مقدمة
تشبه الرموز الشريطية الدوّارة الرموز الشريطية العادية، ولكنّها تتغير بشكل دوري. عادةً كل دقيقة، وتتم برمجة الوحدة الطرفية/القارئ لقبول الأحدث. يحد هذا الإجراء الأمني من المخاطر المرتبطة التقاط لقطة شاشة للرموز الشريطية، ولا سيما سرقة التذاكر أو التذاكر غير المصرّح بها إعادة البيع. يمكن أيضًا استخدام الرموز الشريطية الدوارة كإجراء احتياطي للأجهزة التي لا يمكنها ذلك الاستفادة من ميزة "الدفع الذكي" بسبب عدم توافقها مع تقنية NFC (أي عدم توفُّر الأجهزة أو أو إيقاف البرنامج).
مرجع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
للحصول على تفاصيل فنية حول تدوير الرموز الشريطية، يمكنك الاطلاع على
النوع RotatingBarcode.
مثال على الحمولة
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
الآليات الاحتياطية
على جهاز المستخدم، يتم استخدام آلية واحدة فقط لتحصيل القيمة في وقت معيّن، يعتمد ذلك على كيفية إعداد البطاقة وإمكانيات الجهاز. بترتيب الأولوية، يتم استخدام أنواع تحصيل القيمة التالية:
-
الدفع الذكي: في حال تحديد حمولة الدفع الذكي وما إذا كان الجهاز يتيح
NFC/HCE
- تجدر الإشارة إلى أنه يمكن للمستخدم إلغاء هذا الإجراء بالنقر على زر "عرض الرمز" الذي ستفرض عرض الرمز الشريطي/الرمز الشريطي الثابت الدوران.
- رمز شريطي دوّار: في حال تحديد حمولة بيانات رمز شريطي دوّار
- رمز شريطي ثابت: في حال تحديد حمولة بيانات رمز شريطي
يمكن أن يؤدي تحديد أحمال بيانات أساسية متعددة لتحصيل القيمة إلى إتاحة دعم جميع المستخدمين، ولكن آثار أمنية. وعلى وجه الخصوص، فإن استخدام رمز شريطي ثابت إن الإجراء الاحتياطي لاستخدام رمز شريطي دوّار ينفي معظم مزايا الأمان لاستخدام رموز شريطية دوّارة لن يظهر الرمز الاحتياطي الثابت للرمز الشريطي إلا في طرق عرض الويب أو على العملاء الذين لا يتيحون استخدام الرموز الشريطية بالتناوب. اعتبارًا من اليوم، نتوقع لجميع عملاء محفظة Google لإتاحة تدوير الرموز الشريطية.
حفظ التدفق
توفّر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Google Wallet API العديد من المسارات، منها:
- إنشاء صفوف الولاء في وقت توفير الوقت أو في وقت مبكر
- إرسال الكائنات الكاملة في JWT أو حفظ الكائنات قبلها ثم الإشارة إليها باستخدام المعرف في JWT
- تعديل العناصر بعد حفظها
يتوافق حقل rotatingBarcode المقترح مع جميع هذه المسارات، ومع ذلك، لتحسين مستوى الأمان، نقترح ما يلي:
-
عليك طلب واجهة برمجة تطبيقات
object:insertلإدراج البطاقة في خادم "محفظة Google" وضبط زر "الإضافة إلى محفظة Google" من أجل الإشارة إلى كائن معين باستخدام المعرّف في JWT. يضمن ذلك لا يشتمل JWT الناتج على المفتاح السري للرمز الشريطي الدوار. - استخدِم مفتاحًا سريًا لكلمة المرور لمرة واحدة تم تخصيصه لبطاقة واحدة.
- ومن المتوقع أن يكون المفتاح، ما لم يتم تحديثه، صالحًا لعمر البطاقة. لا نتوقّع أن يتم تحديث هذا المفتاح بأي تكرار أثناء مسار التشغيل الطبيعي.
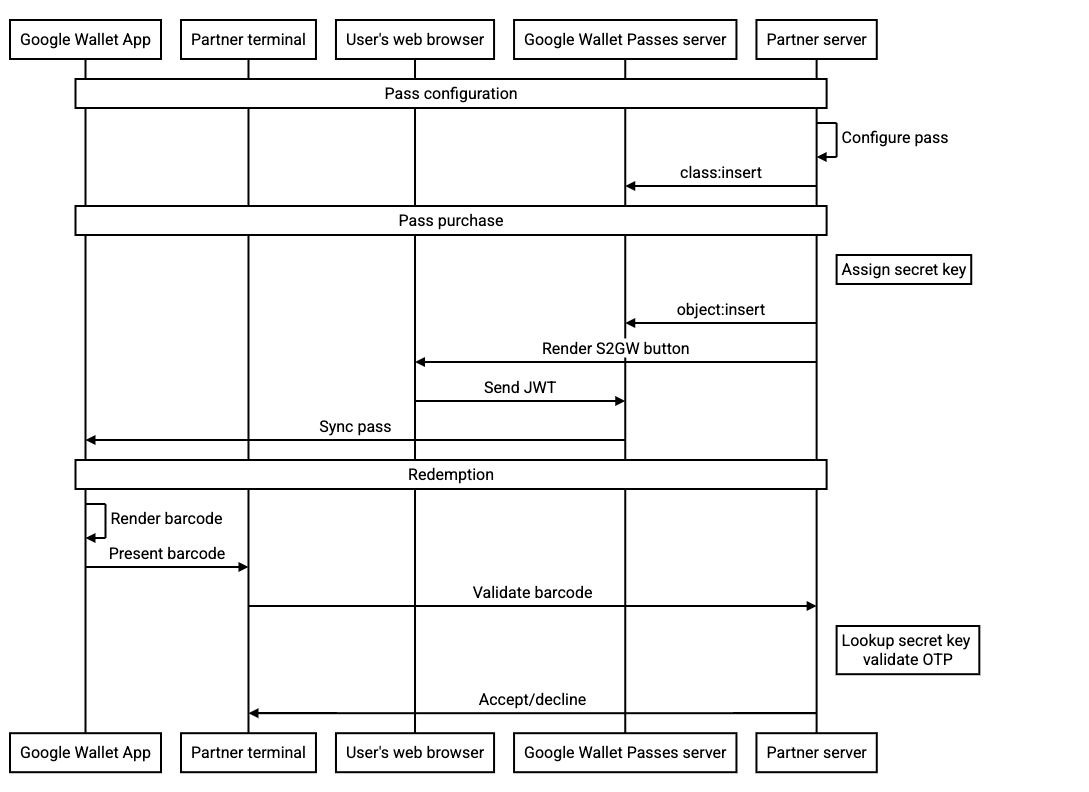
يوضح مخطط التسلسل التالي التدفق بين الجهات الفاعلة المختلفة بالنسبة إلى عملية الدمج النموذجية: