Page Summary
-
Fleet Engine secures communication between your backend server, the Fleet Engine server, and your client applications using Application Default Credentials (ADC) and JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
-
ADC is used for high-privilege communication between your backend server and Fleet Engine, while JWT is used for low-trust environments like client applications.
-
Your backend server generates and issues JWTs to client applications, limiting access based on JWT claims and service account roles for enhanced security.
-
Fleet Engine employs authentication to verify the identity of the requesting entity and authorization to control access to specific resources based on defined roles and claims.
-
To ensure security, you need to configure service accounts, set up ADC for backend communication, implement JWT generation on your server, and enable client applications to fetch and use JWTs for secure interaction with Fleet Engine.
This document explains how Fleet engine secures information exchange between the three primary environments of your Fleet Engine system: your backend server, your Fleet Engine server, and your client applications and websites.
Fleet Engine manages security in two fundamental ways, using the principle of least privilege:
Application Default Credentials (ADC): For high-privileged environments such as server to server communications. Used when your backend server is creating vehicles and trips and managing them in Fleet Engine. For details, see Application Default Credentials.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): For low-trust environments like client applications running on smartphones and browsers. Used to accomplish lower-privileged operations, such as updating vehicle location in Fleet Engine.
The JWTs required by low-trust environments are generated and issued by your backend server to safeguard service account secret keys, and include additional claims specific to Fleet Engine. For details, see JSON Web Tokens.
For example, if you have a driver app, drivers access data from Fleet Engine through the app. The app is authenticated using JWTs it gets from your backend server. The included JWT claims, along with the service account role, determine what parts of your system the driver app has access to and what it can do. This approach limits access to only the data required to complete their driving assignments.
Fleet Engine uses these security approaches to provide the following:
Authentication verifies the identity of the entity making the request. Fleet Engine uses ADC for high-trust environments and JWT for low-trust environments.
Authorization specifies which resources an authenticated entity has access to. Fleet Engine uses service accounts with Google Cloud IAM roles, plus JWT claims that ensure authenticated entities have permissions to see or change the data they're requesting.
Server and client security setup
To enable security with Fleet Engine, set up the required accounts and security on your backend server and on your client applications and websites.
The following diagram shows an overview of the steps to set up security on your backend server and client applications.
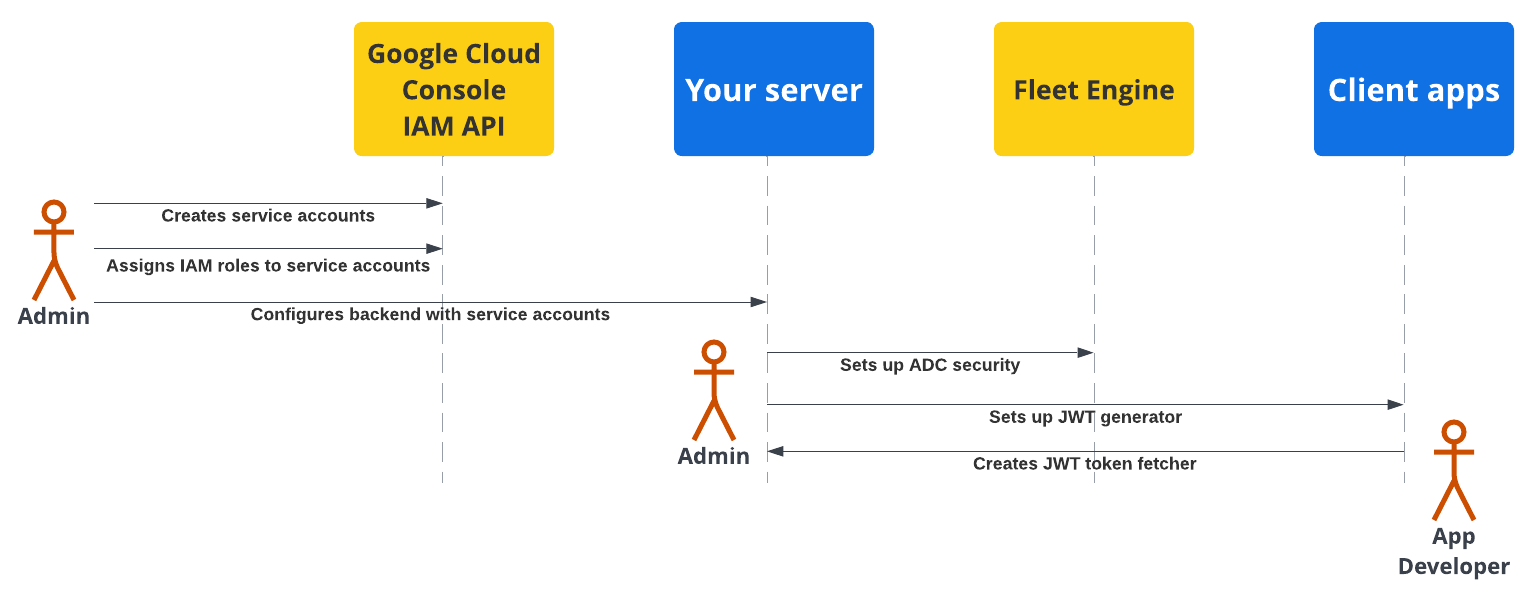
For more details, see the following sections.
Backend server security setup
A fleet administrator needs to follow these steps:
Create and configure service accounts:
In the Google Cloud Console, create service accounts.
Assign specific IAM roles to the service accounts.
Configure your backend server with the created service accounts. For details, see Service account roles.
Configure secure communication with Fleet Engine (ADC): Configure your backend to communicate with your Fleet Engine instance using Application Default Credentials with the appropriate *Admin service account. For details, See Application Default Credentials.
Configure secure communication with client apps (JWT): Create a JSON Web Token generator to create JWTs with appropriate claims for client applications and monitoring websites. For details, see Issue JSON Web Tokens.
Application security setup
Application developers need to include a way to fetch JSON Web Tokens generated by your backend server in your client apps or websites, and use them to securely communicate with Fleet Engine. For details, see the setup instructions in the Driver Experience or Consumer Experience documentation for the applications you need.
Server and client app security flow
The following sequence diagram demonstrates the server and client app authentication and authorization flow with Fleet Engine using ADC with the backend server and JWTs with the client applications and websites.
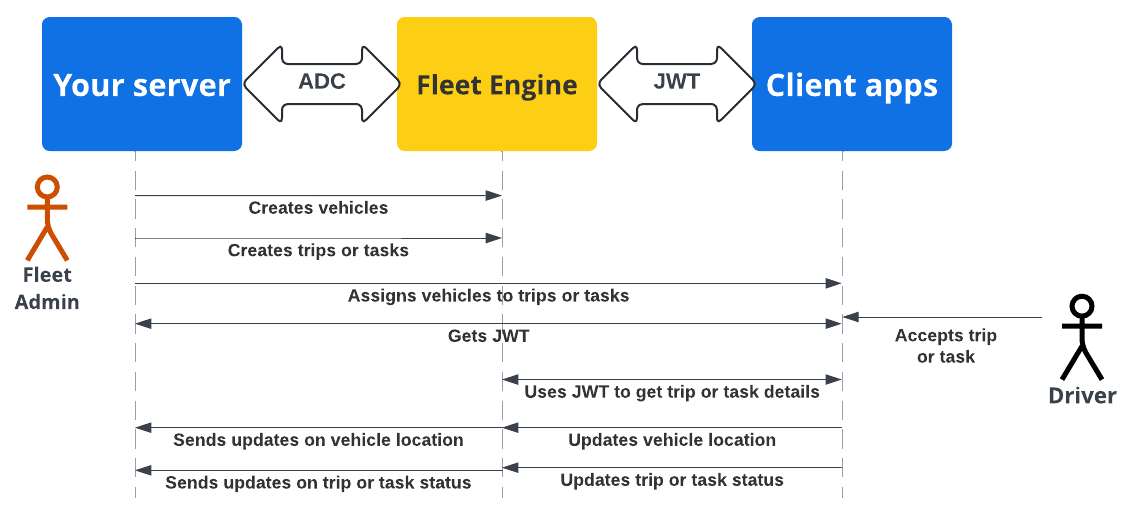
Your backend server creates vehicles and trips or tasks in Fleet Engine.
Your backend server a trip or task to a vehicle: The driver app, when active, retrieves the assignment.
Your backend server: Signs and issues a JWT for the respective service account with the appropriate IAM role for the assigned task or trip.
The client app: The client app uses the received JWT to send vehicle location updates to Fleet Engine.
What's next
- Create your Fleet Engine project.
- Learn how to Issue JSON Web Tokens from your server.
- Learn more about Service account roles.
- Learn more about JWTs.
