جستجوی ابری گوگل به کارمندان یک شرکت اجازه میدهد تا اطلاعاتی مانند اسناد داخلی، فیلدهای پایگاه داده و دادههای CRM را از مخازن داده داخلی شرکت جستجو و بازیابی کنند.
نمای کلی معماری
شکل ۱ تمام اجزای کلیدی پیادهسازی جستجوی ابری گوگل را نشان میدهد:
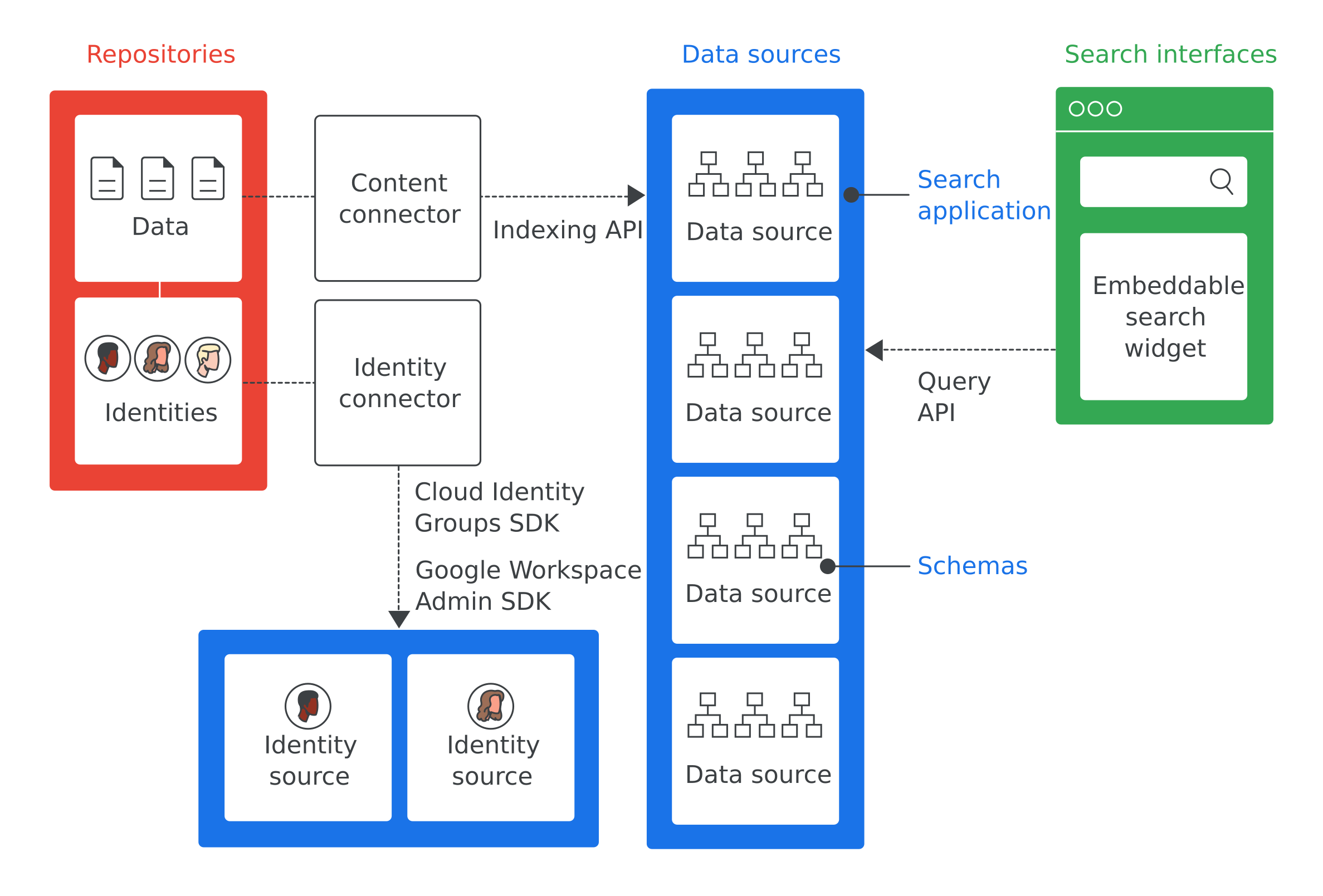
در اینجا تعاریف مهمترین اصطلاحات از شکل 1 آمده است:
- مخزن
- نرمافزاری که توسط یک سازمان برای ذخیره دادههایش استفاده میشود، مانند پایگاه دادهای که برای ذخیره اطلاعات کارمندان استفاده میشود.
- منبع داده
- دادههایی از مخزنی که در جستجوی ابری گوگل ایندکس و ذخیره شده است.
- رابط جستجو
- رابط کاربری که توسط کارمندان برای جستجوی یک منبع داده استفاده میشود. یک رابط جستجو میتواند برای استفاده در هر دستگاهی، از تلفن همراه گرفته تا رایانه رومیزی، توسعه داده شود. ویجت جستجوی ارائه شده توسط گوگل همچنین میتواند برای فعال کردن جستجو در وبسایتهای داخلی شما مستقر شود. شناسه برنامه جستجو با هر جستجو درج میشود تا اطمینان حاصل شود که زمینه آن جستجو، مانند یک ابزار خدمات مشتری، مشخص است. سایت cloudsearch.google.com حاوی یک رابط جستجو است.
- جستجوی برنامه
- گروهی از تنظیمات که وقتی با رابط جستجو مرتبط میشوند، اطلاعات زمینهای در مورد جستجوها ارائه میدهند. اطلاعات زمینهای شامل منابع داده و رتبهبندی جستجو است که باید برای جستجو با استفاده از آن رابط استفاده شود. برنامههای جستجو همچنین شامل مکانیسمهایی برای فیلتر کردن نتایج هستند و گزارشدهی در مورد منابع داده، مانند تعداد پرسوجوهای انجام شده در یک دوره زمانی معین را فعال میکنند.
- طرحواره
- یک ساختار داده که نحوه نمایش دادههای موجود در مخزن یک سازمان برای جستجوی ابری گوگل (Google Cloud Search) را مشخص میکند. یک طرحواره (schema) تجربه جستجوی ابری گوگل (Google Cloud Search) توسط کارمند، مانند نحوه فیلتر کردن و نمایش موارد، را تعریف میکند.
- رابط محتوا
- یک برنامه نرمافزاری که برای پیمایش دادهها در مخزن سازمانی و پر کردن یک منبع داده استفاده میشود.
- رابط هویت
- یک برنامه نرمافزاری که برای همگامسازی هویتهای سازمانی (کاربران و گروهها) با هویتهای مورد نیاز جستجوی ابری گوگل استفاده میشود.
موارد استفاده از جستجوی ابری گوگل
در اینجا چند مورد استفاده وجود دارد که ممکن است توسط جستجوی ابری گوگل حل شوند:
- کارمندان به راهی برای یافتن سیاستهای شرکت، اسناد و محتوای نوشتهشده توسط سایر کارمندان نیاز دارند.
- اعضای تیم خدمات مشتری باید اسناد مربوط به عیبیابی را برای ارسال به مشتریان پیدا کنند.
- کارمندان باید اطلاعات داخلی در مورد پروژههای شرکت را پیدا کنند.
- یک نماینده فروش میخواهد وضعیت تمام مشکلات پشتیبانی یک مشتری خاص را مشاهده کند.
- کارمندان میخواهند تعریفی برای یک اصطلاح خاص شرکت داشته باشند.
اولین قدم در پیادهسازی جستجوی ابری گوگل، شناسایی موارد استفادهای است که توسط جستجوی ابری گوگل حل میشوند.
جستجوی ابری گوگل را پیادهسازی کنید
به طور پیشفرض، جستجوی ابری گوگل (Google Cloud Search) دادههای فضای کاری گوگل (Google Workspace) مانند اسناد و صفحات گسترده گوگل را فهرستبندی میکند. شما نیازی به پیادهسازی جستجوی ابری گوگل برای دادههای فضای کاری گوگل (Google Workspace) ندارید. با این حال، برای دادههای غیر از فضای کاری گوگل، مانند دادههای ذخیره شده در یک پایگاه داده شخص ثالث، سیستمهای فایل مانند Windows Fileshare، OneDrive یا پورتالهای اینترانت مانند Sharepoint، باید جستجوی ابری گوگل را پیادهسازی کنید. مراحل زیر برای پیادهسازی جستجوی ابری گوگل برای سازمان شما ضروری است.
- یک مورد استفاده که جستجوی ابری گوگل به حل آن کمک میکند را تعیین کنید.
- مخازنی را که دادههای مربوط به مورد استفاده را در خود جای دادهاند، شناسایی کنید.
- سیستمهای هویتی مورد استفاده توسط شرکت شما برای مدیریت دسترسی به دادهها در هر مخزن را شناسایی کنید.
- دسترسی به API جستجوی ابری گوگل را پیکربندی کنید .
- یک منبع داده به جستجوی ابری گوگل اضافه کنید .
- برای هر منبع داده، یک طرحواره ایجاد و ثبت کنید .
- بررسی کنید که آیا رابط محتوایی برای مخزن شما موجود است یا خیر. برای مشاهده فهرست رابطهای از پیش ساخته شده، به فهرست رابطهای جستجوی ابری مراجعه کنید. اگر رابط محتوایی موجود است، به مرحله ۹ بروید.
- یک رابط محتوا برای دسترسی به دادهها در هر مخزن ایجاد کنید و آن را در یک منبع داده جستجوی ابری فهرستبندی کنید.
- مشخص کنید که آیا به یک رابط هویت نیاز دارید یا خیر. اگر به یک رابط هویت نیاز ندارید، به مرحله ۱۱ بروید.
- یک رابط هویت ایجاد کنید تا هویتهای مخزن یا سازمان خود را به هویتهای گوگل نگاشت کنید.
- برنامههای جستجو را تنظیم کنید .
- یک رابط جستجو برای انجام جستجوهای پرسوجو ایجاد کنید .
- رابطها و رابطهای جستجوی خود را مستقر کنید. اگر از یک رابط از پیش ساخته شده استفاده کردهاید، دستورالعملهای مربوط به رابط را برای دریافت و استقرار آن دنبال کنید. رابطهای موجود در فهرست رابطهای جستجوی Google Cloud فهرست شدهاند.
مراحل بعدی
در اینجا چند گام بعدی که میتوانید بردارید، آورده شده است:
- آموزش شروع به کار با جستجوی ابری گوگل را امتحان کنید.
- موارد استفادهای را که برای آنها از جستجوی ابری گوگل استفاده خواهید کرد، تعیین کنید.
- مخازن مربوط به این موارد استفاده را شناسایی کنید.
- هرگونه سیستم هویتی مورد استفاده توسط مخازن خود را شناسایی کنید.
- ادامه پیکربندی دسترسی به API جستجوی ابری گوگل .
