Ce document explique comment implémenter un gestionnaire de rappel d'autorisation OAuth 2.0 à l'aide de servlets Java via un exemple d'application Web qui affiche les tâches de l'utilisateur à l'aide de l'API Google Tasks. L'application exemple demande d'abord l'autorisation d'accéder aux tâches Google de l'utilisateur, puis affiche ses tâches dans la liste des tâches par défaut.
Audience
Ce document s'adresse aux personnes qui connaissent bien l'architecture des applications Web Java et J2EE. Il est recommandé d'avoir quelques connaissances sur le flux d'autorisation OAuth 2.0.
Sommaire
Pour obtenir un exemple entièrement fonctionnel, vous devez effectuer plusieurs étapes :
- Déclarer les mappages de servlet dans le fichier web.xml
- Authentifier les utilisateurs sur leur système et demander l'autorisation d'accéder à leurs tâches
- Écoutez le code d'autorisation du point de terminaison d'autorisation Google.
- Échanger le code d'autorisation contre un jeton d'actualisation et un jeton d'accès
- Lire les tâches de l'utilisateur et les afficher
Déclarer les mappages de servlet dans le fichier web.xml
Cette application utilise les deux servlets suivants :
- PrintTasksTitlesServlet (mappé à
/) : point d'entrée de l'application qui gère l'authentification de l'utilisateur et affiche ses tâches - OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet (mappé sur
/oauth2callback) : rappel OAuth 2.0 qui gère la réponse du point de terminaison d'autorisation OAuth
Le fichier web.xml suivant mappe ces deux servlets sur des URL dans notre application :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>PrintTasksTitles</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.google.oauthsample.PrintTasksTitlesServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>PrintTasksTitles</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.google.oauthsample.OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/oauth2callback</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Authentifier les utilisateurs sur leur système et demander l'autorisation d'accéder à leurs tâches
L'utilisateur accède à l'application via l'URL racine "/" qui est mappée au servlet PrintTaskListsTitlesServlet. Dans ce servlet, les tâches suivantes sont effectuées :
- Vérifie si l'utilisateur est authentifié sur le système.
- Si l'utilisateur n'est pas authentifié, il est redirigé vers la page d'authentification.
- Si l'utilisateur est authentifié, une vérification est effectuée pour un jeton d'actualisation déjà présent dans le stockage de données, qui est géré par le
OAuthTokenDaoci-dessous. Si aucun jeton n'est disponible dans le stockage pour l'utilisateur, cela signifie que l'utilisateur n'a pas encore accordé à l'application l'autorisation d'accéder à ses tâches. L'utilisateur est ensuite redirigé vers le point de terminaison d'autorisation OAuth 2.0 de Google.
Voici une façon d'implémenter cela :
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Simple sample Servlet which will display the tasks in the default task list of the user. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class PrintTasksTitlesServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * The OAuth Token DAO implementation, used to persist the OAuth refresh token. * Consider injecting it instead of using a static initialization. Additionally, a * simple memory implementation is used as a mock. Change the implementation to * using the user's own user/login implementation. */ public static OAuthTokenDao oauthTokenDao = new OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the current user // This is using App Engine's User Service but you should replace this to // your own user/login implementation UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService(); User user = userService.getCurrentUser(); // If the user is not logged-in it is redirected to the login service, then back to this page if (user == null) { resp.sendRedirect(userService.createLoginURL(getFullRequestUrl(req))); return; } // Checking if we already have tokens for this user in store AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = oauthTokenDao.getKeys(user.getEmail()); // If tokens are not available for this user if (accessTokenResponse == null) { OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); // Redirects to the Google OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint resp.sendRedirect(new GoogleAuthorizationRequestUrl(oauthProperties.getClientId(), OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet.getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req), oauthProperties .getScopesAsString()).build()); return; } } /** * Construct the request's URL without the parameter part. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getFullRequestUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = req.getServletPath(); String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); String queryString = (req.getQueryString() == null) ? "" : "?" + req.getQueryString(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo + queryString; } }
Remarque : L'implémentation précédente utilise certaines bibliothèques App Engine. Elles sont utilisées pour simplifier le processus. Si vous développez pour une autre plate-forme, réimplémentez l'interface UserService qui gère l'authentification des utilisateurs.
L'application utilise un DAO pour conserver les jetons d'autorisation de l'utilisateur et y accéder.
L'interface OAuthTokenDao et une implémentation fictive (en mémoire) – OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl – utilisées dans cet exemple sont présentées dans les exemples suivants :
package com.google.oauthsample; import com.google.api.client.auth.oauth2.draft10.AccessTokenResponse; /** * Allows easy storage and access of authorization tokens. */ public interface OAuthTokenDao { /** * Stores the given AccessTokenResponse using the {@code username}, the OAuth * {@code clientID} and the tokens scopes as keys. * * @param tokens The AccessTokenResponse to store * @param userName The userName associated wit the token */ public void saveKeys(AccessTokenResponse tokens, String userName); /** * Returns the AccessTokenResponse stored for the given username, clientId and * scopes. Returns {@code null} if there is no AccessTokenResponse for this * user and scopes. * * @param userName The username of which to get the stored AccessTokenResponse * @return The AccessTokenResponse of the given username */ public AccessTokenResponse getKeys(String userName); }
package com.google.oauthsample; import com.google.api.client.auth.oauth2.draft10.AccessTokenResponse; ... /** * Quick and Dirty memory implementation of {@link OAuthTokenDao} based on * HashMaps. */ public class OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl implements OAuthTokenDao { /** Object where all the Tokens will be stored */ private static Map<String, AccessTokenResponse> tokenPersistance = new HashMap<String, AccessTokenResponse>(); public void saveKeys(AccessTokenResponse tokens, String userName) { tokenPersistance.put(userName, tokens); } public AccessTokenResponse getKeys(String userName) { return tokenPersistance.get(userName); } }
Les identifiants OAuth 2.0 de l'application sont stockés dans un fichier de propriétés.
Vous pouvez également les stocker en tant que constante dans l'une de vos classes Java.
Voici la classe OAuthProperties et le fichier oauth.properties utilisés dans l'exemple :
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Object representation of an OAuth properties file. */ public class OAuthProperties { public static final String DEFAULT_OAUTH_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME = "oauth.properties"; /** The OAuth 2.0 Client ID */ private String clientId; /** The OAuth 2.0 Client Secret */ private String clientSecret; /** The Google APIs scopes to access */ private String scopes; /** * Instantiates a new OauthProperties object reading its values from the * {@code OAUTH_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME} properties file. * * @throws IOException IF there is an issue reading the {@code propertiesFile} * @throws OauthPropertiesFormatException If the given {@code propertiesFile} * is not of the right format (does not contains the keys {@code * clientId}, {@code clientSecret} and {@code scopes}) */ public OAuthProperties() throws IOException { this(OAuthProperties.class.getResourceAsStream(DEFAULT_OAUTH_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME)); } /** * Instantiates a new OAuthProperties object, reading its values from the given * properties file. * * @param propertiesFile the InputStream to read an OAuth Properties file. The * file should contain the keys {@code clientId}, {@code * clientSecret} and {@code scopes} * @throws IOException if there is an issue reading the {@code propertiesFile} * @throws OAuthPropertiesFormatException If the given {@code propertiesFile} * is not in the correct format (does not contain the keys {@code * clientId}, {@code clientSecret} and {@code scopes}) */ public OAuthProperties(InputStream propertiesFile) throws IOException { Properties oauthProperties = new Properties(); oauthProperties.load(propertiesFile); clientId = oauthProperties.getProperty("clientId"); clientSecret = oauthProperties.getProperty("clientSecret"); scopes = oauthProperties.getProperty("scopes"); if ((clientId == null) || (clientSecret == null) || (scopes == null)) { throw new OAuthPropertiesFormatException(); } } /** * @return the clientId */ public String getClientId() { return clientId; } /** * @return the clientSecret */ public String getClientSecret() { return clientSecret; } /** * @return the scopes */ public String getScopesAsString() { return scopes; } /** * Thrown when the OAuth properties file was not at the right format, i.e not * having the right properties names. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class OAuthPropertiesFormatException extends RuntimeException { } }
Le fichier oauth.properties, qui contient les identifiants OAuth 2.0 de votre application, est illustré dans l'exemple suivant.
Vous devez modifier les valeurs de ce fichier.
# Client ID and secret. They can be found in the APIs console. clientId=1234567890.apps.googleusercontent.com clientSecret=aBcDeFgHiJkLmNoPqRsTuVwXyZ # API scopes. Space separated. scopes=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks
L'ID client et le code secret du client OAuth 2.0 identifient l'application et permettent à l'API Tasks d'appliquer les filtres et les règles de quota définis pour l'application. L'ID client et le secret sont disponibles dans la console Google APIs. Une fois sur la console, l'utilisateur doit :
- Créez ou sélectionnez un projet.
- Activez l'API Tasks en définissant son état sur ON dans la liste des services.
- Sous Accès à l'API, créez un ID client OAuth 2.0 si vous ne l'avez pas encore fait.
- Assurez-vous que l'URL du gestionnaire de rappel de code OAuth 2.0 du projet est enregistrée/ajoutée à la liste d'autorisation dans URI de redirection. Par exemple, dans cet exemple de projet, l'utilisateur devra enregistrer
https://www.example.com/oauth2callbacksi l'application Web est diffusée à partir du domainehttps://www.example.com.

Gérer le code d'autorisation à partir du point de terminaison d'autorisation Google
Si l'utilisateur n'a pas encore autorisé l'application à accéder à ses tâches et qu'il est donc redirigé vers le point de terminaison d'autorisation OAuth 2.0 de Google, une boîte de dialogue d'autorisation s'affiche pour lui demander d'accorder l'accès à l'application :
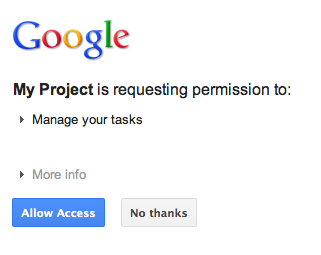
Après avoir accordé ou refusé l'accès, l'utilisateur est redirigé vers le gestionnaire de rappel de code OAuth 2.0 qui a été spécifié comme redirection/rappel lors de la construction de l'URL d'autorisation Google :
new GoogleAuthorizationRequestUrl(oauthProperties.getClientId(),
OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet.getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req), oauthProperties
.getScopesAsString()).build()Le gestionnaire de rappel de code OAuth 2.0 – OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet – gère la redirection depuis le point de terminaison Google OAuth 2.0. Il existe deux cas à gérer :
- L'utilisateur a accordé l'accès : la requête est analysée pour obtenir le code OAuth 2.0 à partir des paramètres d'URL.
- L'utilisateur a refusé l'accès : un message s'affiche.
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Servlet handling the OAuth callback from the authentication service. We are * retrieving the OAuth code, then exchanging it for a refresh and an access * token and saving it. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet extends HttpServlet { /** The name of the Oauth code URL parameter */ public static final String CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME = "code"; /** The name of the OAuth error URL parameter */ public static final String ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME = "error"; /** The URL suffix of the servlet */ public static final String URL_MAPPING = "/oauth2callback"; public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the "error" URL parameter String[] error = req.getParameterValues(ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking if there was an error such as the user denied access if (error != null && error.length > 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE, "There was an error: \""+error[0]+"\"."); return; } // Getting the "code" URL parameter String[] code = req.getParameterValues(CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking conditions on the "code" URL parameter if (code == null || code.length == 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, "The \"code\" URL parameter is missing"); return; } } /** * Construct the OAuth code callback handler URL. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = URL_MAPPING; String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo; } }
Échanger le code d'autorisation contre un jeton d'actualisation et un jeton d'accès
Ensuite, OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet échange le code Auth 2.0 contre un jeton d'actualisation et un jeton d'accès, le conserve dans le data store et redirige l'utilisateur vers l'URL PrintTaskListsTitlesServlet :
Le code ajouté au fichier est mis en surbrillance.
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Servlet handling the OAuth callback from the authentication service. We are * retrieving the OAuth code, then exchanging it for a refresh and an access * token and saving it. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet extends HttpServlet { /** The name of the Oauth code URL parameter */ public static final String CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME = "code"; /** The name of the OAuth error URL parameter */ public static final String ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME = "error"; /** The URL suffix of the servlet */ public static final String URL_MAPPING = "/oauth2callback"; /** The URL to redirect the user to after handling the callback. Consider * saving this in a cookie before redirecting users to the Google * authorization URL if you have multiple possible URL to redirect people to. */ public static final String REDIRECT_URL = "/"; /** The OAuth Token DAO implementation. Consider injecting it instead of using * a static initialization. Also we are using a simple memory implementation * as a mock. Change the implementation to using your database system. */ public static OAuthTokenDao oauthTokenDao = new OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the "error" URL parameter String[] error = req.getParameterValues(ERROR_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking if there was an error such as the user denied access if (error != null && error.length > 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE, "There was an error: \""+error[0]+"\"."); return; } // Getting the "code" URL parameter String[] code = req.getParameterValues(CODE_URL_PARAM_NAME); // Checking conditions on the "code" URL parameter if (code == null || code.length == 0) { resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, "The \"code\" URL parameter is missing"); return; } // Construct incoming request URL String requestUrl = getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req); // Exchange the code for OAuth tokens AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = exchangeCodeForAccessAndRefreshTokens(code[0], requestUrl); // Getting the current user // This is using App Engine's User Service, but the user should replace this // with their own user/login implementation UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService(); String email = userService.getCurrentUser().getEmail(); // Save the tokens oauthTokenDao.saveKeys(accessTokenResponse, email); resp.sendRedirect(REDIRECT_URL); } /** * Construct the OAuth code callback handler URL. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = URL_MAPPING; String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo; } /** * Exchanges the given code for an exchange and a refresh token. * * @param code The code gotten back from the authorization service * @param currentUrl The URL of the callback * @param oauthProperties The object containing the OAuth configuration * @return The object containing both an access and refresh token * @throws IOException */ public AccessTokenResponse exchangeCodeForAccessAndRefreshTokens(String code, String currentUrl) throws IOException { HttpTransport httpTransport = new NetHttpTransport(); JacksonFactory jsonFactory = new JacksonFactory(); // Loading the oauth config file OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); return new GoogleAuthorizationCodeGrant(httpTransport, jsonFactory, oauthProperties .getClientId(), oauthProperties.getClientSecret(), code, currentUrl).execute(); } }
Remarque : L'implémentation précédente utilise certaines bibliothèques App Engine, qui sont utilisées pour simplifier le processus. Si vous développez pour une autre plate-forme, réimplémentez l'interface UserService qui gère l'authentification des utilisateurs.
Lire les tâches de l'utilisateur et les afficher
L'utilisateur a accordé à l'application l'accès à ses tâches. L'application dispose d'un jeton d'actualisation enregistré dans le datastore accessible via OAuthTokenDao. Le servlet PrintTaskListsTitlesServlet peut désormais utiliser ces jetons pour accéder aux tâches de l'utilisateur et les afficher :
Le code ajouté au fichier est mis en surbrillance.
package com.google.oauthsample; import ... /** * Simple sample Servlet which will display the tasks in the default task list of the user. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class PrintTasksTitlesServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * The OAuth Token DAO implementation, used to persist the OAuth refresh token. * Consider injecting it instead of using a static initialization. Additionally, a * simple memory implementation is used as a mock. Change the implementation to * use your own database system. */ public static OAuthTokenDao oauthTokenDao = new OAuthTokenDaoMemoryImpl(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { // Getting the current user // This is using App Engine's User Service but you should replace this to // your own user/login implementation UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService(); User user = userService.getCurrentUser(); // If the user is not logged-in it is redirected to the login service, then back to this page if (user == null) { resp.sendRedirect(userService.createLoginURL(getFullRequestUrl(req))); return; } // Checking if we already have tokens for this user in store AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = oauthTokenDao.getKeys(user.getEmail()); // If we don't have tokens for this user if (accessTokenResponse == null) { OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); // Redirect to the Google OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint resp.sendRedirect(new GoogleAuthorizationRequestUrl(oauthProperties.getClientId(), OAuthCodeCallbackHandlerServlet.getOAuthCodeCallbackHandlerUrl(req), oauthProperties .getScopesAsString()).build()); return; } // Prints the user's task list titles in the response resp.setContentType("text/plain"); resp.getWriter().append("Task Lists titles for user " + user.getEmail() + ":\n\n"); printTasksTitles(accessTokenResponse, resp.getWriter()); } /** * Construct the request's URL without the parameter part. * * @param req the HttpRequest object * @return The constructed request's URL */ public static String getFullRequestUrl(HttpServletRequest req) { String scheme = req.getScheme() + "://"; String serverName = req.getServerName(); String serverPort = (req.getServerPort() == 80) ? "" : ":" + req.getServerPort(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); String servletPath = req.getServletPath(); String pathInfo = (req.getPathInfo() == null) ? "" : req.getPathInfo(); String queryString = (req.getQueryString() == null) ? "" : "?" + req.getQueryString(); return scheme + serverName + serverPort + contextPath + servletPath + pathInfo + queryString; } /** * Uses the Google Tasks API to retrieve a list of the user's tasks in the default * tasks list. * * @param accessTokenResponse The OAuth 2.0 AccessTokenResponse object * containing the access token and a refresh token. * @param output The output stream writer to write the task list titles to. * @return A list of the user's task titles in the default task list. * @throws IOException */ public void printTasksTitles(AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse, Writer output) throws IOException { // Initializing the Tasks service HttpTransport transport = new NetHttpTransport(); JsonFactory jsonFactory = new JacksonFactory(); OAuthProperties oauthProperties = new OAuthProperties(); GoogleAccessProtectedResource accessProtectedResource = new GoogleAccessProtectedResource( accessTokenResponse.accessToken, transport, jsonFactory, oauthProperties.getClientId(), oauthProperties.getClientSecret(), accessTokenResponse.refreshToken); Tasks service = new Tasks(transport, accessProtectedResource, jsonFactory); // Using the initialized Tasks API service to query the list of tasks lists com.google.api.services.tasks.model.Tasks tasks = service.tasks.list("@default").execute(); for (Task task : tasks.items) { output.append(task.title + "\n"); } } }
Les tâches de l'utilisateur s'affichent :
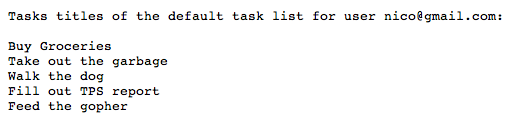
Exemple d'application
Vous pouvez télécharger le code de cet exemple d'application.