应用类型及其用例(是在驾车时还是停车时使用)决定了 Android for Cars 应用的设计流程。
某些应用基于同时适用于驾车和停车场景的模板构建而成。其他应用(例如媒体应用)需要针对驾驶界面优化应用内容和操作。
如果汽车内置 Google 服务,您可以将现有应用改为适用于车载屏幕,以提供停车和乘客体验。
车载应用体验
用户可通过两种方式在汽车中体验 Android 应用:Android Auto(从手机投影)或内置 Google 的 Android Automotive OS。
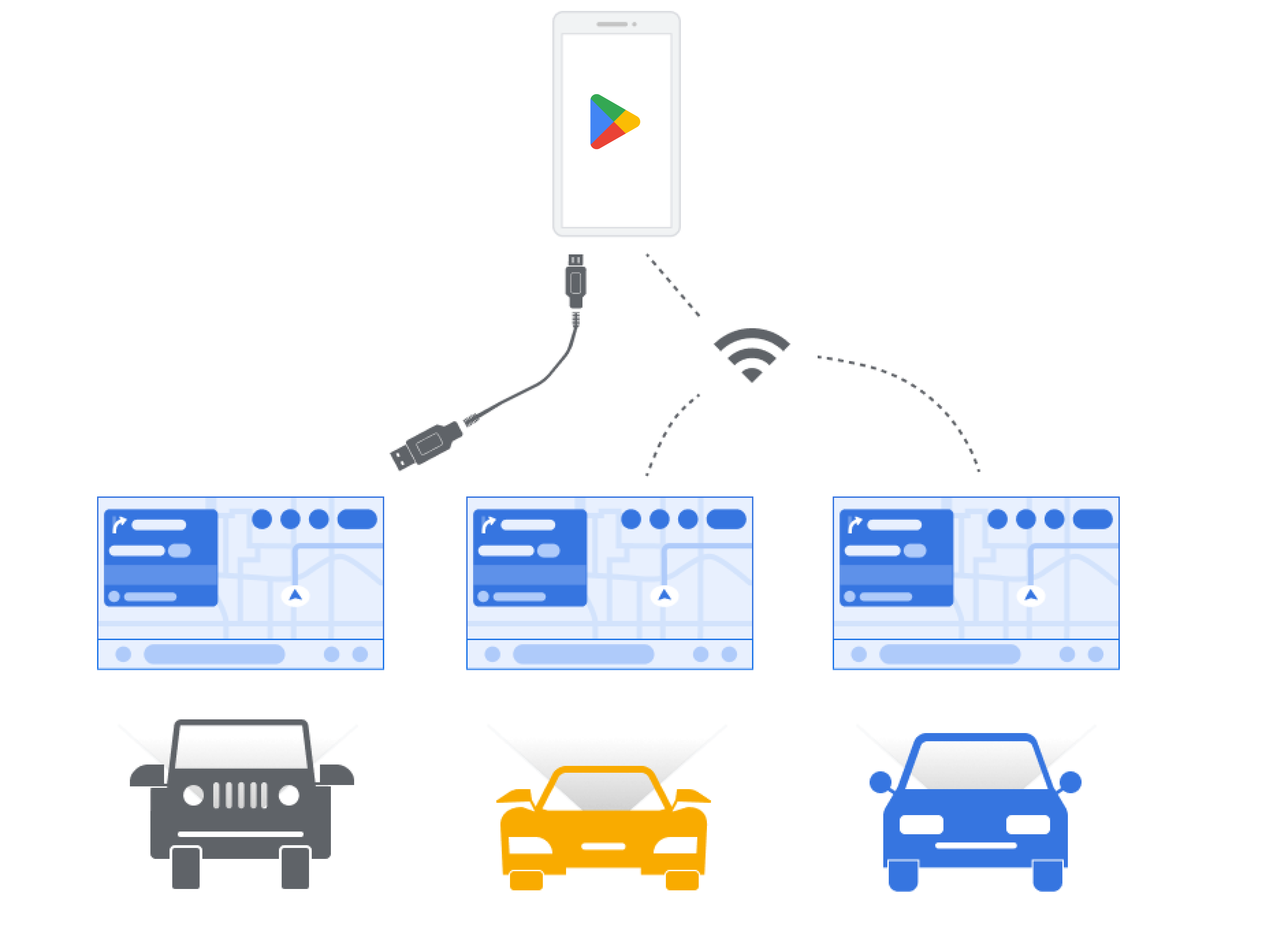
从手机投影 (Android Auto)
Android Auto 用户可以直接通过手机在车载屏幕上访问兼容的应用。应用的界面会通过无线或 USB 连接从用户的移动电话投影到车载屏幕。
应用的视觉呈现(包括配色方案和样式)在所有兼容的汽车中保持一致。
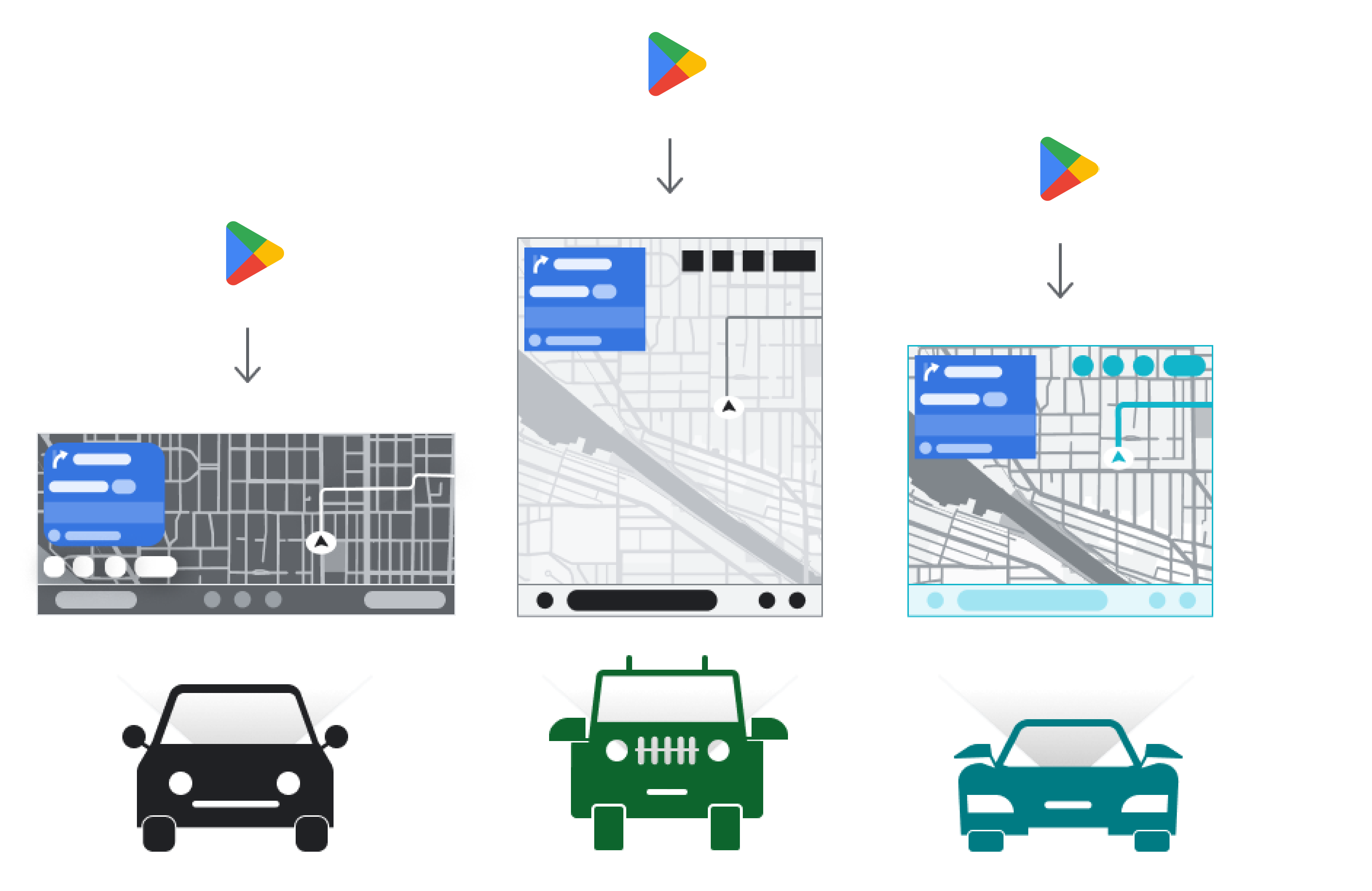
下载到汽车中(Google 内置)
搭载 AAOS 的汽车可让用户直接在汽车的信息娱乐系统中从 Google Play 商店安装应用,而无需连接移动电话。
汽车制造商 (OEM) 可以修改已安装应用的调色板和样式,使其与其品牌的视觉身份保持一致。
当您的应用下载到汽车中时,汽车 OEM 可以调整颜色并自定义样式,以适应特定车型。
在设计应用时,请注意应用的使用体验在一定程度上取决于用户是在 Android Auto 还是 Google 内置(可由汽车制造商自定义)上运行应用。本部分介绍的流程适用于 Android for Cars 系统(Android Auto 和 AAOS),但在另有说明的情况下除外(例如,对于搭载 Google 产品的汽车)。
应用的合作伙伴角色
多方合作伙伴共同打造 Android for Cars 中的应用体验:应用开发者、Google 和汽车制造商。
应用开发者、Google 和汽车制造商通力合作,共同打造 Android for Cars 中的应用体验。每位合作伙伴的设计责任取决于他们开发的应用类型。虽然使用 Android for Cars 应用库 (CAL) 模板创建的应用遵循特定的合作伙伴模式,但界面较不灵活的应用或专为停车状态和乘客使用而设计的应用遵循不同的模式。
如需详细了解其中一些合作伙伴模式,请参阅下表。
| 应用类型 | 关于应用设计中合作伙伴角色的讨论 |
|---|---|
| 使用 Android for Cars 应用库创建的应用 | |
| 媒体应用 |
如需简要了解 AAOS 整体体验(包括系统界面)的合作伙伴角色,请参阅合作伙伴角色。

使用模板构建应用
使用 Android for Cars 应用库中的模板,创建以下类别的应用:导航、地图注点、物联网 (IoT) 和天气
创建媒体应用
为 Android for Cars 界面创建音频内容应用的版本

自适应停车状态下使用的应用
下载相关准则,了解如何将现有的停车状态应用调整为在搭载 Google 产品的汽车中运行
