এই পৃষ্ঠাটি আপনাকে "ডিসিশন ট্রিস" ইউনিটে আলোচিত উপাদান সম্পর্কে একাধিক পছন্দের অনুশীলনের একটি সিরিজের উত্তর দেওয়ার জন্য চ্যালেঞ্জ করে।
প্রশ্ন 1
একটি সিদ্ধান্ত গাছের অনুমান একটি উদাহরণ রাউটিং দ্বারা সঞ্চালিত হয় ...
পাতা থেকে মূল পর্যন্ত।
সমস্ত অনুমান মূল থেকে শুরু হয় (প্রথম শর্ত)।
এক পাতা থেকে অন্য পাতায়।
সমস্ত অনুমান মূল থেকে শুরু হয়, পাতা থেকে নয়।
মূল থেকে পাতা পর্যন্ত।
ভালো হয়েছে!
প্রশ্ন 2
সমস্ত শর্ত কি শুধুমাত্র একটি বৈশিষ্ট্য জড়িত?
হ্যাঁ।
তির্যক বৈশিষ্ট্য একাধিক বৈশিষ্ট্য পরীক্ষা করে।
না.
যদিও অক্ষ-সারিবদ্ধ অবস্থা শুধুমাত্র একটি একক বৈশিষ্ট্য জড়িত, তির্যক অবস্থা একাধিক বৈশিষ্ট্য জড়িত।
প্রশ্ন 3
দুটি বৈশিষ্ট্য x1 এবং x2 এর উপর নিম্নলিখিত পূর্বাভাস মানচিত্র বিবেচনা করুন:
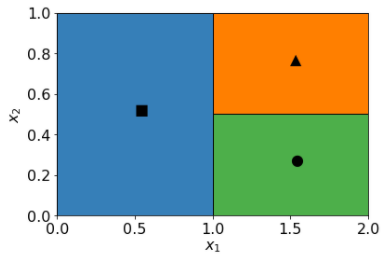
নিচের কোন সিদ্ধান্ত গাছ ভবিষ্যদ্বাণী মানচিত্রের সাথে মেলে? 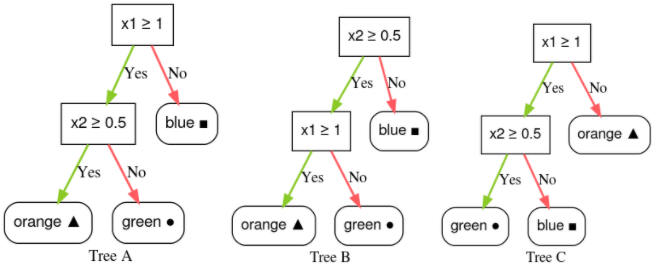

সিদ্ধান্ত গাছ A.
হ্যাঁ!
সিদ্ধান্ত গাছ বি.
যদি শর্ত x2 ≥ 0.5 না হয়, তাহলে পাতাটি নীল হতে পারে বা নাও হতে পারে, তাই এটি একটি খারাপ অবস্থা।
সিদ্ধান্ত গাছ গ.
যদি x1 ≥ 1.0 না হয়, তাহলে পাতাটি 'কমলা' না হয়ে 'নীল' হওয়া উচিত, তাই এটি ভুল পাতা।
