این سند نحوه پیادهسازی یک کنترلکننده فراخوانی مجوز OAuth 2.0 را با استفاده از سرولتهای جاوا از طریق یک برنامه وب نمونه که وظایف کاربر را با استفاده از API وظایف گوگل نمایش میدهد، توضیح میدهد. برنامه نمونه ابتدا درخواست مجوز برای دسترسی به وظایف گوگل کاربر را میدهد و سپس وظایف کاربر را در لیست وظایف پیشفرض نمایش میدهد.
مخاطب
این سند برای افرادی که با معماری برنامههای وب جاوا و J2EE آشنا هستند، مناسب است. آشنایی با جریان مجوزدهی OAuth 2.0 توصیه میشود.
فهرست مطالب
برای داشتن چنین نمونهی کاملاً کاربردی، چندین مرحله لازم است، شما باید:
- نگاشتهای سرولت را در فایل web.xml تعریف کنید.
- کاربران سیستم خود را احراز هویت کنید و برای دسترسی به وظایف آنها درخواست مجوز دهید
- به کد مجوز از نقطه پایانی مجوز گوگل گوش دهید
- کد مجوز را با یک توکن بهروزرسانی و دسترسی تعویض کنید
- خواندن وظایف کاربر و نمایش آنها
نگاشتهای سرولت را در فایل web.xml تعریف کنید.
این برنامه از دو سرولت زیر استفاده میکند:
- PrintTasksTitlesServlet (به
/نگاشت شده است): نقطه ورودی برنامه که احراز هویت کاربر را مدیریت میکند و وظایف کاربر را نمایش میدهد. - OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet (نگاشت شده به
/oauth2callback): فراخوانی OAuth 2.0 که پاسخ از نقطه پایانی مجوز OAuth را مدیریت میکند.
فایل web.xml زیر که این دو سرولت را به URL های برنامه ما نگاشت میکند:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>PrintTasksTitles</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.google.oauthsample.PrintTasksTitlesServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>PrintTasksTitles</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.google.oauthsample.OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/oauth2callback</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>کاربران را در سیستم خود تأیید اعتبار کنید و برای دسترسی به وظایف خود درخواست مجوز دهید
کاربر از طریق آدرس اینترنتی ریشه '/' که به سرولت PrintTaskListsTitlesServlet نگاشت شده است، وارد برنامه میشود. در آن سرولت، وظایف زیر انجام میشود:
- بررسی میکند که آیا کاربر در سیستم احراز هویت شده است یا خیر.
- اگر کاربر احراز هویت نشده باشد، به صفحه احراز هویت هدایت میشود.
- اگر کاربر احراز هویت شود، بررسی وجود توکن بهروزرسانی که از قبل در حافظهی دادهها وجود دارد، انجام میشود که توسط
OAuthTokenDaoدر زیر مدیریت میشود. اگر توکنها در حافظهی کاربر موجود نباشند، به این معنی است که کاربر هنوز مجوز دسترسی به وظایف خود را به برنامه اعطا نکرده است. سپس کاربر به نقطهی پایانی مجوز OAuth 2.0 گوگل هدایت میشود.
در ادامه روشی برای پیادهسازی این مورد نشان داده شده است:
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Simple sample Servlet which will display the tasks in the default task list of the user. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class PrintTasksTitlesServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * The OAuth Token DAO implementation, used to persist the OAuth refresh token. * Consider injecting it instead of using a static initialization. Additionally, a * simple memory implementation is used as a mock. Change the implementation to * using the user's own user/login implementation. */ public static OAuthTokenDao oauthTokenDao = new OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the current user // This is using App Engine's User Service but you should replace this to // your own user/login implementation UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService(); User user = userService.getCurrentUser(); // If the user is not logged-in it is redirected to the login service, then back to this page if (user == null) { resp.sendRedirect(userService.createLoginURL(getFullRequestUrl(req))); return; } // Checking if we already have tokens for this user in store AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = oauthTokenDao.getKeys(user.getEmail()); // If tokens are not available for this user if (accessTokenResponse == null) { OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); // Redirects to the Google OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint resp.sendRedirect(new GoogleAuthorizationRequestUrl(oauthProperties.getClientId(), OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet.getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req), oauthProperties .getScopesAsString()).build()); return; } } /** * Construct the request's URL without the parameter part. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getFullRequestUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = req.getServletPath(); String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); String queryString = (req.getQueryString() == null) ? "" : "?" + req.getQueryString(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo + queryString; } }
نکته: پیادهسازی قبلی از برخی کتابخانههای App Engine استفاده میکند. این کتابخانهها صرفاً جهت سادهسازی استفاده شدهاند. اگر در حال توسعه برای پلتفرم دیگری هستید، رابط UserService که احراز هویت کاربر را مدیریت میکند، مجدداً پیادهسازی کنید.
این برنامه از یک DAO برای ذخیره و دسترسی به توکنهای مجوز کاربر استفاده میکند. رابط OAuthTokenDao و یک پیادهسازی شبیهسازیشده (درون حافظه) - OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl - که در این نمونه استفاده شدهاند، در مثالهای زیر نشان داده شدهاند:
package com.google.oauthsample; import com.google.api.client.auth.oauth2.draft10.AccessTokenResponse; /** * Allows easy storage and access of authorization tokens. */ public interface OAuthTokenDao { /** * Stores the given AccessTokenResponse using the {@code username}, the OAuth * {@code clientID} and the tokens scopes as keys. * * @param tokens The AccessTokenResponse to store * @param userName The userName associated wit the token */ public void saveKeys(AccessTokenResponse tokens, String userName); /** * Returns the AccessTokenResponse stored for the given username, clientId and * scopes. Returns {@code null} if there is no AccessTokenResponse for this * user and scopes. * * @param userName The username of which to get the stored AccessTokenResponse * @return The AccessTokenResponse of the given username */ public AccessTokenResponse getKeys(String userName); }
package com.google.oauthsample; import com.google.api.client.auth.oauth2.draft10.AccessTokenResponse; ... /** * Quick and Dirty memory implementation of {@link OAuthTokenDao} based on * HashMaps. */ public class OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl implements OAuthTokenDao { /** Object where all the Tokens will be stored */ private static Map<String, AccessTokenResponse> tokenPersistance = new HashMap<String, AccessTokenResponse>(); public void saveKeys(AccessTokenResponse tokens, String userName) { tokenPersistance.put(userName, tokens); } public AccessTokenResponse getKeys(String userName) { return tokenPersistance.get(userName); } }
اعتبارنامههای OAuth 2.0 برای برنامه در یک فایل properties ذخیره میشوند. به عنوان یک روش جایگزین، میتوانید آنها را به عنوان یک ثابت در جایی از یکی از کلاسهای جاوای خود ذخیره کنید. در اینجا کلاس OAuthProperties و فایل oauth.properties که در نمونه استفاده میشود، آمده است:
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Object representation of an OAuth properties file. */ public class OAuthProperties { public static final String DEFAULT_OAUTH_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME = "oauth.properties"; /** The OAuth 2.0 Client ID */ private String clientId; /** The OAuth 2.0 Client Secret */ private String clientSecret; /** The Google APIs scopes to access */ private String scopes; /** * Instantiates a new OauthProperties object reading its values from the * {@code OAUTH_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME} properties file. * * @throws IOException IF there is an issue reading the {@code propertiesFile} * @throws OauthPropertiesFormatException If the given {@code propertiesFile} * is not of the right format (does not contains the keys {@code * clientId}, {@code clientSecret} and {@code scopes}) */ public OAuthProperties() throws IOException { this(OAuthProperties.class.getResourceAsStream(DEFAULT_OAUTH_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME)); } /** * Instantiates a new OAuthProperties object, reading its values from the given * properties file. * * @param propertiesFile the InputStream to read an OAuth Properties file. The * file should contain the keys {@code clientId}, {@code * clientSecret} and {@code scopes} * @throws IOException if there is an issue reading the {@code propertiesFile} * @throws OAuthPropertiesFormatException If the given {@code propertiesFile} * is not in the correct format (does not contain the keys {@code * clientId}, {@code clientSecret} and {@code scopes}) */ public OAuthProperties(InputStream propertiesFile) throws IOException { Properties oauthProperties = new Properties(); oauthProperties.load(propertiesFile); clientId = oauthProperties.getProperty("clientId"); clientSecret = oauthProperties.getProperty("clientSecret"); scopes = oauthProperties.getProperty("scopes"); if ((clientId == null) || (clientSecret == null) || (scopes == null)) { throw new OAuthPropertiesFormatException(); } } /** * @return the clientId */ public String getClientId() { return clientId; } /** * @return the clientSecret */ public String getClientSecret() { return clientSecret; } /** * @return the scopes */ public String getScopesAsString() { return scopes; } /** * Thrown when the OAuth properties file was not at the right format, i.e not * having the right properties names. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class OAuthPropertiesFormatException extends RuntimeException { } }
فایل oauth.properties که شامل اعتبارنامههای OAuth 2.0 برای برنامه شما است، در مثال زیر نشان داده شده است. شما باید مقادیر این فایل را تغییر دهید.
# Client ID and secret. They can be found in the APIs console. clientId=1234567890.apps.googleusercontent.com clientSecret=aBcDeFgHiJkLmNoPqRsTuVwXyZ # API scopes. Space separated. scopes=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks
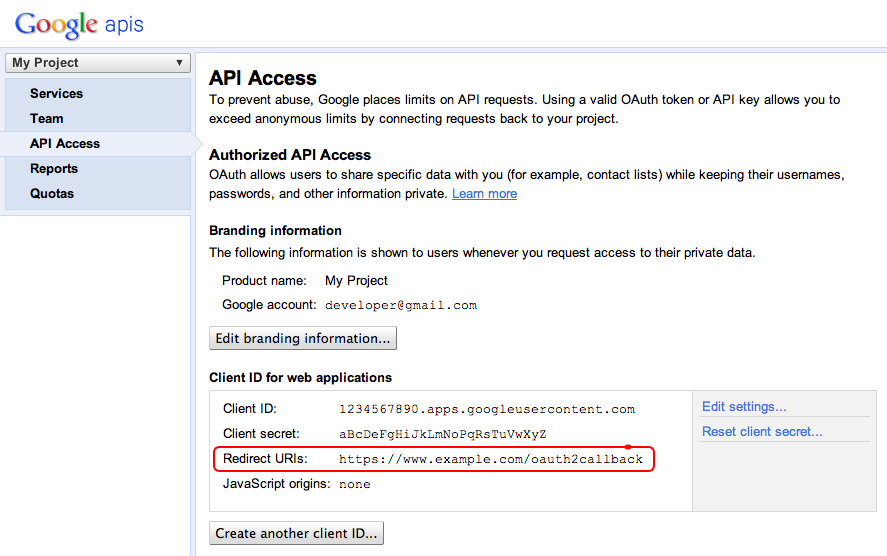
شناسه کلاینت OAuth 2.0 و رمز کلاینت، برنامه را شناسایی میکنند و به Tasks API اجازه میدهند تا فیلترها و قوانین سهمیهبندی تعریفشده برای برنامه را اعمال کند. شناسه کلاینت و رمز را میتوان در کنسول Google APIs یافت. پس از ورود به کنسول، کاربر باید:
- یک پروژه ایجاد یا انتخاب کنید.
- با تنظیم وضعیت Tasks API روی ON در لیست سرویسها، Tasks API را فعال کنید.
- در قسمت API Access، اگر هنوز یک شناسه کلاینت OAuth 2.0 ایجاد نکردهاید، آن را ایجاد کنید.
- مطمئن شوید که آدرس اینترنتی (URL) مربوط به کنترلکنندهی فراخوانی کد OAuth 2.0 پروژه در Redirect URIها ثبت/مجاز شده باشد. برای مثال، در این پروژهی نمونه، اگر برنامهی وب از دامنهی
https://www.example.comارائه میشود، کاربر بایدhttps://www.example.com/oauth2callbackثبت کند.
کد مجوز را از نقطه پایانی مجوز گوگل مدیریت کنید
در مواردی که کاربر هنوز به برنامه اجازه دسترسی به وظایف خود را نداده است و بنابراین به نقطه پایانی مجوز OAuth 2.0 گوگل هدایت میشود، یک کادر محاورهای مجوز از گوگل به کاربر نشان داده میشود که از او میخواهد به برنامه اجازه دسترسی به وظایف خود را بدهد:
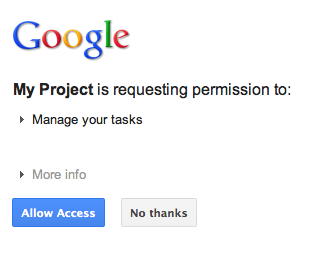
پس از اعطای یا رد دسترسی، کاربر به کنترلکنندهی فراخوانی کد OAuth 2.0 که هنگام ساخت URL مجوز گوگل به عنوان یک ریدایرکت/فراخوانی مشخص شده بود، هدایت میشود:
new GoogleAuthorizationRequestUrl(oauthProperties.getClientId(),
OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet.getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req), oauthProperties
.getScopesAsString()).build() کنترلکنندهی فراخوانی کد OAuth 2.0 - OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet - تغییر مسیر از نقطهی پایانی Google OAuth 2.0 را مدیریت میکند. دو حالت برای مدیریت وجود دارد:
- کاربر دسترسی را اعطا کرده است: درخواست برای دریافت کد OAuth 2.0 از پارامترهای URL تجزیه و تحلیل میشود.
- کاربر دسترسی را رد کرده است: پیامی به کاربر نمایش داده میشود.
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Servlet handling the OAuth callback from the authentication service. We are * retrieving the OAuth code, then exchanging it for a refresh and an access * token and saving it. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet extends HttpServlet { /** The name of the Oauth code URL parameter */ public static final String CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME = "code"; /** The name of the OAuth error URL parameter */ public static final String ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME = "error"; /** The URL suffix of the servlet */ public static final String URL_MAPPING = "/oauth2callback"; public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the "error" URL parameter String[] error = req.getParameterValues(ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking if there was an error such as the user denied access if (error != null && error.length > 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE, "There was an error: \""+error[0]+"\"."); return; } // Getting the "code" URL parameter String[] code = req.getParameterValues(CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking conditions on the "code" URL parameter if (code == null || code.length == 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, "The \"code\" URL parameter is missing"); return; } } /** * Construct the OAuth code callback handler URL. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = URL_MAPPING; String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo; } }
کد مجوز را با یک توکن بهروزرسانی و دسترسی تعویض کنید
سپس، OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet کد Auth 2.0 را برای بهروزرسانی و توکنهای دسترسی مبادله میکند، آن را در پایگاه داده حفظ میکند و کاربر را به URL PrintTaskListsTitlesServlet هدایت میکند:
کد اضافه شده به فایل هایلایت شده است.
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Servlet handling the OAuth callback from the authentication service. We are * retrieving the OAuth code, then exchanging it for a refresh and an access * token and saving it. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet extends HttpServlet { /** The name of the Oauth code URL parameter */ public static final String CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME = "code"; /** The name of the OAuth error URL parameter */ public static final String ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME = "error"; /** The URL suffix of the servlet */ public static final String URL_MAPPING = "/oauth2callback"; /** The URL to redirect the user to after handling the callback. Consider * saving this in a cookie before redirecting users to the Google * authorization URL if you have multiple possible URL to redirect people to. */ public static final String REDIRECT_URL = "/"; /** The OAuth Token DAO implementation. Consider injecting it instead of using * a static initialization. Also we are using a simple memory implementation * as a mock. Change the implementation to using your database system. */ public static OAuthTokenDao oauthTokenDao = new OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the "error" URL parameter String[] error = req.getParameterValues(ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking if there was an error such as the user denied access if (error != null && error.length > 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE, "There was an error: \""+error[0]+"\"."); return; } // Getting the "code" URL parameter String[] code = req.getParameterValues(CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking conditions on the "code" URL parameter if (code == null || code.length == 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, "The \"code\" URL parameter is missing"); return; } // Construct incoming request URL String requestUrl = getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req); // Exchange the code for OAuth tokens AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = exchangeCodeForAccessAndRefreshTokens(code[0], requestUrl); // Getting the current user // This is using App Engine's User Service, but the user should replace this // with their own user/login implementation UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService(); String email = userService.getCurrentUser().getEmail(); // Save the tokens oauthTokenDao.saveKeys(accessTokenResponse, email); resp.sendRedirect(REDIRECT_URL); } /** * Construct the OAuth code callback handler URL. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = URL_MAPPING; String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo; } /** * Exchanges the given code for an exchange and a refresh token. * * @param code The code gotten back from the authorization service * @param currentUrl The URL of the callback * @param oauthProperties The object containing the OAuth configuration * @return The object containing both an access and refresh token * @throws IOException */ public AccessTokenResponse exchangeCodeForAccessAndRefreshTokens(String code, String currentUrl) throws IOException { HttpTransport httpTransport = new NetHttpTransport(); JacksonFactory jsonFactory = new JacksonFactory(); // Loading the oauth config file OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); return new GoogleAuthorizationCodeGrant(httpTransport, jsonFactory, oauthProperties .getClientId(), oauthProperties.getClientSecret(), code, currentUrl).execute(); } }
نکته: پیادهسازی قبلی از برخی کتابخانههای App Engine استفاده میکند که به منظور سادهسازی استفاده میشوند. اگر در حال توسعه برای پلتفرم دیگری هستید، رابط UserService را که احراز هویت کاربر را مدیریت میکند، مجدداً پیادهسازی کنید.
خواندن وظایف کاربر و نمایش آنها
کاربر به برنامه اجازه دسترسی به وظایفش را داده است. برنامه یک توکن refresh دارد که در datastore ذخیره شده و از طریق OAuthTokenDao قابل دسترسی است. Servlet PrintTaskListsTitlesServlet اکنون میتواند از این توکنها برای دسترسی به وظایف کاربر و نمایش آنها استفاده کند:
کد اضافه شده به فایل هایلایت شده است.
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Simple sample Servlet which will display the tasks in the default task list of the user. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class PrintTasksTitlesServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * The OAuth Token DAO implementation, used to persist the OAuth refresh token. * Consider injecting it instead of using a static initialization. Additionally, a * simple memory implementation is used as a mock. Change the implementation to * use your own database system. */ public static OAuthTokenDao oauthTokenDao = new OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the current user // This is using App Engine's User Service but you should replace this to // your own user/login implementation UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService(); User user = userService.getCurrentUser(); // If the user is not logged-in it is redirected to the login service, then back to this page if (user == null) { resp.sendRedirect(userService.createLoginURL(getFullRequestUrl(req))); return; } // Checking if we already have tokens for this user in store AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = oauthTokenDao.getKeys(user.getEmail()); // If we don't have tokens for this user if (accessTokenResponse == null) { OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); // Redirect to the Google OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint resp.sendRedirect(new GoogleAuthorizationRequestUrl(oauthProperties.getClientId(), OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet.getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req), oauthProperties .getScopesAsString()).build()); return; } // Prints the user's task list titles in the response resp.setContentType("text/plain"); resp.getWriter().append("Task Lists titles for user " + user.getEmail() + ":\n\n"); printTasksTitles(accessTokenResponse, resp.getWriter()); } /** * Construct the request's URL without the parameter part. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getFullRequestUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = req.getServletPath(); String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); String queryString = (req.getQueryString() == null) ? "" : "?" + req.getQueryString(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo + queryString; } /** * Uses the Google Tasks API to retrieve a list of the user's tasks in the default * tasks list. * * @param accessTokenResponse The OAuth 2.0 AccessTokenResponse object * containing the access token and a refresh token. * @param output The output stream writer to write the task list titles to. * @return A list of the user's task titles in the default task list. * @throws IOException */ public void printTasksTitles(AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse, Writer output) throws IOException { // Initializing the Tasks service HttpTransport transport = new NetHttpTransport(); JsonFactory jsonFactory = new JacksonFactory(); OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); GoogleAccessProtectedResource accessProtectedResource = new GoogleAccessProtectedResource( accessTokenResponse.accessToken, transport, jsonFactory, oauthProperties.getClientId(), oauthProperties.getClientSecret(), accessTokenResponse.refreshToken); Tasks service = new Tasks(transport, accessProtectedResource, jsonFactory); // Using the initialized Tasks API service to query the list of tasks lists com.google.api.services.tasks.model.Tasks tasks = service.tasks.list("@default").execute(); for (Task task : tasks.items) { output.append(task.title + "\n"); } } }
وظایف کاربر نمایش داده میشود:
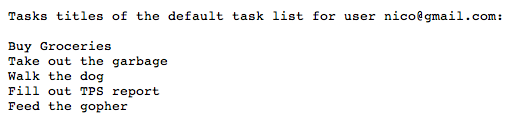
نمونه درخواست
میتوانید کد مربوط به این نمونه برنامه را دانلود کنید.
