这是牛。

图 19. 牛。
1906 年,英国举办了举重比赛。787 名参与者猜测了一头牛的体重。单个猜测值的平均误差为 37 磅(误差为 3.1%)。不过,猜测的中位数总和与牛的实际重量 (1198 磅) 相差只有 9 磅,误差仅为 0.7%。
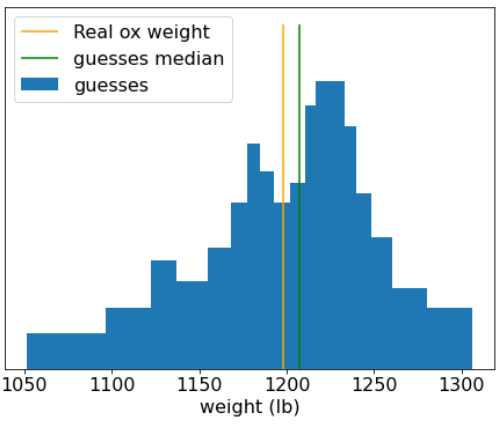
图 20. 各个体重猜测值的直方图。
这个轶事说明了众人之智:在某些情况下,集体意见可以提供非常准确的判断。
从数学角度来看,可以用中心极限定理对众人智慧进行建模:通俗地说,某个值与对该值进行 N 次带噪估计的平均值之间的误差平方趋于零,误差平方因子为 1/N。但是,如果变量不独立,方差会更大。
在机器学习中,集成模型是指一组模型,其预测结果会被平均(或以某种方式汇总)。如果多个模型足够不同,且各自的效果都不是太差,那么该模型集合的质量通常会优于各个模型的质量。与单个模型相比,集成模型需要更多的训练和推理时间。毕竟,您必须对多个模型(而非单个模型)执行训练和推理。
一般来说,为了让集成模型发挥最佳效果,各个模型应是独立的。举例来说,由 10 个完全相同的模型(即完全不独立)组成的集成学习模型不会比单个模型的效果更好。另一方面,强制使模型独立可能意味着使其性能变差。要想有效地进行模型集成,需要在模型独立性和其子模型质量之间取得平衡。
