母子关系
Google 问题跟踪器支持父子关系。父子关系通常用于表示给定工作中的任务细分。父级可以有多个子级,子级也可以有多个父级。
父/子级关系具有以下特征:
| 特征 |
详细信息 |
| 关系 |
N:N |
| 订购 |
支持对父级中的子项进行排序。 |
| 周期检测 |
系统会防止出现循环依赖项。 |
| 直接子元素的数量上限 |
500 |
| 祖先数量上限 |
1000 |
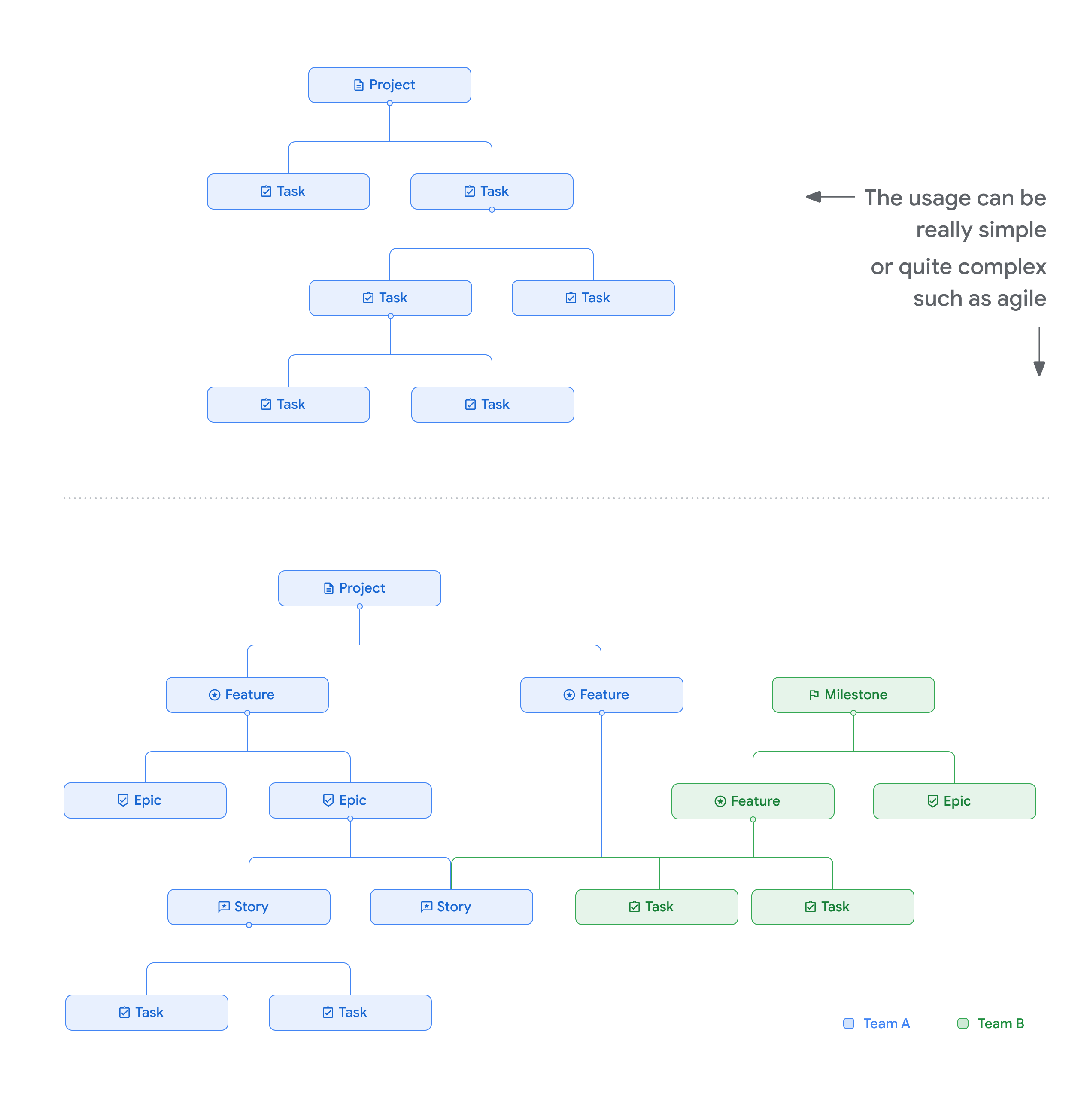
示例
下图显示了一些父级-子级关系示例。
父子关系和屏蔽
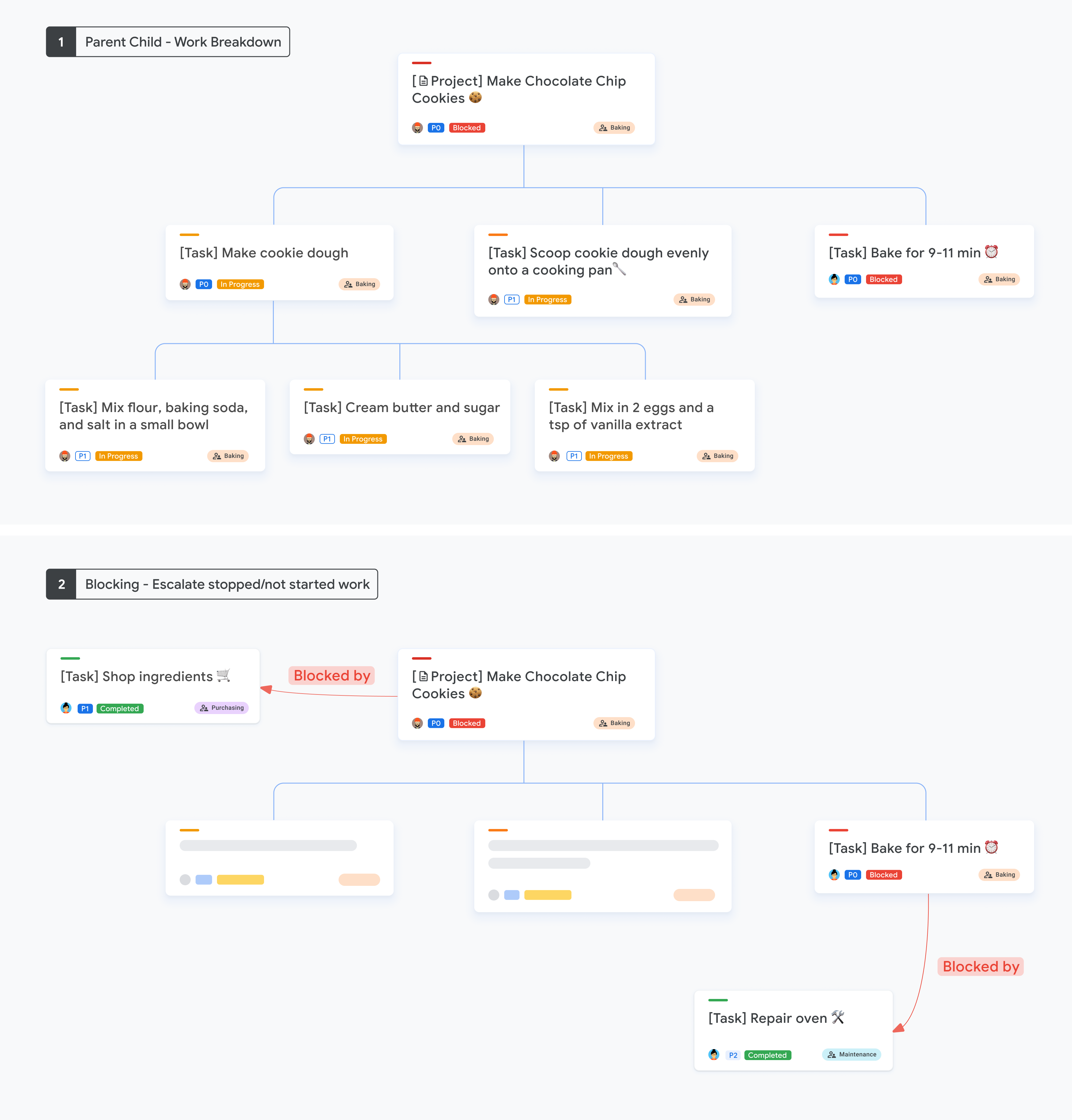
使用父子关系时,系统仍支持现有的屏蔽和被屏蔽关系。将父子关系与屏蔽功能结合使用时,请注意以下事项:
- 使用父子关系将工作分解成更小的单元。
- 如果时间和顺序至关重要,并且您希望在界面中提供明确的指示来上报已停止或未开始的工作,请使用正在阻塞和被阻塞。
下图显示了父子工作和阻塞工作细分的示例。
保留所有权利。Java 是 Oracle 和/或其关联公司的注册商标。
最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-02-05。
[null,null,["最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-02-05。"],[[["Google Issue Tracker enables the creation of parent-child relationships to represent the hierarchical breakdown of work within a project."],["Issues can have multiple parents and children, but the system prevents circular dependencies and limits the number of direct children to 500 and total ancestors to 1000."],["While parent-child relationships are ideal for structuring tasks, \"Blocking\" and \"Blocked by\" relationships should be used to indicate critical timing and sequencing dependencies."],["Users are encouraged to leverage both relationship types to manage work effectively, using parent-child for work breakdown and blocking for highlighting time-sensitive dependencies."]]],[]]
![]()
![]()
