获取数据
您可以通过多种方式获取收集的位置数据。下面,我们将介绍两种获取数据以用于 Roads API 的贴合道路功能的技术。
GPX
GPX 是一种基于 XML 的开放格式,用于分享 GPS 设备捕获的路线、轨迹和途经点。此示例使用 XmlPull 解析器,这是一种轻量级 XML 解析器,适用于 Java 服务器和移动环境。
/** * Parses the waypoint (wpt tags) data into native objects from a GPX stream. */ private List<LatLng> loadGpxData(XmlPullParser parser, InputStream gpxIn) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { // We use a List<> as we need subList for paging later List<LatLng> latLngs = new ArrayList<>(); parser.setInput(gpxIn, null); parser.nextTag(); while (parser.next() != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (parser.getEventType() != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } if (parser.getName().equals("wpt")) { // Save the discovered latitude/longitude attributes in each <wpt>. latLngs.add(new LatLng( Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lat")), Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lon")))); } // Otherwise, skip irrelevant data } return latLngs; }
以下是一些已加载到地图中的原始 GPX 数据。
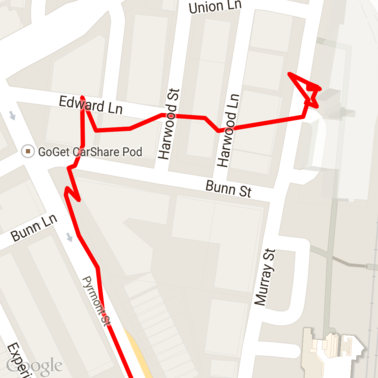
Android 位置信息服务
从安卓设备获取 GPS 数据的最佳方法取决于您的使用场景。请查看 Android 培训课程中的接收位置信息更新,以及 GitHub 上的 Google Play 位置信息示例。
处理长路径
由于 捕捉到道路 功能是根据完整路径而不是单个点来推断位置的,因此在处理长路径(即超过每次请求 100 个点限制的路径)时需要格外小心。
为了将各个请求视为一条长路径,您应该包含一些重叠部分,以便将前一个请求的最后几个点作为后一个请求的第一个点。要包含的点数取决于数据的准确性。对于低准确度请求,您应添加更多点。
此示例使用 Java 版 Google 地图服务客户端发送分页请求,然后将数据(包括插值点)重新加入到返回的列表中。
/** * Snaps the points to their most likely position on roads using the Roads API. */ private List<SnappedPoint> snapToRoads(GeoApiContext context) throws Exception { List<SnappedPoint> snappedPoints = new ArrayList<>(); int offset = 0; while (offset < mCapturedLocations.size()) { // Calculate which points to include in this request. We can't exceed the API's // maximum and we want to ensure some overlap so the API can infer a good location for // the first few points in each request. if (offset > 0) { offset -= PAGINATION_OVERLAP; // Rewind to include some previous points. } int lowerBound = offset; int upperBound = Math.min(offset + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, mCapturedLocations.size()); // Get the data we need for this page. LatLng[] page = mCapturedLocations .subList(lowerBound, upperBound) .toArray(new LatLng[upperBound - lowerBound]); // Perform the request. Because we have interpolate=true, we will get extra data points // between our originally requested path. To ensure we can concatenate these points, we // only start adding once we've hit the first new point (that is, skip the overlap). SnappedPoint[] points = RoadsApi.snapToRoads(context, true, page).await(); boolean passedOverlap = false; for (SnappedPoint point : points) { if (offset == 0 || point.originalIndex >= PAGINATION_OVERLAP - 1) { passedOverlap = true; } if (passedOverlap) { snappedPoints.add(point); } } offset = upperBound; } return snappedPoints; }
以下是运行 snap to roads 请求后从上述数据中获得的结果。红线是原始数据,蓝线是贴合后的数据。
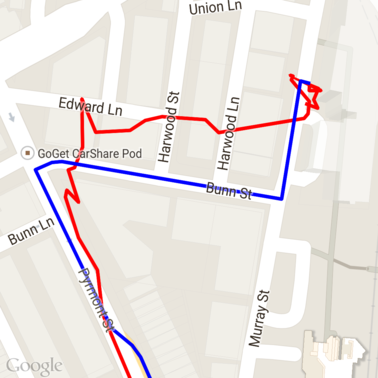
高效利用配额
对贴合到道路请求的响应包含一个地点 ID 列表,这些 ID 会映射到您提供的点,如果您设置了 interpolate=true,则可能还会包含其他点。
为了有效利用您允许的限速请求配额,您应该只在请求中查询唯一的地点 ID。此示例使用 Java Client for Google Maps Services 从地点 ID 列表中查询限速。
/** * Retrieves speed limits for the previously-snapped points. This method is efficient in terms * of quota usage as it will only query for unique places. * * Note: Speed limit data is only available for requests using an API key enabled for a * Google Maps APIs Premium Plan license. */ private Map<String, SpeedLimit> getSpeedLimits(GeoApiContext context, List<SnappedPoint> points) throws Exception { Map<String, SpeedLimit> placeSpeeds = new HashMap<>(); // Pro tip: Save on quota by filtering to unique place IDs. for (SnappedPoint point : points) { placeSpeeds.put(point.placeId, null); } String[] uniquePlaceIds = placeSpeeds.keySet().toArray(new String[placeSpeeds.keySet().size()]); // Loop through the places, one page (API request) at a time. for (int i = 0; i < uniquePlaceIds.length; i += PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT) { String[] page = Arrays.copyOfRange(uniquePlaceIds, i, Math.min(i + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, uniquePlaceIds.length)); // Execute! SpeedLimit[] placeLimits = RoadsApi.speedLimits(context, page).await(); for (SpeedLimit sl : placeLimits) { placeSpeeds.put(sl.placeId, sl); } } return placeSpeeds; }
以下是上述数据,其中在每个唯一地点 ID 处都标记了限速。
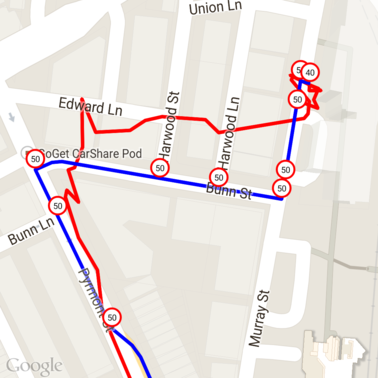
与其他 API 交互
在 捕捉到道路 响应中返回地点 ID 的好处之一是,您可以在许多 Google Maps Platform API 中使用该地点 ID。本示例使用 Google Maps Services Java 客户端 对上述 snap to road 请求返回的地点进行地理编码。
/** * Geocodes a snapped point using the place ID. */ private GeocodingResult geocodeSnappedPoint(GeoApiContext context, SnappedPoint point) throws Exception { GeocodingResult[] results = GeocodingApi.newRequest(context) .place(point.placeId) .await(); if (results.length > 0) { return results[0]; } return null; }
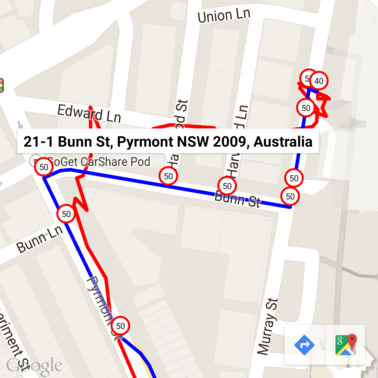
此处的限速标志已通过地理编码 API 添加了地址注释。
示例代码
注意事项
支持本文档的代码以单个 Android 应用的形式提供,仅用于说明目的。实际上,您不应在 Android 应用中分发服务器端 API 密钥,因为您的密钥无法防止第三方未经授权的访问。为了保护密钥,您应将面向 API 的代码部署为服务器端代理,并让 Android 应用使用该代理发送请求,以确保请求已获得授权。
下载
从 GitHub 下载代码。

