This document provides a high level overview of the Google Analytics Google Tag Manager API.
Introduction
The Google Tag Manager API provides access to Google Tag Manager configuration data for an authorized user. With this API you can manage:
- Accounts
- Containers
- Tags
- Rules
- Triggers
- Folders
- Variables
- Container Versions
- User Permissions
- Environments
Getting Started
Want to get started right away? Read the Developer's Guide. Each application that uses the API will have to go through a couple of steps to register, authorize the user, and work with the API. The developer's guide will walk you through each step and in the end, you will have a working application that you can customize.
Conceptual Overview
The API exposes multiple Google Tag Manager configuration entities, organized hierarchically: Each user's Accounts resource can have one or more Containers, each of which can have one or more Macros / Variables, Rules / Triggers, Tags, and Versions. A Permission resource allows you to manage user permissions at the Accounts level. The following diagram represents the parent-child relationships among the entities:
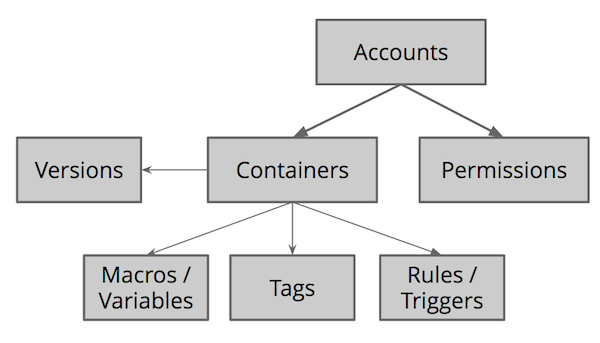
The Google Tag Manager API exposes each of the entities as a resource. A list of resources of a particular kind make up a collection. The API exposes each collection at a URI that can be queried to return the list of entities in it.
See the Tag Manager API Reference to get a detailed description of the methods in the API and the data they return.
Quota Policies
The Google Tag Manager API handles millions of operations. To protect the system from receiving more operations than it can handle, and to ensure an equitable distribution of system resources, it is necessary to employ a quota system. Read the Limits and Quotas guide for specific limits.
Next Steps
Resources to help you learn more about the API:
- Read the Developer's Guide to learn how to work with the API.
- Review the Tag Manager API Reference to familiarize yourself with Tag Manager resources and available operations.