Publishers typically diversify their ad demand sources to optimize for revenue and invoke multiple companies (for example, publisher ad servers, supply-side platforms, and demand-side platforms) to determine the best ad for a given ad slot on the page. Header bidding allows publishers to capture bids for an ad slot from a variety of demand sources. In a sequential auction setup, header bidding library may be used to run an auction with contextual data and Protected Audience is used to run an auction with cross-site data.
Before you begin, learn about the fundamentals header bidding from the Prebid.js documentation.
Definitions
The following tables describe some terms used in this document.
Auctions
| Auction | Definition |
|---|---|
| Protected Audience auction | An ad auction that involves bidding on an interest group created on another site. |
| Protected Audience multi-seller auction | A two-tier Protected Audience auction that first involves multiple parallel component auctions that then submit their top scoring ad to the final top-level auction. |
| Top-level auction | The final ad auction within a Protected Audience multi-seller auction that provides the scoring for the component auction winners from the component auctions. |
| Component auction | A nested auction within a Protected Audience multi-seller auction where each component seller is running their component auctions in parallel. The top scoring ads from each component auction is passed up to the top-level auction. |
Participants
| Participant | Definition |
|---|---|
| Advertiser | The party that desires an ad placement and builds the ad creative. |
| Publisher | The party that provides ad inventory for auction. |
| Buyer | The party that bids in an auction to buy the ad space from a seller. Commonly a demand-side platform (DSP). |
| Publisher Ad Server | A service used by publishers to manage and choose ads to be rendered on
the site. A Publisher Ad Server may combine its own auction results, header
bidder responses, direct-sold inventory, and more, to determine the ad that
will provide the most revenue to a publisher. A Publisher Ad Server may provide a client-side library for interacting with the server. |
| Top-level seller | The party that invokes (that is, creates) the Protected Audience multi-seller auction and participates in the top-level auction. |
| Component seller | The party that runs a component auction within the Protected Audience multi-seller auction to sell the publisher's ad space to the buyers. Commonly a supply-side platform (SSP). |
Sequential auction setup
In a sequential auction setup, the contextual auctions are executed first, then the Protected Audience auction is executed. This setup allows publishers to maximize their earning potential by running an auction with the contextual data available on the page, and also running an auction with cross-site data in a secure environment to protect users' privacy.
A header bidding library may be executed first on the page to collect bids for the Publisher Ad Server's contextual auction. Then, the adjusted winning bid price of the contextual auction can be entered into the Protected Audience auction as a bid floor. During the scoring step, the top-level seller can drop component auction bid prices below the bid floor by assigning them a zero score when the desirability score is calculated. If no Protected Audience component auction bid is above the bid floor, then the contextual auction winning ad is rendered to the user. If the Protected Audience auction returns a winner, it means it is above the bid floor, and the Protected Audience winning ad is rendered to the user.
In this sequential auction setup example, three major auctions may be executed on the page in order:
- Contextual auction by header bidding library
- Contextual auction by the Publisher Ad Server
- Protected Audience auction.
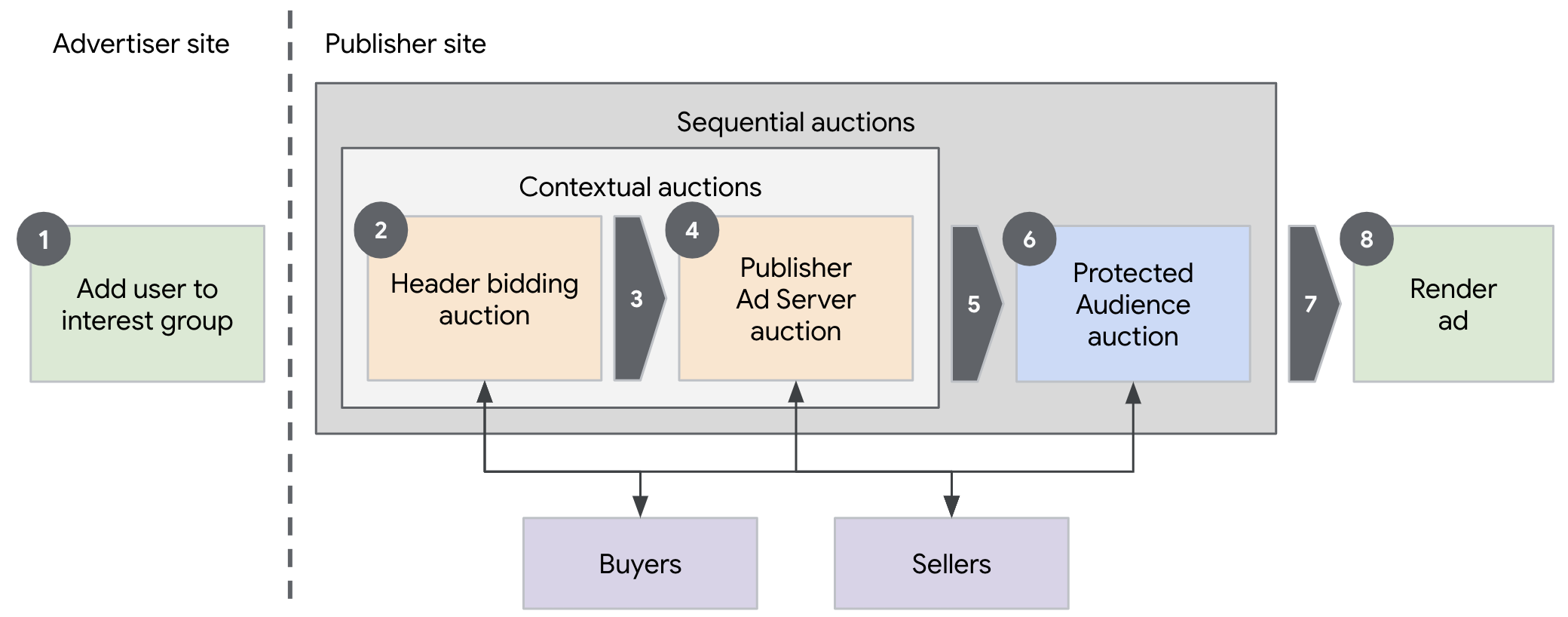
Detailed description of the overview diagram:
- Before the auction, the user is added to an interest group on an advertiser site.
- When the user visits the publisher page at a later time, Prebid.js runs a contextual auction to collect the bid responses from header bidders. During this step, the buyers may provide the signals and the sellers may provide component auction configs to be used in the subsequent Protected Audience auction. Prebid.js provides a module for propagating these signals and configs to the Protected Audience auction.
- The bid responses collected by Prebid.js are sent to the Publisher Ad Server for a server-side contextual auction.
- The Publisher Ad Server may combine its own auction results, header bidding results, direct-sold inventory, and more, to determine the ad that will provide the most revenue to a publisher. The winning ad is returned to the client-side library of the Publisher Ad Server.
- The adjusted bid price from the contextual auction winner, along with the
buyer's signals (
perBuyerSignals) and seller's component auction configs gathered by Prebid.js can be passed into the Protected Audience auction by the Publisher Ad Server's client-side library. - The Protected Audience multi-seller auction is executed by the top-level
seller. During the top-level seller's scoring step, the top-level seller may
compare each component auction winning bid price against the contextual auction
adjusted winning bid price. If the component bid price is lower than the
contextual auction bid price, then the top-level seller returns the desirability
score of 0. If all bids are scored 0, then the
runAdAuction()call returns null which signifies that the contextual auction winning ad should be rendered. - The Publisher Ad Server client-side library either renders the winning
Protected Audience ad or contextual ad, based on what was returned from the
runAdAuction()call. - The winning ad is rendered to the user.
Contextual auctions with Prebid.js and Publisher Ad Server
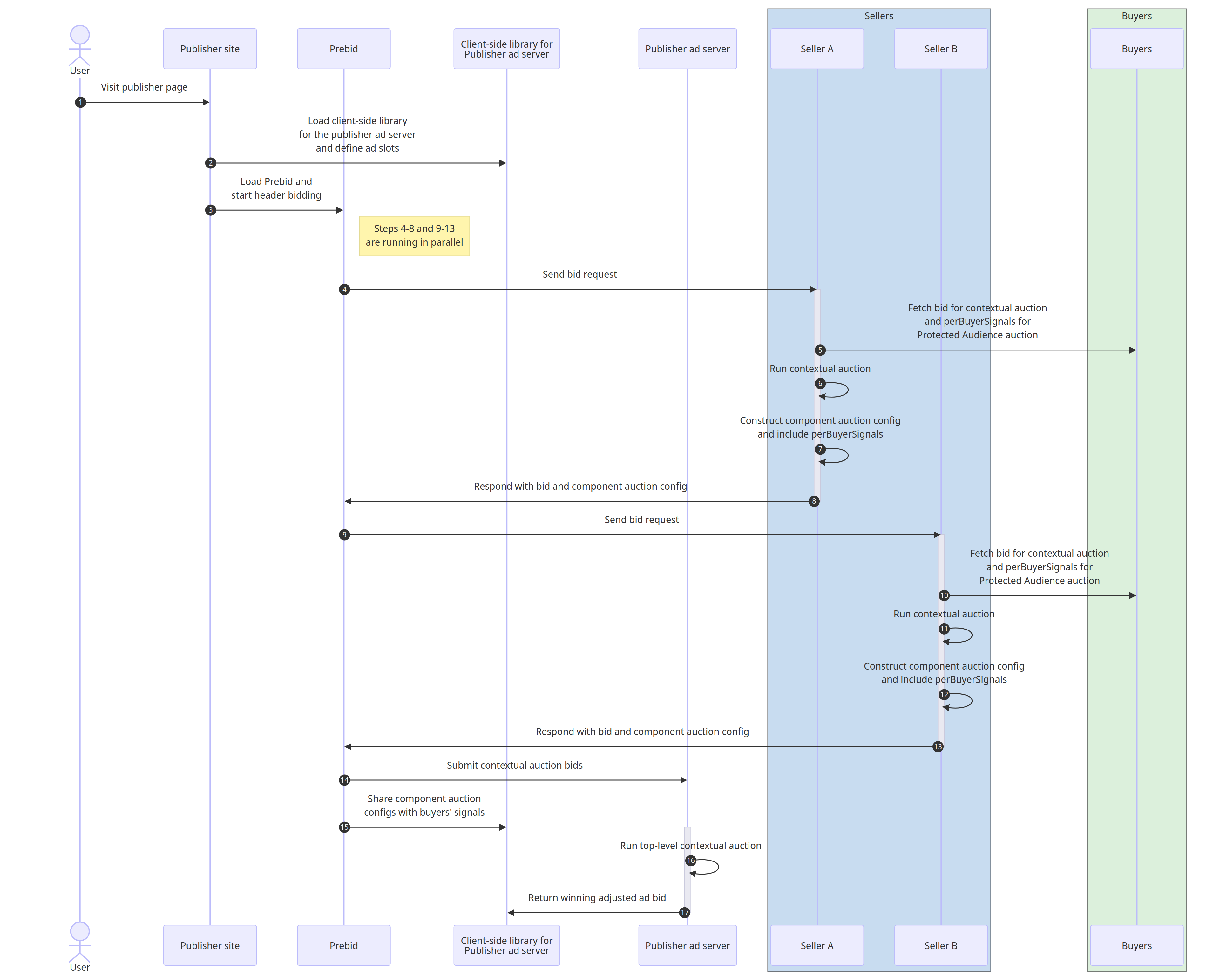
In a sequential auction setup, all contextual auctions are executed before the Protected Audience auction runs. In the setup explained in this document, we run a header bidding contextual auction by Prebid.js that feeds into a server-side auction by the Publisher Ad Server.
The publisher first initiates a header bidding contextual auction by calling
Prebid.js with a flag to note that a Protected Audience auction will be
executed afterwards. Then Prebid.js collects the bid responses and sends
them to the Publisher Ad Server for a server-side contextual auction. During the
bid response collection step, the buyers and sellers have the opportunity to
provide component auction configs and buyers' signals (perBuyerSignals) to be
used for the subsequent Protected Audience auction, if they want to participate.
That component auction config will eventually pass into the subsequent Protected
Audience auction.
- Contextual auction initialization The user visits the publisher page.
- The publisher page loads the Publisher Ad Server client-side library and defines ad slots.
- The publisher page loads Prebid and starts the header bidding contextual auction.
- Seller A's contextual auction (running in parallel to Seller B's contextual auction). Prebid.js sends a bid request to Seller A.
- Seller A retrieves the bid responses and perBuyerSignals from the buyers.
- Seller A executes a contextual auction.
- Seller A constructs the component auction config with
perBuyerSignalsincluded. - Seller A responds to Prebid.js with the winning bid and its component auction config.
- Seller B's contextual auction (runs in parallel to Sellers A's contextual auction). Prebid.js sends a bid request to Seller B.
- Seller B retrieves the bid responses and
perBuyerSignalsfrom the buyers. - Seller B executes a contextual auction.
- Seller B constructs the component auction config with perBuyerSignals included.
- Seller B responds to Prebid.js with the winning bid and its component auction config.
- Publisher Ad Server's contextual auction The bid responses collected by Prebid.js are sent to the Publisher Ad Server for the contextual auction.
- The component auction configs with buyers' signals are shared with the client-side library of the Publisher Ad Server
- The Publisher Ad Server runs a contextual auction to determine the best ad between direct sold campaigns, programmatic bids, Prebid's contextual bids, and other inventory.
- The Publisher Ad Server returns the adjusted winning bid.
Consider contextual ad demand with Protected Audience ad demand
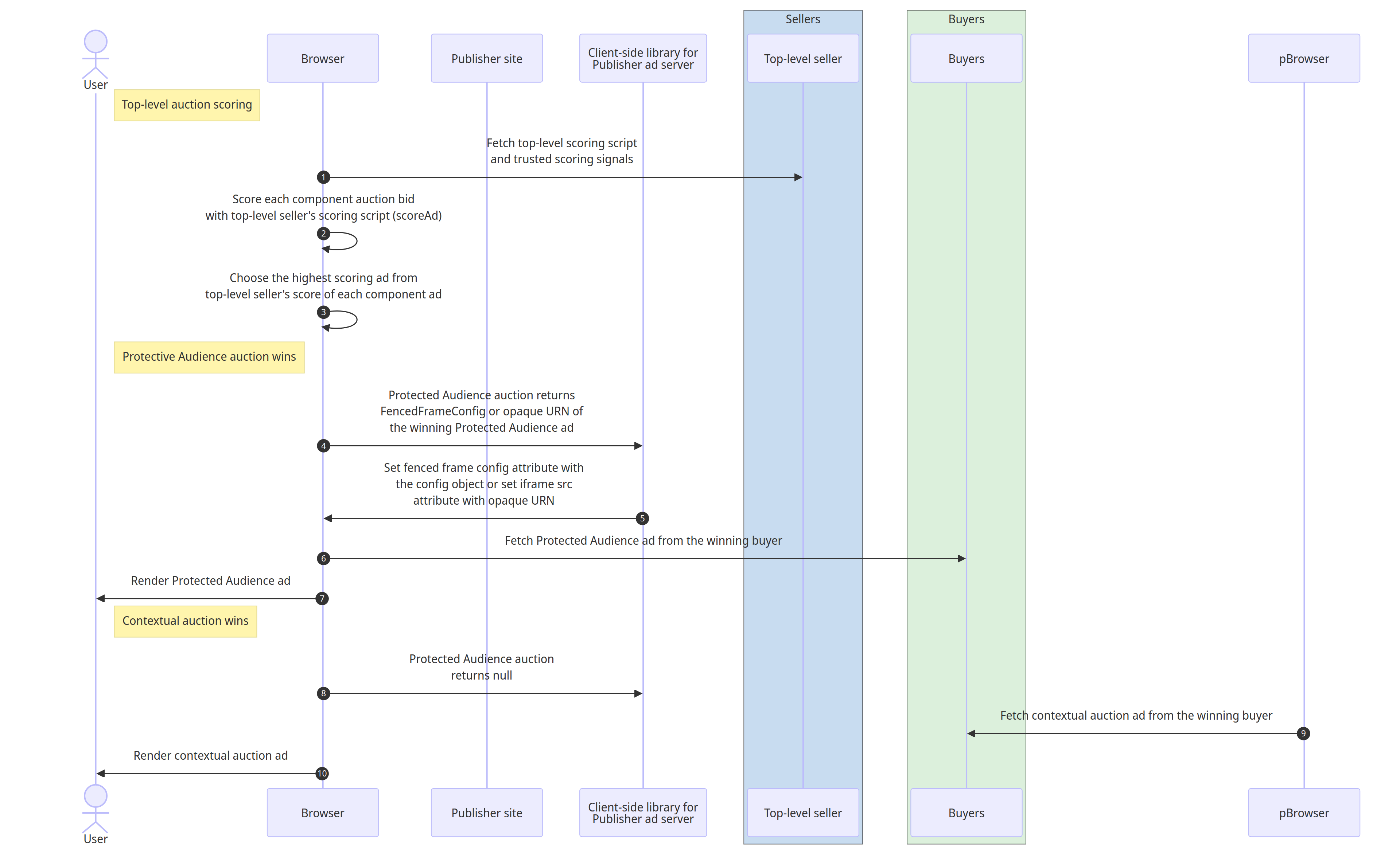
At this point, contextual auctions have concluded, and the Publisher Ad Server's client-side library can pass the contextual auction winning adjusted bid price, component auction configs, and signals from buyers that are participating in the Protected Audience auction to the top-level seller. The contextual auction bid price as a floor can be passed into the auction config as a signal for scoring at the top-level auction.
- The browser fetches the scoring script from seller along with trusted scoring signals of each ad.
- The browser executes the top-level seller's scoring logic for each winning
bid of all component auctions. Inside the top-level seller's
scoreAd()script, the logic has access to the contextual auction adjusted winning bid price that may have been passed in assellerSignalsin the auction config. The script can compare the winning contextual bid price with component Protected Audience bid price and return a desirability score of 0 if the contextual price is higher. Otherwise the script calculates the desirability score, likely based on the component Protected Audience bid price. - The browser chooses the ad with the highest desirability score submitted by the top-level seller's scoring logic.
- If the Protected Audience auction wins The Protected Audience auction
returns a
FencedFrameConfigobject or an opaque URN to the publisher's ad server client-side library. - Client-side library sets the fenced frame's
configattribute to theFencedFrameConfigobject or sets the iframe'ssrcattribute to the opaque URN of the winning Protected Audience ad. - The browser fetches the Protected Audience auction winning ad from the buyer.
- The browser renders the ad to the user.
- If the contextual auction wins The Protected Audience auction returns
null. - The browser sets the iframe's
srcattribute to the winning contextual ad. - The browser fetches the contextual auction winning ad from the buyer.
- The browser renders the ad to the user.
