상위-하위 관계
Google Issue Tracker는 상위-하위 관계를 지원합니다. 상위-하위 관계는 일반적으로 특정 작업 내의 작업 분류를 나타내는 데 사용됩니다. 상위 요소에는 하위 요소가 여러 개 있을 수 있으며 하위 요소에는 상위 요소가 여러 개 있을 수 있습니다.
상위-하위 관계의 특징은 다음과 같습니다.
| 특성 |
세부정보 |
| 관계 |
N:N |
| 순서 지정 |
상위 요소 내 하위 요소의 순서 지정이 지원됩니다. |
| 주기 감지 |
순환 종속 항목은 시스템에서 방지됩니다. |
| 최대 직접 하위 요소 |
500 |
| 최대 조상 |
1000 |
예
다음 그래픽은 일부 상위-하위 관계 샘플을 보여줍니다.
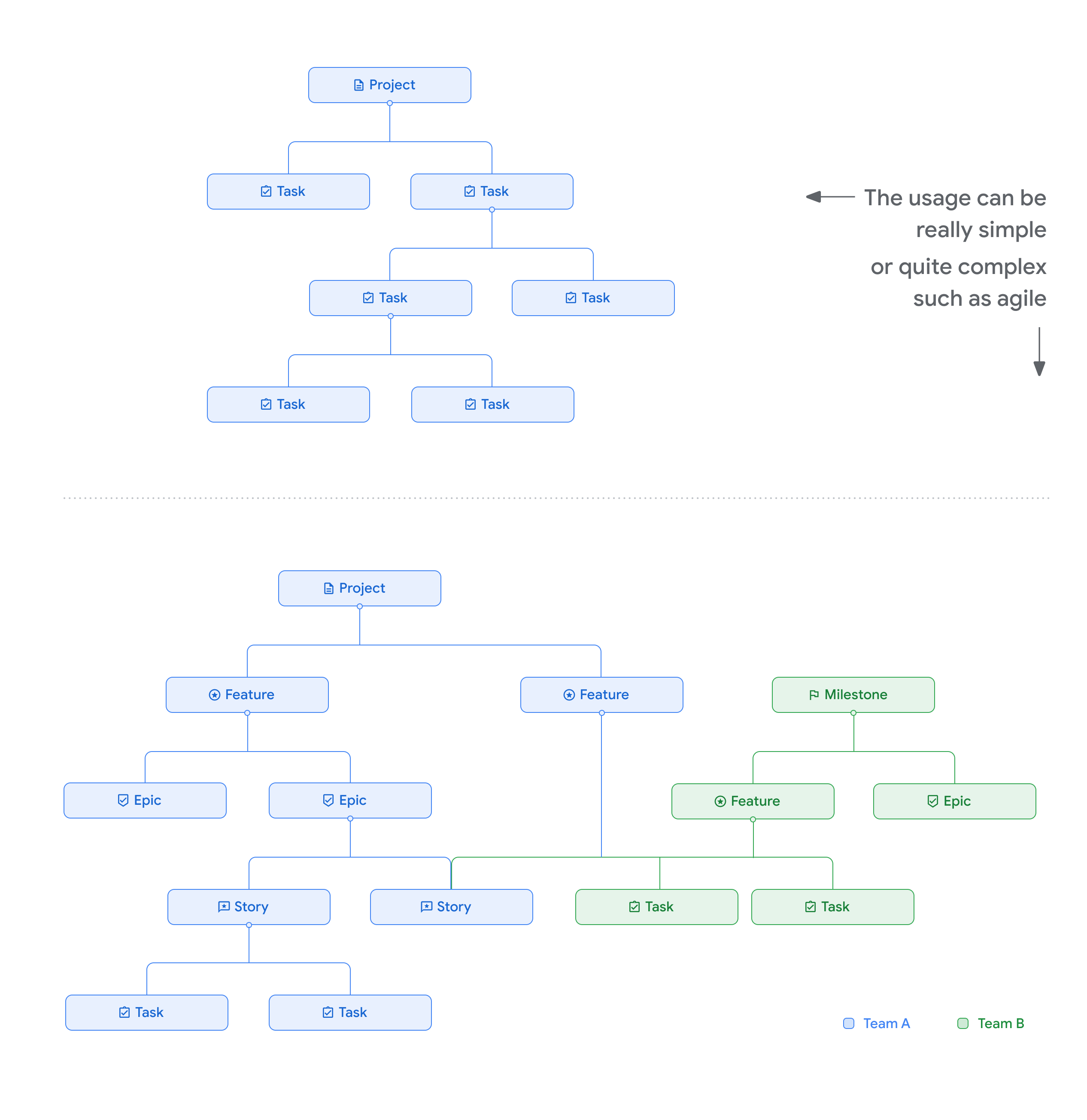
상위-하위 관계 및 차단
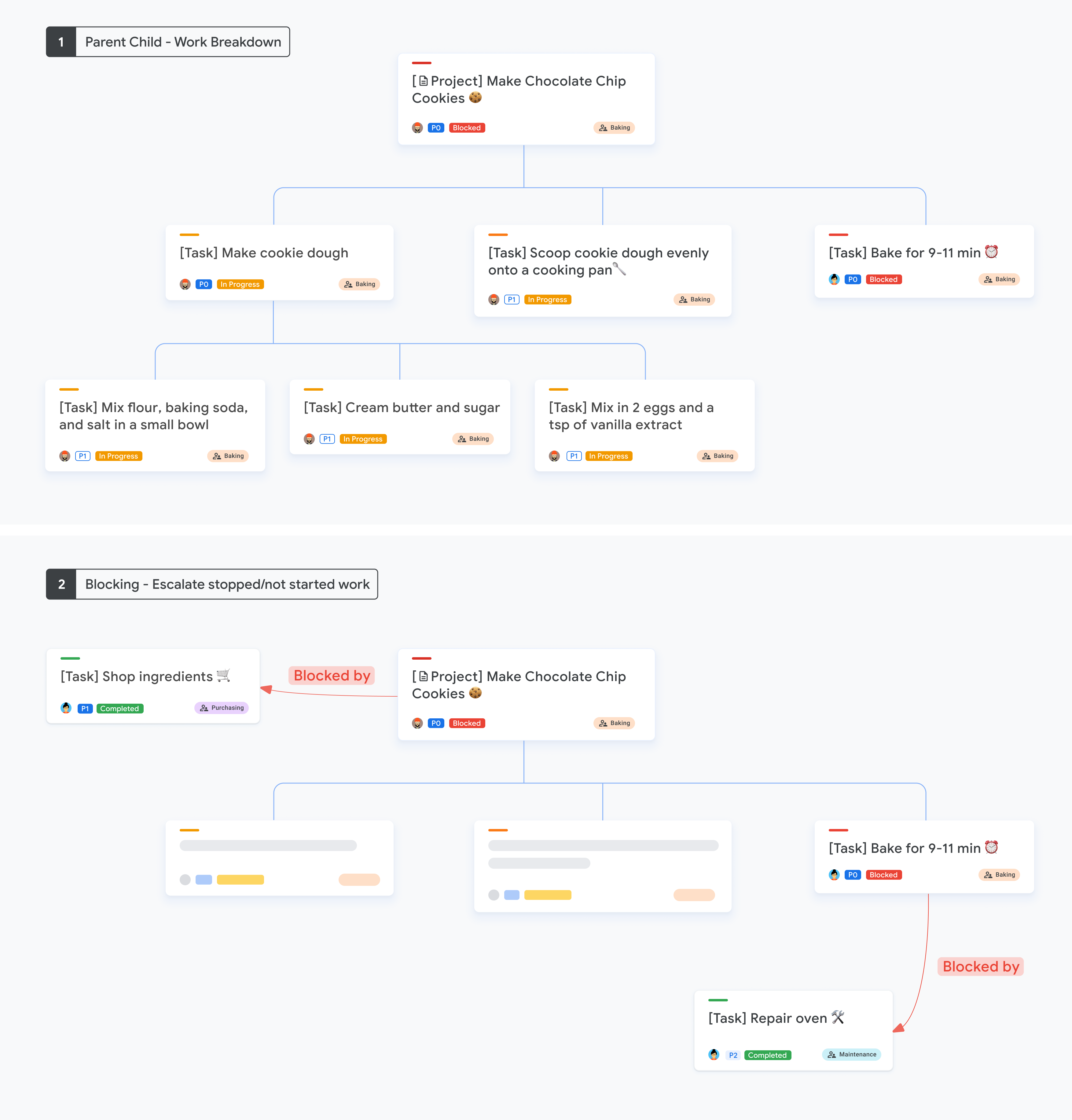
상위-하위 관계를 사용할 때 기존 차단 및 차단됨 관계는 계속 지원됩니다. 차단과 상위-하위 관계를 결합하는 경우 다음 사항에 유의하세요.
- 상위-하위 관계를 사용하여 작업을 더 작은 단위로 분할합니다.
- 타이밍과 시퀀스가 중요하고 중지되었거나 시작되지 않은 작업을 에스컬레이션하기 위해 UI에 명확한 표시를 제공하려는 경우 blocking 및 blocked by를 사용하세요.
다음 그래픽은 상위-하위 및 차단 작업 분류의 예를 보여줍니다.
All rights reserved. 자바는 Oracle 및/또는 Oracle 계열사의 등록 상표입니다.
최종 업데이트: 2025-02-05(UTC)
[null,null,["최종 업데이트: 2025-02-05(UTC)"],[[["Google Issue Tracker enables the creation of parent-child relationships to represent the hierarchical breakdown of work within a project."],["Issues can have multiple parents and children, but the system prevents circular dependencies and limits the number of direct children to 500 and total ancestors to 1000."],["While parent-child relationships are ideal for structuring tasks, \"Blocking\" and \"Blocked by\" relationships should be used to indicate critical timing and sequencing dependencies."],["Users are encouraged to leverage both relationship types to manage work effectively, using parent-child for work breakdown and blocking for highlighting time-sensitive dependencies."]]],[]]
![]()
![]()
