This document answers common questions about RCS for Business data security and associated topics.
RBM is a messaging platform that businesses use to send One-Time Passwords (OTPs) and engage customers in dialog about transactions, customer service, promotions, and more. Google provides an RBM API to deliver messages between businesses and end users through Google servers.
Typically, businesses work with messaging partners (including aggregators, Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers, carriers, and other RCS solution providers) who connect to the Google API to build and maintain RBM agents on the business's behalf. Partners who want to use RBM through the API or the Business Communications Developer Console must agree to Google's RBM Terms of Service and Acceptable Use Policy. Because Google is acting as a Data Processor, partners are also governed by Google's Data Processing Addendum.
Certification and compliance
Is RBM certified by any third parties?
RBM and Google's RCS infrastructure are independently audited on an annual basis to ensure compliance with widely recognized quality and data security standards. Our services hold ISO 27001, SOC 2, and SOC 3 certifications. Contact your account manager if you'd like copies of the certificates.
Is RBM compliant with the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
While Google's processing of data as a processor is GDPR compliant, GDPR compliance is the responsibility of the individual business using the platform. As with most marketing channels, businesses are responsible for their own processes around data collection, data usage, and data storage.
Is RBM compliant with EU Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2)?
Yes, RBM is compliant with PSD2, which requires Strong Customer Authentication (SCA). Because RBM is associated with the end user's verified phone number and SIM card, a One-Time Password (OTP) sent using RBM constitutes a compliant SCA "possession element" as described by the European Banking Authority.
Is RBM compliant with HIPAA?
No, RBM is not compliant with HIPAA.
Restricted content and use cases
What types of healthcare use cases are supported in RBM?
RBM supports healthcare-related use cases, provided that Protected Health Information (PHI) is excluded from such messages. For example, sending an appointment reminder or a notification with a link to log in to a secure patient portal are supported. Messages containing PHI or promoting restricted healthcare products are prohibited. The list of restricted healthcare-related products and services can be found in the Acceptable Use Policy.
Data processing
What does it mean for Google to be a Data Processor?
With RBM, Google serves as a Data Processor and the business or partner serves as a Data Controller. The Data Processing Addendum (DPA) explains that Google is a Data Processor and it governs the terms for handing data on behalf of businesses and partners.
Does the DPA apply to all end users who interact with an RBM agent?
Yes, the DPA applies to all end users and their data. Google built the RBM platform to comply with the DPA and ensure that all end users receive the same high level of data security.
Message storage and encryption
What data is stored on the end user's device?
Metadata about RBM agents and the messages exchanged with them are stored on the end user's device. These messages may include personal information shared with an RBM agent.
How is the agent's "region" related to message storage?
The region that a partner specifies during agent setup tells RBM where the agent is located (North America, Europe, or Asia Pacific). Google uses this information to determine where message data should be stored and to optimize the routing of message traffic to the agent.
Within the specified region, data may move between Google's multiple data centers for resilience, scalability, and as required for a global messaging product. For security and privacy reasons, Google doesn't disclose the specific locations of these data centers. (Refer to the DPA for more information on data center and network security.)
In the exceptional event of a complete regional outage, Google may temporarily process message traffic in another region to maintain service availability. This failover is a temporary measure designed to prevent a total service disruption and ensure message delivery.
What is the messaging architecture and flow for RCS for Business? Which elements are encrypted?
Messages sent between businesses and end users are encrypted between the end user's device and Google's servers and between Google's servers and the messaging partner through Google's RCS Business Messaging API.
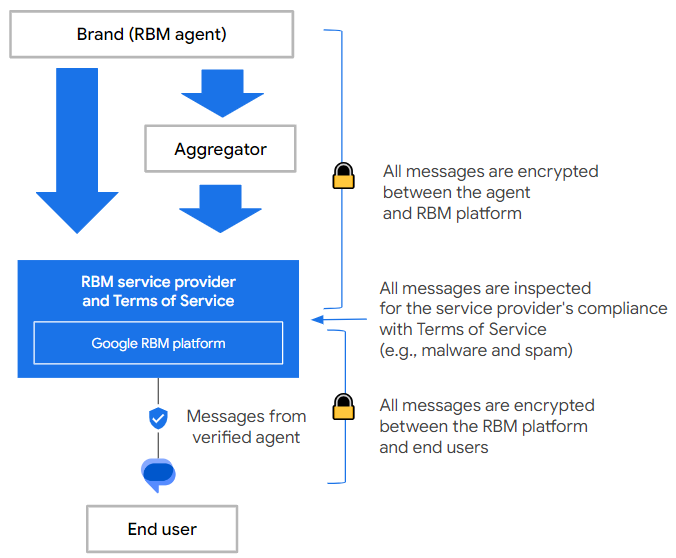
Messages are encrypted across Google's network using keys that are only accessible to specific service components. The encryption keys enable inspection by Google systems for policy compliance.
Refer to How it works for an overview of the end-to-end messaging flow and the roles of all parties involved.
Are stored messages encrypted?
Storage on Google servers
Agent-to-person (A2P) messages are held on Google servers if the recipient is offline. The developer may choose to revoke these messages and send them over another channel. Person-to-application (P2A) messages are held on Google servers if the agent is unable to receive them. Google holds these messages for seven days before dropping them.
Messages stored on Google servers are encrypted at rest.
Google's access to stored messages is only available in the following cases:
- Google may ephemerally process the content of messages sent by businesses to detect and prevent spam and abuse, and may use those signals to train AI models to improve spam prevention and detection. To learn more about data handling for spam reports, see Does Google ever read messages between businesses and end users?
- Stored messages may be shared with external law enforcement agencies under the terms of Google's obligations to meet applicable law. Refer to Google's transparency report for more information.
For how long are messages stored?
Storage on Google servers
- RBM agent assets (logo, name, description, etc): Persistently stored in global Google storage.
- Person-to-agent messages (P2A messages): Held on a store-and-forward basis for no longer than seven days. As soon as the RBM agent receives and acknowledges the message, it's deleted.
- Agent-to-person messages (A2P messages): Held until delivered, for up to 30 days. Prior to the 30-day limit, agents can revoke undelivered messages, which are removed from the delivery queue and deleted from Google servers. If a delivered message contains media files, these files are stored for 60 days. A2P messages may be held on Google servers for 14 days after delivery to detect and prevent spam and abuse.
Storage on mobile devices
Messages on the end user's device are stored there until the end user deletes them or changes the storage mechanism.
Is RBM end-to-end encrypted?
No, RBM doesn't offer end-to-end encryption. This is why you won't see a lock icon displayed within the Messages UI for RBM conversations. However, RBM uses point-to-point encryption to protect messages as they travel between user devices and Google's servers, as well as between Google's servers and messaging partners.
What type of encryption is used for RBM, and can a business control the associated keys?
RBM uses point-to-point encryption to protect messages as they travel between devices and Google's servers. Businesses cannot control the encryption keys. Google manages these keys for security purposes, including scanning for malicious content like phishing and malware URLs, to protect users from spam. For more details on message access and review, see Does Google ever read messages between businesses and end users?
Which entities have access to RBM messages? What responsibility do messaging partners, businesses, and carriers have to ensure data security?
RBM is a transit technology powered by Google. RBM moves messages between end users and the agents that represent businesses. These agents are built and operated by messaging partners, businesses, and in some cases carriers. The entities that operate RBM agents, and, in some cases, carriers, have access to RBM message content for message delivery and other purposes. Google also has access to RBM message content to apply spam and abuse protections.
Messaging partners, businesses, and carriers are individually responsible for complying with all relevant data security, privacy, and local regulatory requirements.
RBM API security
Can Google obtain the access tokens sent by the OAuth provider?
No, Google never obtains the access tokens sent by the OAuth provider during user authentication. OAuth 2.0 uses the Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) to secure the authentication flow.
How is data encrypted between an RBM developer and Google?
Developers access the RBM API over HTTPS, the global standard for secure web transactions. The RBM API supports TLS 1.3 with AES 256 and SHA384 ciphers.
Run the following command to check the certificate chain, TLS version, and supported ciphers:
openssl s_client -connect rcsbusinessmessaging.googleapis.com:443
Phone number verification
To maintain the security of Google's Messages app, how does Google verify that a phone number still belongs to its original user?
Initial verification of phone number: Google uses a variety of techniques to identify the end user's phone number (i.e., their MSISDN or Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number). These techniques include direct API integration with carriers, mobile-originated SMS, and asking the end user to enter their phone number. Once the phone number is identified, Google may send an invisible One-Time Password (OTP) SMS to verify it.
Maintaining security after initial verification: When a carrier has a direct API integration, they can periodically send a SIM/MSISDN deactivation feed to Google to disable RCS and thereby disable RBM for phone numbers that are no longer active. Google may also monitor changes in phone number ownership through device signals like SIM removal and SIM activity and by periodically reverifying the phone number.
Privacy and security
What reporting does Google do on RBM agents?
Google has internal reporting on the gross number of end users, messages, and responses for each agent based on the last 28 days' data. Google uses this data for diagnostics, system improvements, and to generate billing reports for carriers. Message contents are not stored for reporting purposes. Beyond 28 days, Google stores only aggregate reporting data; there is no time limit on this storage. Any aggregate data shared externally has a Time to Live (TTL) lifespan of 63 days.
The billing reports and activity logs that carriers receive are stored for 30 days on Google's servers. Carrier partners may choose to download these files and hold them for as long as they deem necessary.
Does Google use end user data outside of RBM?
Google uses end user data only to provide and improve the RBM service, as stated in section 5.2 of the DPA.
For example, Google may do the following with end user data:
- Detect and prevent spam and fraud.
- Share unaggregated billing reports and activity logs with carrier partners.
- Measure and improve RBM performance for end users and businesses.
As part of this effort, Google shares aggregated data with partners so they can improve the messaging experience. See What reporting does Google do on RBM agents? for details.
But Google will not do the following with end user data:
- Perform ad targeting based on message contents.
- Share message contents with any competitors or third parties, with the exception of law enforcement agencies as required by applicable law.
Does Google ever read messages between businesses and end users?
Google spam detection and prevention may scan the content of messages sent by businesses for violations against the Acceptable Use Policy. Google doesn't have access to the contents of any messages sent by users to businesses. However, when the end user reports a conversation as spam:
- The sender's information and recent messages sent by the business will go to Google and may go to the user's carrier.
- Google spam detection and prevention may ephemerally process the contents of messages sent by businesses, and use those signals to train AI models to improve spam detection and prevention.
- Google employees and contractors may review spam information to help improve Google's protections against spam and abuse. Human reviewers have restricted and audited access to this information for 30 days. The end user's phone number is redacted for the purposes of spam review.
What information about end users does Google provide to the business?
To enable an RBM conversation, Google shares the end user's telephone number with the business to identify the end user in the conversation. No other personal information is shared with the business.
In the Acceptable Use Policy, does the Privacy and Security section limit a business's ability to collect and use information about its own customers?
Google doesn't intend to restrict a business's ability to serve its customers. A conversation between an end user and a business that is created through the RBM API can be stored by the business, according to the terms of its own privacy policy.
In the RBM Terms of Service, what does the following mean? "You will obtain and maintain any required consents necessary to permit the processing of personal data under these RBM Terms."
Google expects all businesses using RBM to adhere to the relevant data and security regulations (such as GDPR) and to supply a privacy policy that clarifies how they use and/or share end user data. A developer must provide their privacy policy for an agent to be considered for launch review.
How does RBM protect end users from malicious URLs?
To protect end users, RBM uses Google Safe Browsing to scan links in messages and automatically block messages containing malware or phishing links. If a message containing a link is not blocked by Safe Browsing, the messaging app may generate a thumbnail preview to show where the link leads.
Google's cooperation when a business is audited
Our business is subject to regulations and may be audited. Will Google comply?
It's the business's responsibility to ensure their company meets the relevant regulations. Google will only respond to law enforcement and regulator inquiries in accordance with applicable law.
Incident response
How does Google handle data breaches?
Refer to section 7.2 Data Incidents in the DPA.
Unsupported network capabilities
What network capabilities are not supported by RBM?
- Custom headers to allow firewall pass-throughs
- Classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) block ranges from Google's services