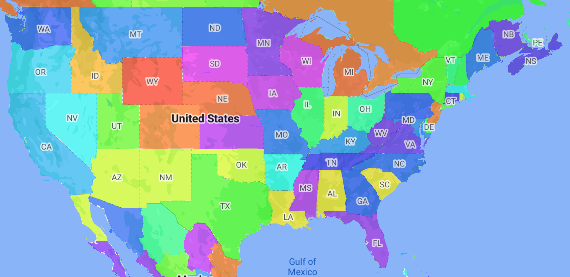
Um mapa coroplético é um tipo temático em que áreas administrativas ficam coloridas ou sombreadas de acordo com um valor de dados. Você pode usar uma função de fábrica de estilos para estilizar um mapa com base em dados em que cada área administrativa está associada a um intervalo de valores numéricos. O exemplo abaixo mostra um mapa coroplético dos estados dos Estados Unidos.
Neste exemplo, os dados consistem no ID do lugar do estado. A função de fábrica de estilo colore condicionalmente cada estado com base em um valor hash do ID do lugar.
Consulte Começar para criar um novo ID e estilo de mapa, caso ainda não tenha feito isso. Ative a camada de elemento Área administrativa de nível 1.
Receba uma referência à camada de elemento de área administrativa nível 1 quando o mapa for inicializado. Nos Estados Unidos, esses níveis administrativos correspondem aos estados.
Java
private FeatureLayer areaLevel1Layer;
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { areaLevel1Layer = map.getFeatureLayer(new FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build());
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer(); }Kotlin
private var areaLevel1Layer: FeatureLayer? = null
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Get the ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 feature layer. areaLevel1Layer = googleMap.getFeatureLayer(FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build())
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer() }Crie uma função de fábrica de estilos e aplique-a à camada de elementos de área administrativa de nível 1. O exemplo a seguir aplica a função ao polígono que representa cada estado dos Estados Unidos.
Java
private void styleAreaLevel1Layer() { FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> { if (feature instanceof PlaceFeature) { PlaceFeature placeFeature = (PlaceFeature) feature;
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. int hueColor = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300; if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300; }
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, new float[] {hueColor, 1, 1})) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }Kotlin
private fun styleAreaLevel1Layer() { val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature -> if (feature is PlaceFeature) { val placeFeature: PlaceFeature = feature as PlaceFeature
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. var hueColor: Int = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300 if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300 } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, floatArrayOf(hueColor.toFloat(), 1f, 1f))) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }
