分展示了一些示例。您应参阅应用所用 SDK 的文档,了解如何处理 Google OAuth 2.0,以确定您的应用是否会受到影响。以下示例中的指导可供您参考。
Google Identity 服务
以下 Google Identity 服务 JavaScript 库代码段使用多个非登录范围初始化 TokenClient。当 Web 应用向用户请求授权时,系统会显示精细的权限同意屏幕。
const client = google.accounts.oauth2.initTokenClient({ client_id: 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID', scope: 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly \ https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly', callback: (response) => { ... }, });
Python
以下代码段使用 google-auth-oauthlib.flow 模块来构建授权请求;scope 参数包含两个非登录范围。当 Web 应用向用户请求授权时,系统会显示精细的权限同意屏幕。
import google.oauth2.credentials import google_auth_oauthlib.flow # Use the client_secret.json file to identify the application requesting # authorization. The client ID (from that file) and access scopes are required. flow = google_auth_oauthlib.flow.Flow.from_client_secrets_file( 'client_secret.json', scopes=['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly', 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly'])
Node.js
以下代码段创建了一个 google.auth.OAuth2 对象,该对象定义了授权请求中的参数,其 scope 参数包含两个非登录范围。当 Web 应用向用户请求授权时,系统会显示精细的权限同意屏幕。
const {google} = require('googleapis'); /** * To use OAuth2 authentication, we need access to a CLIENT_ID, CLIENT_SECRET, AND REDIRECT_URI * from the client_secret.json file. To get these credentials for your application, visit * https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials. */ const oauth2Client = new google.auth.OAuth2( YOUR_CLIENT_ID, YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET, YOUR_REDIRECT_URL ); // Access scopes for read-only Calendar and Contacts. const scopes = [ 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly', 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly'] ]; // Generate a url that asks permissions const authorizationUrl = oauth2Client.generateAuthUrl({ // 'online' (default) or 'offline' (gets refresh_token) access_type: 'offline', /** Pass in the scopes array defined above. * Alternatively, if only one scope is needed, you can pass a scope URL as a string */ scope: scopes, // Enable incremental authorization. Recommended as best practices. include_granted_scopes: true });
检查传出网络调用
- Web 应用 - 在 Chrome 中检查网络活动
- Android - 使用网络检查器检查网络流量
-
Chrome 应用
- 前往 Chrome 扩展程序页面
- 选中扩展程序页面右上角的开发者模式复选框
- 选择要监控的扩展程序
- 在扩展程序页面的检查视图部分中,点击背景页面链接
- 系统随即会打开一个开发者工具弹出式窗口,您可以在其中通过 “网络”标签页监控网络流量
- iOS - 使用 Instruments 分析 HTTP 流量
- 通用 Windows 平台 (UWP) - 在 Visual Studio 中检查网络流量
- 桌面应用 - 使用应用所开发针对的操作系统可用的网络捕获工具
检查网络调用时,请查找发送到 Google OAuth 授权端点的请求,并检查 scope 参数。
这些值会导致系统显示精细权限同意屏幕。
scope参数包含登录范围和非登录范围。以下示例请求包含所有三个登录范围和一个非登录范围,用于查看用户 Google 云端硬盘文件的元数据:
https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth? access_type=offline& scope=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fuserinfo.email%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fuserinfo.profile%20openid%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fdrive.metadata.readonly& include_granted_scopes=true& response_type=code& redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URL& client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID
scope参数包含多个非登录范围。以下示例请求包含两个非登录范围,用于查看用户的 Google 云端硬盘元数据和管理特定的 Google 云端硬盘文件:
https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth? access_type=offline& scope=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fdrive.metadata.readonly%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fdrive.file& include_granted_scopes=true& response_type=code& redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URL& client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID
处理精细权限的最佳实践
如果您确定需要更新应用以处理精细权限,则应更新代码以正确处理多个范围的同意情况。所有应用都应遵循以下最佳实践:
- 查看 Google API 服务:用户数据政策,并确保您遵守这些政策。
- 请求任务所需的特定范围。您必须遵守 Google OAuth 2.0 政策,仅请求您需要的权限范围。您应避免在登录时请求多个范围,除非这是应用核心功能所必需的。将多个范围捆绑在一起,尤其是对于不熟悉应用功能的新用户,可能会让他们难以理解为何需要这些权限。这可能会引发警报,并阻止用户进一步与您的应用互动。
- 在请求授权之前,先向用户提供理由。清楚说明您的应用为何需要所请求的权限、您将如何处理用户的数据,以及用户批准请求后会获得哪些好处。 我们的研究表明,这些说明有助于提高用户信任度和互动度。
- 每当应用请求范围时,请使用 增量授权,以免管理多个访问令牌。
- 检查用户授予的范围。当同时请求多个范围时,用户可能不会授予您的应用所请求的所有范围。您的应用应始终检查用户授予了哪些范围,并通过停用相关功能来处理任何范围拒绝情况。请遵循 Google OAuth 2.0 政策,处理多个范围的同意情况,并且仅在用户明确表示有意使用需要相应范围的特定功能时,才再次提示用户征求同意。
更新您的应用以处理精细权限
Android 应用
您应查阅用于与 Google OAuth 2.0 交互的 SDK 的文档,并根据最佳实践更新应用以处理精细权限。
如果您使用 Play 服务的 auth.api.signin SDK 与 Google OAuth 2.0 进行交互,则可以使用 requestPermissions 函数请求所需的最少范围,并使用 hasPermissions 函数检查用户在请求精细权限时授予了哪些范围。
Chrome 扩展程序应用
您应使用 Chrome Identity API 来处理基于最佳实践的 Google OAuth 2.0。
以下示例展示了如何正确处理精细权限。
manifest.json
示例清单文件为 Chrome 扩展程序应用声明了两个非登录范围。
{
"name": "Example Chrome extension application",
...
"permissions": [
"identity"
],
"oauth2" : {
"client_id": "YOUR_CLIENT_ID",
"scopes":["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly",
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly"]
}
}方法不正确
全有或全无
用户点击该按钮即可开始授权流程。此代码段假定系统会向用户显示一个“全有或全无”的同意情况界面,其中包含 manifest.json 文件中指定的两个范围。它忽略了对用户授予的范围的检查。
oauth.js
... document.querySelector('button').addEventListener('click', function () { chrome.identity.getAuthToken({ interactive: true }, function (token) { if (token === undefined) { // User didn't authorize both scopes. // Updating the UX and application accordingly ... } else { // User authorized both or one of the scopes. // It neglects to check which scopes users granted and assumes users granted all scopes. // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } }); });
正确方法
最小范围
选择所需的最小权限集
应用应仅请求所需的最少范围。建议您的应用在需要完成任务时一次请求一个范围。
在此示例中,假设 manifest.json 文件中声明的两个范围是所需的最小范围集。oauth.js 文件使用 Chrome Identity API 启动与 Google 的授权流程。您应选择启用
精细权限,以便用户更好地控制向您的应用授予的权限。您的应用应通过检查用户授权的范围来正确处理用户的响应。
oauth.js
... document.querySelector('button').addEventListener('click', function () { chrome.identity.getAuthToken({ interactive: true, enableGranularPermissions: true }, function (token, grantedScopes) { if (token === undefined) { // User didn't authorize any scope. // Updating the UX and application accordingly ... } else { // User authorized the request. Now, check which scopes were granted. if (grantedScopes.includes('https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly')) { // User authorized Calendar read permission. // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } else { // User didn't authorize Calendar read permission. // Update UX and application accordingly ... } if (grantedScopes.includes('https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly')) { // User authorized Contacts read permission. // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } else { // User didn't authorize Contacts read permission. // Update UX and application accordingly ... } } }); });
iOS、iPadOS 和 macOS 应用
您应查阅用于与 Google OAuth 2.0 交互的 SDK 的文档,并根据最佳实践更新应用以处理精细权限。
如果您使用 Google Sign-In for iOS and macOS 库与 Google OAuth 2.0 进行交互,则应查看有关处理精细权限的文档。
Web 应用
您应查阅用于与 Google OAuth 2.0 交互的 SDK 的文档,并根据最佳实践更新应用以处理精细权限。
服务器端(离线)访问
- 启动服务器并定义可公开访问的端点以接收授权代码。
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台的 Clients page 中配置公共端点的 重定向 URI 。
以下代码段展示了一个 NodeJS 示例,该示例请求了两个非登录范围。用户将看到精细权限同意界面。
方法不正确
全有或全无
用户会被重定向到授权网址。此代码段假设系统会向用户显示一个“全有或全无”的同意情况界面,其中包含 scopes 数组中指定的两个范围。它忽略了对用户授予的范围的检查。
main.js
... const oauth2Client = new google.auth.OAuth2( YOUR_CLIENT_ID, YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET, YOUR_REDIRECT_URL ); // Access scopes for two non-Sign-In scopes - Google Calendar and Contacts const scopes = [ 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly', 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly' ]; // Generate a url that asks permissions for the Google Calendar and Contacts scopes const authorizationUrl = oauth2Client.generateAuthUrl({ // 'online' (default) or 'offline' (gets refresh_token) access_type: 'offline', // Pass in the scopes array defined above scope: scopes, // Enable incremental authorization. Recommended as best practices. include_granted_scopes: true }); async function main() { const server = http.createServer(async function (req, res) { // Example on redirecting user to Google OAuth 2.0 server. if (req.url == '/') { res.writeHead(301, { "Location": authorizationUrl }); } // Receive the callback from Google OAuth 2.0 server. if (req.url.startsWith('/oauth2callback')) { // Handle the Google OAuth 2.0 server response let q = url.parse(req.url, true).query; if (q.error) { // User didn't authorize both scopes. // Updating the UX and application accordingly ... } else { // User authorized both or one of the scopes. // It neglects to check which scopes users granted and assumes users granted all scopes. // Get access and refresh tokens (if access_type is offline) let { tokens } = await oauth2Client.getToken(q.code); // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } } res.end(); }).listen(80); }
正确方法
最小范围
选择所需的最小权限集
应用应仅请求所需的最少范围。建议您的应用在需要完成任务时一次请求一个范围。 每当应用请求范围时,都应使用增量授权,以避免管理多个访问令牌。
如果您的应用必须请求多个非登录范围,则在请求时应始终使用增量授权,并检查用户授予了哪些范围。
在此示例中,假设应用需要这两个范围才能正常运行。您应选择启用 精细权限,以便用户更好地控制向您的应用授予的权限。您的应用应通过检查用户已授权的范围来正确处理用户的响应。
main.js
... const oauth2Client = new google.auth.OAuth2( YOUR_CLIENT_ID, YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET, YOUR_REDIRECT_URL ); // Access scopes for two non-Sign-In scopes - Google Calendar and Contacts const scopes = [ 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly', 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly' ]; // Generate a url that asks permissions for the Google Calendar and Contacts scopes const authorizationUrl = oauth2Client.generateAuthUrl({ // 'online' (default) or 'offline' (gets refresh_token) access_type: 'offline', // Pass in the scopes array defined above scope: scopes, // Enable incremental authorization. Recommended as best practices. include_granted_scopes: true, // Set to true to enable more granular permissions for Google OAuth 2.0 client IDs created before 2019. // No effect for newer Google OAuth 2.0 client IDs, since more granular permissions is always enabled for them. enable_granular_consent: true }); async function main() { const server = http.createServer(async function (req, res) { // Redirect users to Google OAuth 2.0 server. if (req.url == '/') { res.writeHead(301, { "Location": authorizationUrl }); } // Receive the callback from Google OAuth 2.0 server. if (req.url.startsWith('/oauth2callback')) { // Handle the Google OAuth 2.0 server response let q = url.parse(req.url, true).query; if (q.error) { // User didn't authorize both scopes. // Updating the UX and application accordingly ... } else { // Get access and refresh tokens (if access_type is offline) let { tokens } = await oauth2Client.getToken(q.code); oauth2Client.setCredentials(tokens); // User authorized the request. Now, check which scopes were granted. if (tokens.scope.includes('https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly')) { // User authorized Calendar read permission. // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } else { // User didn't authorize Calendar read permission. // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } // Check which scopes user granted the permission to application if (tokens.scope.includes('https://www.googleapis.com/auth/contacts.readonly')) { // User authorized Contacts read permission. // Calling the APIs, etc. ... } else { // User didn't authorize Contacts read permission. // Update UX and application accordingly ... } } } res.end(); }).listen(80); }
查看有关如何从基于服务器的应用访问 Google API 的 服务器端 Web 应用指南。
仅限客户端访问
- 对于使用 Google Identity 服务 JavaScript 库与 Google OAuth 2.0 互动的应用,您应查看有关处理精细权限的文档。
- 对于直接使用 JavaScript 调用 Google OAuth 2.0 授权端点的应用,您应查看有关处理精细权限的文档。
测试更新后的应用在处理细化权限方面的表现
- 概述用户可以对权限请求做出的所有响应,以及应用的预期行为。例如,如果用户仅授权了所请求的三个范围中的两个,您的应用应相应地调整行为。
-
测试已启用精细权限的应用。您可以通过以下两种方式启用精细权限:
- 检查应用的 OAuth 2.0 权限请求页面,看看是否已为应用启用精细权限。您还可以通过 Google Cloud 控制台创建新的 Web、Android 或 iOS Google OAuth 2.0 客户端 ID 以进行测试,因为这些客户端 ID 始终启用精细权限。
-
在调用 Google OAuth
授权端点时,将参数
enable_granular_consent设置为true。部分 SDK 明确支持此参数。对于其他平台,请查看相关文档,了解如何手动添加此参数及其值。 如果您的实现不支持添加该参数,您可以按照上一点所述,仅出于测试目的通过 Google Cloud 控制台创建新的 Web、Android 或 iOS Google OAuth 2.0 客户端 ID。
- 测试更新后的应用时,请使用个人 Google 账号 (@gmail.com) 而不是 Workspace 账号。这是因为,具有网域范围的授权委托或标记为可信的 Workspace 企业版应用目前不受精细权限变更的影响。因此,使用贵组织的 Workspace 账号进行测试可能无法按预期显示新的精细化意见征求界面。
