Google 文件專用的 Apps Script 可讓您從任何瀏覽器存取內容 標籤,
什麼是分頁?
Google 文件提供了組織層,稱為「分頁」。文件 使用者可以在單一文件中建立一或多個分頁,做法類似 試算表現在會顯示分頁每個分頁都有專屬的標題和 ID (附加 之後)。分頁標籤也可以有子分頁,也就是巢狀結構的分頁。 顯示在另一個分頁中
我們目前已推出子項分頁的 API 支援,但近期也將支援 UI。 您可以立即在程式碼中處理子分頁,以便在支援 UI 時啟動 因此您不需要進一步更新程式碼
存取分頁
可透過以下方式存取分頁屬性和內容:
Document.getTabs()、
會傳回 Tab 的清單後續章節會簡單介紹
Tab 類別;分頁類別說明文件
也提供更詳細的資訊
分頁屬性
您可以透過下列方法擷取分頁屬性:
Tab.getId() 和
Tab.getTitle()。
分頁內容
每個分頁中的文件內容均可透過
Tab.asDocumentTab()。
文件類別結構變更
一節介紹此指標的使用方式。
分頁階層
在 Google Apps Script 中,下層分頁會顯示在以下位置:
Tab.getChildTabs()。
如要存取所有分頁中的內容,必須穿越「樹狀圖」下層分頁
例如,假設文件包含分頁階層,如下所示:
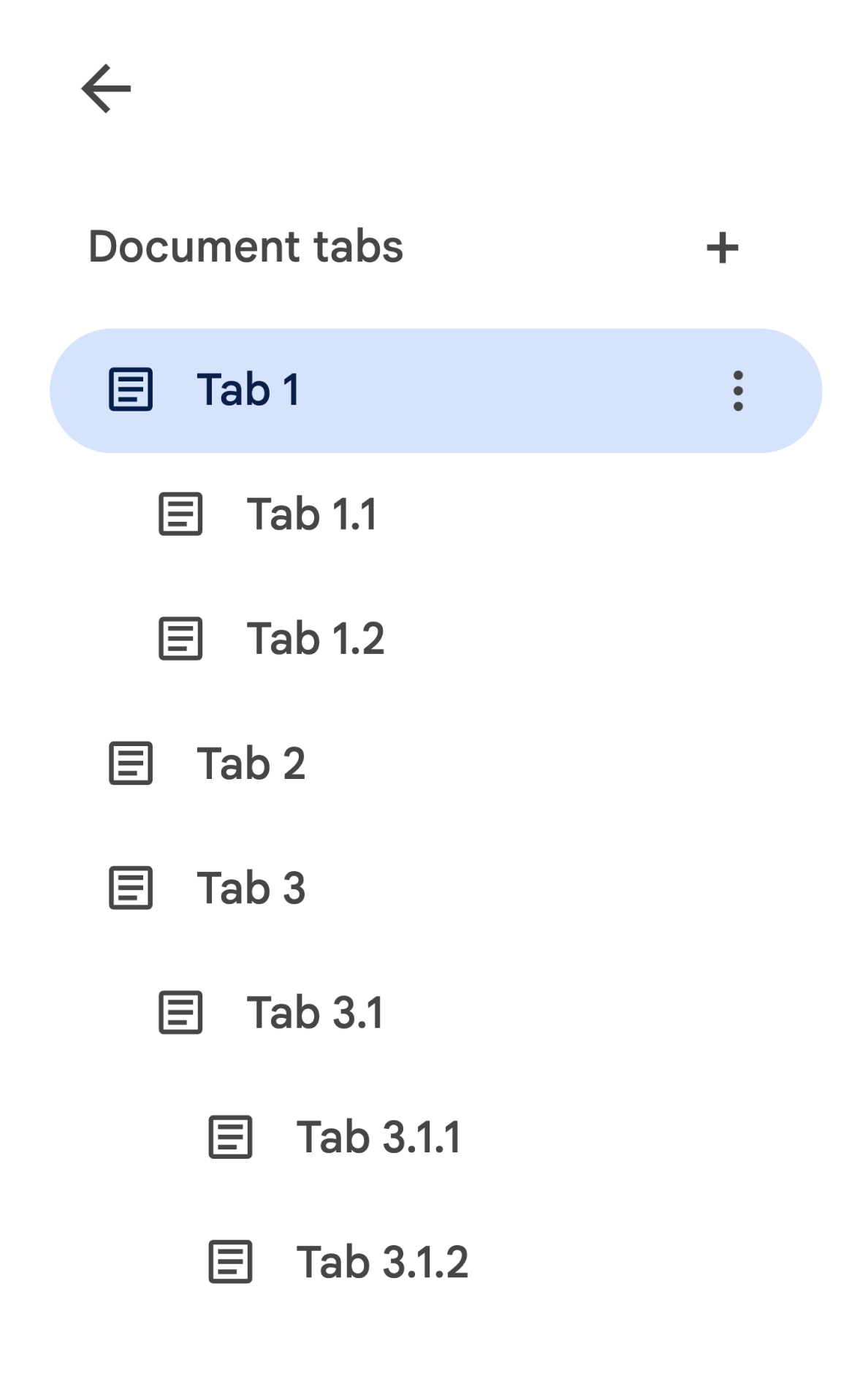
如要存取 Tab 3.1.2,請執行下列步驟:
// Print the ID of Tab 3.1.2. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const tab = doc.getTabs()[2].getChildTabs()[0].getChildTabs()[1]; console.log(tab.getId());
請參閱後續章節中的程式碼範例區塊,取得 將焦點移至文件中的所有分頁
其他擷取分頁的方式
您還可以使用其他兩種方式擷取分頁:
Document.getTab(tabId): 傳回含有指定 ID 的 Tab。Document.getActiveTab(): 傳回使用者使用中的分頁。僅適用於 「繫結」至文件的指令碼。 則會在後續章節中詳細說明。
文件類別結構變更
文件過去並沒有分頁概念,因此文件類別 公開方法,以便直接存取及修改文件的文字內容。 以下方法可分為以下類別:
Document.addBookmark(position)Document.addFooter()Document.addHeader()Document.addNamedRange(name, range)Document.getBody()Document.getBookmark(id)Document.getBookmarks()Document.getFooter()Document.getFootnotes()Document.getHeader()Document.getNamedRangeById(id)Document.getNamedRanges()Document.getNamedRanges(name)Document.newPosition(element, offset)Document.newRange()
有了額外的分頁結構階層,這些方法就不再出現
以語意方式呈現文件中所有分頁的文字內容。文字
內容將在另一個圖層中上述所有
文字方法可透過 DocumentTab 存取。
Document 類別的這些現有方法會存取或修改內容
從使用中的分頁 (在指令碼中繫結至
特定文件) 或第一個分頁 (如果無法使用有效的分頁)。
存取特定分頁中的文字內容
建議您使用 Document 以外的文字方法
而應改用 DocumentTab 類別所提供的方法 (
提供的管道
Tab.asDocumentTab()敬上
方法)。例如:
// Print the text from the body of the active tab. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const documentTab = doc.getActiveTab().asDocumentTab(); const body = documentTab.getBody(); console.log(body.getText());
使用者選取項目有所變更
文字選取方法
Document 類別提供 getter 和 setter 來管理文字內容中的位置
使用者在作用中的文件中選取的動作這些方法的運作方式
執行指令碼的使用者使用中分頁的狀態。
Document.getCursor(): 傳回使用者在使用中分頁的遊標位置。Document.getSelection(): 系統會傳回使用中分頁中的使用者選取範圍。Document.setCursor(position): 設定使用者在使用中文件中的遊標位置。如果位置在 使用者使用中的分頁也會切換至相關聯的分頁 與該位置重疊。Document.setSelection(range): 設定使用者在使用中的文件中選取範圍。如果範圍是 使用者使用中的分頁也會切換至相關聯的分頁 符合該範圍
分頁選取方法和用途
推出分頁之後,如要查看及設定 執行指令碼的使用者可使用下列方法完成:
Document.getActiveTab(): 傳回使用者在使用中文件中正在使用的Tab。Document.setActiveTab(tabId): 使用者在目前文件中選取的Tab設為分頁,其中包含 指定的 ID
使用者全面「選擇」包含使用中分頁 以及目前遊標位置或選取範圍。兩者 您必須先明確修改 使用者使用中的分頁,或使用使用者使用中的分頁。
您可使用
Document.setActiveTab(tabId)。
或者,您也可以撥打
Document.setCursor(position)敬上
或 Document.setSelection(range)
如果分頁處於閒置狀態中的 Position 或 Range,則會讓該分頁
有效。
如果指令碼的預期行為是使用使用者使用中的分頁,
但沒有變更
Document.setActiveTab(tabId)敬上
則不需要。
Document.getCursor()敬上
和 Document.getSelection()
方法會在使用中的分頁運作
執行指令碼的使用者
請注意,文件不支援選取多個分頁或多個分頁
在不同標籤中的位置或範圍因此,使用
Document.setActiveTab(tabId)敬上
會清除先前的遊標位置或選取範圍。
特定分頁的位置和範圍方法
具體分頁的作用是說明
《Position》和《Range》。也就是遊標位置或選取範圍
只有在指令碼知道位置或
範圍內。
方法是使用
DocumentTab.newPosition(element, offset) 和
DocumentTab.newRange()
方法,即可建構定位特定
呼叫該方法的 DocumentTab。相對地
Document.newPosition(element, offset)敬上
和 Document.newRange()
會建立位置或範圍,並指定使用中分頁 (或第一個
定位點)。
請參閱後續章節中的程式碼範例區塊,取得 如何搭配選取項目
常見的分頁使用模式
以下程式碼範例說明與分頁互動的各種方式。
朗讀文件中所有分頁的分頁內容
先前執行過的程式碼在分頁功能之前完成遷移,現在仍能支援
藉由掃遍分頁樹狀結構,然後從 Tab 和
DocumentTab,而不是 Document。下列部分程式碼範例說明
列印文件每個分頁的文字內容。這個分頁
週遊程式碼可用於許多其他不關心用途
分頁的實際結構
/** Logs all text contents from all tabs in the active document. */
function logAllText() {
// Generate a list of all the tabs in the document, including any
// nested child tabs. DocumentApp.openById('abc123456') can also
// be used instead of DocumentApp.getActiveDocument().
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc);
// Log the content from each tab in the document.
for (const tab of allTabs) {
// Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab object.
const documentTab = tab.asDocumentTab();
// Get the body from the given DocumentTab.
const body = documentTab.getBody();
// Get the body text and log it to the console.
console.log(body.getText());
}
}
/**
* Returns a flat list of all tabs in the document, in the order
* they would appear in the UI (i.e. top-down ordering). Includes
* all child tabs.
*/
function getAllTabs(doc) {
const allTabs = [];
// Iterate over all tabs and recursively add any child tabs to
// generate a flat list of Tabs.
for (const tab of doc.getTabs()) {
addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs);
}
return allTabs;
}
/**
* Adds the provided tab to the list of all tabs, and recurses
* through and adds all child tabs.
*/
function addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs) {
allTabs.push(tab);
for (const childTab of tab.getChildTabs()) {
addCurrentAndChildTabs(childTab, allTabs);
}
}
朗讀文件第一個分頁的分頁內容
這與讀取所有分頁的方式類似。
/**
* Logs all text contents from the first tab in the active
* document.
*/
function logAllText() {
// Generate a list of all the tabs in the document, including any
// nested child tabs.
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc);
// Log the content from the first tab in the document.
const firstTab = allTabs[0];
// Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab object.
const documentTab = firstTab.asDocumentTab();
// Get the body from the DocumentTab.
const body = documentTab.getBody();
// Get the body text and log it to the console.
console.log(body.getText());
}
更新第一個分頁中的分頁內容
下列部分程式碼範例說明如何在 更新。
/** Inserts text into the first tab of the active document. */
function insertTextInFirstTab() {
// Get the first tab's body.
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const firstTab = doc.getTabs()[0];
const firstDocumentTab = firstTab.asDocumentTab();
const firstTabBody = firstDocumentTab.getBody();
// Append a paragraph and a page break to the first tab's body
// section.
firstTabBody.appendParagraph("A paragraph.");
firstTabBody.appendPageBreak();
}
更新使用中或所選分頁中的分頁內容
下列部分程式碼範例說明如何在 更新。
/**
* Inserts text into the active/selected tab of the active
* document.
*/
function insertTextInActiveTab() {
// Get the active/selected tab's body.
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const activeTab = doc.getActiveTab();
const activeDocumentTab = activeTab.asDocumentTab();
const activeTabBody = activeDocumentTab.getBody();
// Append a paragraph and a page break to the active tab's body
// section.
activeTabBody.appendParagraph("A paragraph.");
activeTabBody.appendPageBreak();
}
在使用中的分頁中設定遊標位置或選取範圍
以下部分程式碼範例說明如何更新遊標位置 使用者使用中分頁內的選取範圍這僅適用於 指令碼
/**
* Changes the user's selection to select all tables within the tab
* with the provided ID.
*/
function selectAllTables(tabId) {
const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument();
const tab = doc.getTab(tabId);
const documentTab = tab.asDocumentTab();
// Build a range that encompasses all tables within the specified
// tab.
const rangeBuilder = documentTab.newRange();
const tables = documentTab.getBody().getTables();
for (let i = 0; i < tables.length; i++) {
rangeBuilder.addElement(tables[i]);
}
// Set the document's selection to the tables within the specified
// tab. Note that this actually switches the user's active tab as
// well.
doc.setSelection(rangeBuilder.build());
}
設定使用中或所選分頁
下列部分程式碼範例說明如何變更使用者使用中的分頁。 這只適用於繫結指令碼。
/** * Changes the user's selected tab to the tab immediately following * the currently selected one. Handles child tabs. * *Only changes the selection if there is a tab following the * currently selected one. */ function selectNextTab() { const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); const activeTab = doc.getActiveTab(); // Find the index of the currently active tab. let activeTabIndex = -1; for (let i = 0; i < allTabs.length; i++) { if (allTabs[i].getId() === activeTab.getId()) { activeTabIndex = i; } } // Update the user's selected tab if there is a valid next tab. const nextTabIndex = activeTabIndex + 1; if (nextTabIndex < allTabs.length) { doc.setActiveTab(allTabs[nextTabIndex].getId()); } }
