데이터 획득
수집된 위치 데이터를 가져오는 여러 가지 방법이 있습니다. 여기서는 Roads API의 도로에 맞추기 기능과 함께 사용할 데이터를 획득하는 두 가지 기법을 설명합니다.
GPX
GPX는 GPS 기기에서 캡처한 경로, 트랙, 경유지를 공유하기 위한 개방형 XML 기반 형식입니다. 이 예에서는 Java 서버와 모바일 환경 모두에서 사용할 수 있는 경량 XML 파서인 XmlPull 파서를 사용합니다.
/** * Parses the waypoint (wpt tags) data into native objects from a GPX stream. */ private List<LatLng> loadGpxData(XmlPullParser parser, InputStream gpxIn) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { // We use a List<> as we need subList for paging later List<LatLng> latLngs = new ArrayList<>(); parser.setInput(gpxIn, null); parser.nextTag(); while (parser.next() != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (parser.getEventType() != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } if (parser.getName().equals("wpt")) { // Save the discovered latitude/longitude attributes in each <wpt>. latLngs.add(new LatLng( Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lat")), Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lon")))); } // Otherwise, skip irrelevant data } return latLngs; }
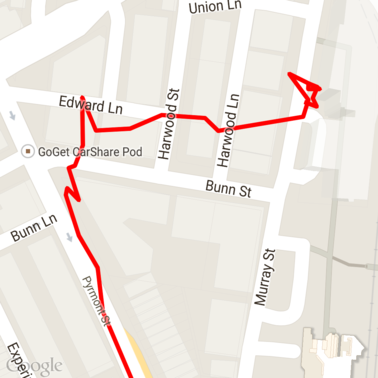
다음은 지도에 로드된 원시 GPX 데이터입니다.
Android 위치 서비스
Android 기기에서 GPS 데이터를 캡처하는 가장 좋은 방법은 사용 사례에 따라 다릅니다. 위치 업데이트 수신에 관한 Android 교육 클래스와 GitHub의 Google Play 위치 샘플을 참고하세요.
긴 경로 처리
도로에 맞추기 기능은 개별 포인트가 아닌 전체 경로를 기반으로 위치를 추론하므로 긴 경로 (즉, 요청당 100포인트 제한을 초과하는 경로)를 처리할 때 주의해야 합니다.
개별 요청을 하나의 긴 경로로 처리하려면 이전 요청의 최종 지점이 후속 요청의 첫 번째 지점으로 포함되도록 일부 중복을 포함해야 합니다. 포함할 포인트 수는 데이터의 정확도에 따라 달라집니다. 정확도가 낮은 요청의 경우 포인트를 더 많이 포함해야 합니다.
이 예에서는 Google 지도 서비스용 Java 클라이언트를 사용하여 페이지로 나눈 요청을 전송한 다음 보간된 점을 포함한 데이터를 반환된 목록에 다시 결합합니다.
/** * Snaps the points to their most likely position on roads using the Roads API. */ private List<SnappedPoint> snapToRoads(GeoApiContext context) throws Exception { List<SnappedPoint> snappedPoints = new ArrayList<>(); int offset = 0; while (offset < mCapturedLocations.size()) { // Calculate which points to include in this request. We can't exceed the API's // maximum and we want to ensure some overlap so the API can infer a good location for // the first few points in each request. if (offset > 0) { offset -= PAGINATION_OVERLAP; // Rewind to include some previous points. } int lowerBound = offset; int upperBound = Math.min(offset + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, mCapturedLocations.size()); // Get the data we need for this page. LatLng[] page = mCapturedLocations .subList(lowerBound, upperBound) .toArray(new LatLng[upperBound - lowerBound]); // Perform the request. Because we have interpolate=true, we will get extra data points // between our originally requested path. To ensure we can concatenate these points, we // only start adding once we've hit the first new point (that is, skip the overlap). SnappedPoint[] points = RoadsApi.snapToRoads(context, true, page).await(); boolean passedOverlap = false; for (SnappedPoint point : points) { if (offset == 0 || point.originalIndex >= PAGINATION_OVERLAP - 1) { passedOverlap = true; } if (passedOverlap) { snappedPoints.add(point); } } offset = upperBound; } return snappedPoints; }
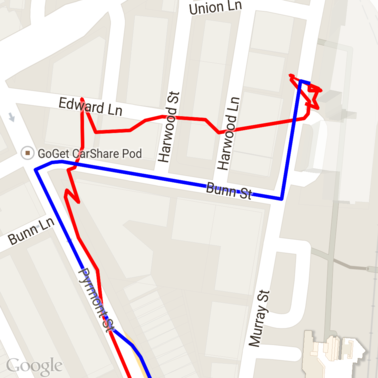
도로에 맞추기 요청을 실행한 후의 데이터는 다음과 같습니다. 빨간색 선은 원시 데이터이고 파란색 선은 스냅된 데이터입니다.
할당량 효율적으로 사용
도로에 맞추기 요청에 대한 응답에는 제공한 포인트에 매핑되는 장소 ID 목록이 포함되며, interpolate=true를 설정한 경우 추가 포인트가 포함될 수 있습니다.
속도 제한 요청에 허용된 할당량을 효율적으로 사용하려면 요청에서 고유한 장소 ID만 쿼리해야 합니다. 이 예에서는 Google Maps 서비스용 Java 클라이언트를 사용하여 장소 ID 목록에서 제한 속도를 쿼리합니다.
/** * Retrieves speed limits for the previously-snapped points. This method is efficient in terms * of quota usage as it will only query for unique places. * * Note: Speed limit data is only available for requests using an API key enabled for a * Google Maps APIs Premium Plan license. */ private Map<String, SpeedLimit> getSpeedLimits(GeoApiContext context, List<SnappedPoint> points) throws Exception { Map<String, SpeedLimit> placeSpeeds = new HashMap<>(); // Pro tip: Save on quota by filtering to unique place IDs. for (SnappedPoint point : points) { placeSpeeds.put(point.placeId, null); } String[] uniquePlaceIds = placeSpeeds.keySet().toArray(new String[placeSpeeds.keySet().size()]); // Loop through the places, one page (API request) at a time. for (int i = 0; i < uniquePlaceIds.length; i += PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT) { String[] page = Arrays.copyOfRange(uniquePlaceIds, i, Math.min(i + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, uniquePlaceIds.length)); // Execute! SpeedLimit[] placeLimits = RoadsApi.speedLimits(context, page).await(); for (SpeedLimit sl : placeLimits) { placeSpeeds.put(sl.placeId, sl); } } return placeSpeeds; }
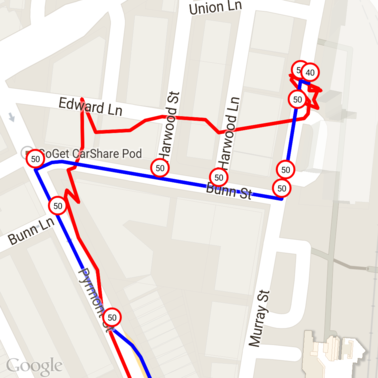
다음은 각 고유한 장소 ID에 제한 속도가 표시된 위의 데이터입니다.
다른 API와의 상호 작용
도로에 스냅 응답에서 장소 ID가 반환되는 이점 중 하나는 다양한 Google Maps Platform API에서 장소 ID를 사용할 수 있다는 것입니다. 이 예제에서는 Google Maps Services용 Java 클라이언트를 사용하여 위의 도로 스냅 요청에서 반환된 장소의 지오코딩을 수행합니다.
/** * Geocodes a snapped point using the place ID. */ private GeocodingResult geocodeSnappedPoint(GeoApiContext context, SnappedPoint point) throws Exception { GeocodingResult[] results = GeocodingApi.newRequest(context) .place(point.placeId) .await(); if (results.length > 0) { return results[0]; } return null; }
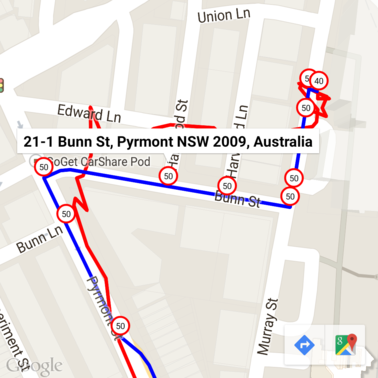
여기서 속도 제한 표시에는 지오코딩 API의 주소가 주석으로 지정되었습니다.
샘플 코드
고려사항
이 문서를 지원하는 코드는 설명을 위해 단일 Android 앱으로 제공됩니다. 실제로 서드 파티의 무단 액세스로부터 키를 보호할 수 없으므로 Android 앱에 서버 측 API 키를 배포해서는 안 됩니다. 대신, 키를 보호하려면 API에 연결되는 코드를 서버 측 프록시로 배포하고 Android 앱에서 프록시를 사용하여 요청을 보내 요청이 승인되었는지 확인해야 합니다.
다운로드
GitHub에서 코드를 다운로드하세요.
