כדי להשתמש בשירותי Google בשם משתמש כשהמשתמש אופליין, צריך להשתמש בתהליך היברידי בצד השרת שבו המשתמש מאשר את האפליקציה בצד הלקוח באמצעות לקוח JavaScript API, ואתם שולחים קוד הרשאה חד-פעמי מיוחד לשרת. השרת מחליף את הקוד לשימוש חד-פעמי הזה כדי לקבל מ-Google אסימוני גישה ואסימוני רענון משלו, כדי שהשרת יוכל לבצע קריאות API משלו, ואפשר לעשות זאת בזמן שהמשתמש אופליין. לתהליך הקוד החד-פעמי יש יתרונות אבטחה גם על פני תהליך טהור בצד השרת וגם על פני שליחת אסימוני גישה לשרת.
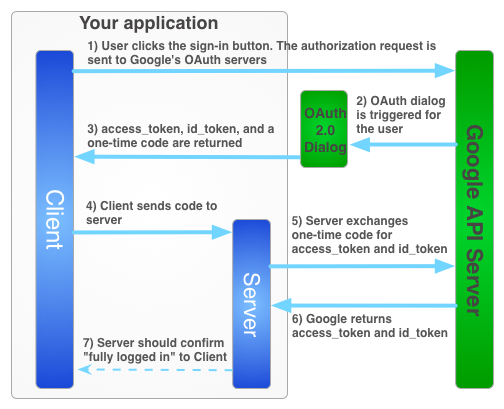
באיור הבא מתואר תהליך הכניסה לקבלת אסימון גישה לאפליקציה בצד השרת.
לקודים חד-פעמיים יש כמה יתרונות אבטחה. באמצעות קודים, Google מספקת אסימונים ישירות לשרת שלכם בלי גורמים מקשרים. אנחנו לא ממליצים לחשוף קודים, אבל קשה מאוד להשתמש בהם בלי הסוד של הלקוח. חשוב לשמור בסוד את סוד הלקוח!
הטמעת התהליך של הקוד החד-פעמי
הלחצן 'כניסה באמצעות חשבון Google' מספק גם אסימון גישה וגם קוד הרשאה. הקוד הוא קוד חד-פעמי שהשרת יכול להחליף עם שרתי Google תמורת אסימון גישה.
דוגמת הקוד הבאה מראה איך לבצע את התהליך של קוד לשימוש חד-פעמי.
כדי לאמת את הכניסה באמצעות חשבון Google בתהליך של קוד חד-פעמי, צריך:
שלב 1: יוצרים מזהה לקוח וסוד לקוח
כדי ליצור מזהה לקוח וסוד לקוח, יוצרים פרויקט ב-Google API Console, מגדירים מזהה לקוח OAuth ומרשמים את מקורות ה-JavaScript:
נכנסים למסוף Google API.
בתפריט הנפתח של הפרויקטים, בוחרים פרויקט קיים או לוחצים על Create a new project כדי ליצור פרויקט חדש.
בסרגל הצד, בקטע 'APIs & Services' (ממשקי API ושירותים), בוחרים באפשרות Credentials (פרטי כניסה) ולוחצים על Configure consent screen (הגדרת מסך הסכמה).
בוחרים כתובת אימייל, מציינים שם מוצר ולוחצים על שמירה.
בכרטיסייה Credentials, בוחרים ברשימה הנפתחת Create credentials ובאפשרות OAuth client ID.
בקטע Application type בוחרים באפשרות Web application.
כך רושמים את המקור שממנו לאפליקציה מותר לגשת ל-Google APIs: מקור הוא שילוב ייחודי של פרוטוקול, שם מארח ויציאה.
בשדה Authorized JavaScript origins מזינים את המקור של האפליקציה. אפשר להזין כמה מקורות כדי לאפשר לאפליקציה לפעול בפרוטוקולים, בדומיינים או בתת-דומיינים שונים. אי אפשר להשתמש בתווים כלליים לחיפוש. בדוגמה הבאה, כתובת ה-URL השנייה יכולה להיות כתובת URL בסביבת הייצור.
http://localhost:8080 https://myproductionurl.example.comבשדה Authorized redirect URI לא נדרש ערך. לא משתמשים במזהי URI להפניה אוטומטית עם ממשקי API של JavaScript.
לוחצים על הלחצן Create.
מעתיקים את מזהה הלקוח מתיבת הדו-שיח OAuth client שנפתחת. מזהה הלקוח מאפשר לאפליקציה לגשת לממשקי ה-API של Google שמופעלים.
שלב 2: הוספת ספריית הפלטפורמה של Google לדף
מוסיפים את הסקריפטים הבאים שממחישים פונקציה אנונימית שמוסיפה סקריפט ל-DOM של דף האינטרנט index.html.
<!-- The top of file index.html -->
<html itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/Article">
<head>
<!-- BEGIN Pre-requisites -->
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.8.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script src="https://apis.google.com/js/client:platform.js?onload=start" async defer>
</script>
<!-- END Pre-requisites -->
שלב 3: מאתחלים את האובייקט GoogleAuth
טוענים את ספריית auth2 וקוראים ל-gapi.auth2.init() כדי לאתחל את האובייקט GoogleAuth. כשקוראים ל-init(), צריך לציין את מזהה הלקוח ואת ההיקפים שרוצים לבקש.
<!-- Continuing the <head> section -->
<script>
function start() {
gapi.load('auth2', function() {
auth2 = gapi.auth2.init({
client_id: 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID.apps.googleusercontent.com',
// Scopes to request in addition to 'profile' and 'email'
//scope: 'additional_scope'
});
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- ... -->
</body>
</html>
שלב 4: מוסיפים את לחצן הכניסה לדף
מוסיפים את לחצן הכניסה לדף האינטרנט ומצרפים טיפול בקליק כדי לקרוא ל-grantOfflineAccess() ולהתחיל את תהליך הקוד החד-פעמי.
<!-- Add where you want your sign-in button to render -->
<!-- Use an image that follows the branding guidelines in a real app -->
<button id="signinButton">Sign in with Google</button>
<script>
$('#signinButton').click(function() {
// signInCallback defined in step 6.
auth2.grantOfflineAccess().then(signInCallback);
});
</script>
שלב 5: כניסה של המשתמש
המשתמש לוחץ על לחצן הכניסה ומעניק לאפליקציה גישה להרשאות שביקשת. לאחר מכן, פונקציית הקריאה החוזרת שציינתם ב-method grantOfflineAccess().then() מועברת לאובייקט JSON עם קוד הרשאה. לדוגמה:
{"code":"4/yU4cQZTMnnMtetyFcIWNItG32eKxxxgXXX-Z4yyJJJo.4qHskT-UtugceFc0ZRONyF4z7U4UmAI"}
שלב 6: שולחים את קוד ההרשאה לשרת
הערך code הוא הקוד החד-פעמי שהשרת יכול להמיר באסימון הגישה ובאסימון הרענון שלו. אפשר לקבל אסימון רענון רק אחרי שהוצגה למשתמש תיבת דו-שיח של הרשאה שבה הוא מתבקש להעניק גישה אופליין.
אם ציינתם את select-account prompt ב-OfflineAccessOptions בשלב 4, צריך לאחסן את אסימון הרענון שמאחזרים לשימוש מאוחר יותר, כי החלפות הבאות יחזירו null עבור אסימון הרענון. התהליך הזה מספק אבטחה משופרת בהשוואה לתהליך הרגיל של OAuth 2.0.
אסימוני הגישה תמיד מוחזרים יחד עם החלפה של קוד הרשאה תקף.
הסקריפט הבא מגדיר פונקציית קריאה חוזרת ללחצן הכניסה. כשהכניסה מתבצעת בהצלחה, הפונקציה שומרת את אסימון הגישה לשימוש בצד הלקוח ושולחת את הקוד החד-פעמי לשרת באותו דומיין.
<!-- Last part of BODY element in file index.html -->
<script>
function signInCallback(authResult) {
if (authResult['code']) {
// Hide the sign-in button now that the user is authorized, for example:
$('#signinButton').attr('style', 'display: none');
// Send the code to the server
$.ajax({
type: 'POST',
url: 'http://example.com/storeauthcode',
// Always include an `X-Requested-With` header in every AJAX request,
// to protect against CSRF attacks.
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
},
contentType: 'application/octet-stream; charset=utf-8',
success: function(result) {
// Handle or verify the server response.
},
processData: false,
data: authResult['code']
});
} else {
// There was an error.
}
}
</script>
שלב 7: ממירים את קוד ההרשאה לטוקן גישה
בשרת, מחליפים את קוד האימות באסימוני גישה ורענון. משתמשים באסימון הגישה כדי להפעיל Google APIs בשם המשתמש, ואפשר גם לאחסן את אסימון הרענון כדי לקבל אסימון גישה חדש כשיפוג התוקף של אסימון הגישה.
אם ביקשת גישה לפרופיל, תקבל גם אסימון מזהה שמכיל את פרטי הפרופיל הבסיסיים של המשתמש.
לדוגמה:
Java
// (Receive authCode via HTTPS POST) if (request.getHeader("X-Requested-With") == null) { // Without the `X-Requested-With` header, this request could be forged. Aborts. } // Set path to the Web application client_secret_*.json file you downloaded from the // Google API Console: https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials // You can also find your Web application client ID and client secret from the // console and specify them directly when you create the GoogleAuthorizationCodeTokenRequest // object. String CLIENT_SECRET_FILE = "/path/to/client_secret.json"; // Exchange auth code for access token GoogleClientSecrets clientSecrets = GoogleClientSecrets.load( JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance(), new FileReader(CLIENT_SECRET_FILE)); GoogleTokenResponse tokenResponse = new GoogleAuthorizationCodeTokenRequest( new NetHttpTransport(), JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance(), "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token", clientSecrets.getDetails().getClientId(), clientSecrets.getDetails().getClientSecret(), authCode, REDIRECT_URI) // Specify the same redirect URI that you use with your web // app. If you don't have a web version of your app, you can // specify an empty string. .execute(); String accessToken = tokenResponse.getAccessToken(); // Use access token to call API GoogleCredential credential = new GoogleCredential().setAccessToken(accessToken); Drive drive = new Drive.Builder(new NetHttpTransport(), JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance(), credential) .setApplicationName("Auth Code Exchange Demo") .build(); File file = drive.files().get("appfolder").execute(); // Get profile info from ID token GoogleIdToken idToken = tokenResponse.parseIdToken(); GoogleIdToken.Payload payload = idToken.getPayload(); String userId = payload.getSubject(); // Use this value as a key to identify a user. String email = payload.getEmail(); boolean emailVerified = Boolean.valueOf(payload.getEmailVerified()); String name = (String) payload.get("name"); String pictureUrl = (String) payload.get("picture"); String locale = (String) payload.get("locale"); String familyName = (String) payload.get("family_name"); String givenName = (String) payload.get("given_name");
Python
from apiclient import discovery import httplib2 from oauth2client import client # (Receive auth_code by HTTPS POST) # If this request does not have `X-Requested-With` header, this could be a CSRF if not request.headers.get('X-Requested-With'): abort(403) # Set path to the Web application client_secret_*.json file you downloaded from the # Google API Console: https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials CLIENT_SECRET_FILE = '/path/to/client_secret.json' # Exchange auth code for access token, refresh token, and ID token credentials = client.credentials_from_clientsecrets_and_code( CLIENT_SECRET_FILE, ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.appdata', 'profile', 'email'], auth_code) # Call Google API http_auth = credentials.authorize(httplib2.Http()) drive_service = discovery.build('drive', 'v3', http=http_auth) appfolder = drive_service.files().get(fileId='appfolder').execute() # Get profile info from ID token userid = credentials.id_token['sub'] email = credentials.id_token['email']