Z tego dokumentu dowiesz się, jak przestrzegać stylu Glass i wdrożyć typowe sprawdzone metody dotyczące interfejsu, które pomogą Ci zoptymalizować wrażenia użytkowników. Obejmuje on te elementy interfejsu:
Motyw
Motyw Glass, którego zalecamy, ma te cechy:
- Pokazuje aktywność na pełnym ekranie bez paska działań.
- Stosuje jednolicie czarne tło.
- Ustawia jaśniejszy kolor efektu krawędzi kolorów.
- Stosuje biały kolor tekstu.
Oto zalecane ustawienia motywu w Google Glass:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.NoActionBar"> <item name="android:windowBackground">@android:color/black</item> <item name="android:colorEdgeEffect">@android:color/white</item> <item name="android:textColor">@android:color/white</item> </style>
Układy XML
Oto 2 podstawowe układy kart, które mogą być uwzględniane we fragmentach:
Układ główny
Ten układ określa sugerowane dopełnienie standardowe i stopkę karty. Umieść własne widoki w pustym polu FrameLayout.
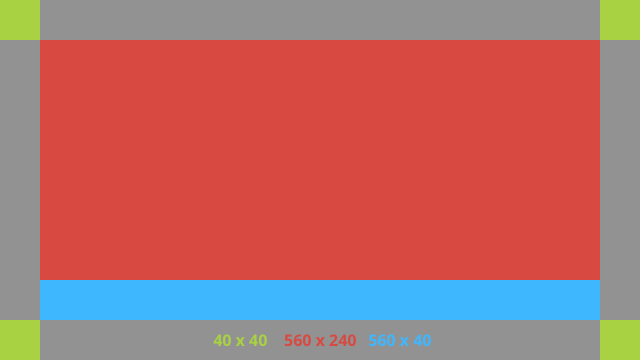
Oto przykładowy układ XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/body_layout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@id/footer"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent">
<!-- Put your widgets inside this FrameLayout. -->
</FrameLayout>
<!-- The footer view will grow to fit as much content as possible while the
timestamp view keeps its width. If the footer text is too long, it
will be ellipsized with a 40dp margin between it and the timestamp. -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/footer"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/timestamp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/timestamp"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textAlignment="viewEnd"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Układ kolumny po lewej stronie
Ten układ określa kolumnę z jedną trzecią i trzecią szerokością w formacie 2 klasach FrameLayout, w których możesz umieszczać widoki danych. Aby dowiedzieć się więcej, zapoznaj się z poniższym zdjęciem.
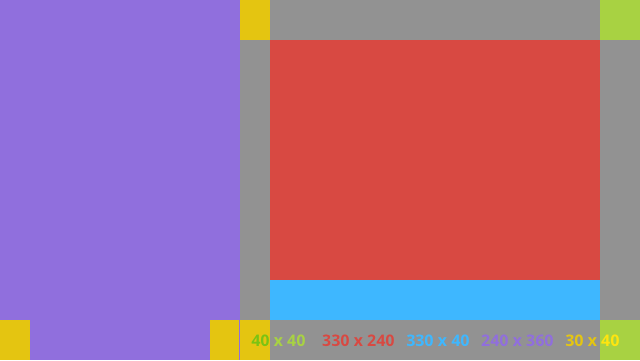
Oto przykładowy układ XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/left_column"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#303030"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent=".333">
<!-- Put widgets for the left column inside this FrameLayout. -->
</FrameLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/right_column"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/glass_card_two_column_margin"
android:layout_marginStart="@dimen/glass_card_two_column_margin"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/glass_card_two_column_margin"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@id/footer"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/left_column"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent">
<!-- Put widgets for the right column inside this FrameLayout. -->
</FrameLayout>
<!-- The footer view will grow to fit as much content as possible while the
timestamp view keeps its width. If the footer text is too long, it
will be ellipsized with a 40dp margin between it and the timestamp. -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/footer"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/timestamp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/left_column" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/timestamp"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/glass_card_margin"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textAlignment="viewEnd"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Wymiary standardowe
Wykonaj te czynności w połączeniu z poprzednimi układami lub własnymi układami, aby utworzyć plik zgodny ze stylem Glass. Utwórz ten plik jako res/values/dimens.xml w projekcie Android.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <!-- The recommended margin for the top, left, and right edges of a card. --> <dimen name="glass_card_margin">40dp</dimen> <!-- The recommended margin between the bottom of the card and the footer. --> <dimen name="glass_card_footer_margin">50dp</dimen> <!-- The recommended margin for the left column of the two-column card. --> <dimen name="glass_card_two_column_margin">30dp</dimen> </resources>
Menu
Sugerujemy użycie właściwości RecyclerView do utworzenia menu. Powinny być one oparte na standardowym pliku menu Androida w zasobach projektu Android Studio. Android umożliwia zastąpienie standardowego tworzenia menu i zastąpienie go implementacją. Aby to zrobić:
- Utwórz układ za pomocą
RecyclerViewi ustaw go jako widok dlaActivity. - Ustaw
RecyclerViewi jego adapter, aby użyć nowo utworzonego zbioru elementów menu. - Zastąp metodę
onCreateOptionsMenu.- Rozwiń menu i dodaj nowy element do kolekcji dla każdego elementu menu.
- Wywołaj metodę
notifyDataSetChangedna adapterze.
Kotlin
override fun onCreateOptionsMenu(menu: Menu): Boolean { val menuResource = intent .getIntExtra(EXTRA_MENU_KEY, EXTRA_MENU_ITEM_DEFAULT_VALUE) if (menuResource != EXTRA_MENU_ITEM_DEFAULT_VALUE) { menuInflater.inflate(menuResource, menu) for (i in 0 until menu.size()) { val menuItem = menu.getItem(i) menuItems.add( GlassMenuItem( menuItem.itemId, menuItem.icon, menuItem.title.toString() ) ) adapter.notifyDataSetChanged() } } return super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu) }Java
@Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { final int menuResource = getIntent() .getIntExtra(EXTRA_MENU_KEY, EXTRA_MENU_ITEM_DEFAULT_VALUE); if (menuResource != EXTRA_MENU_ITEM_DEFAULT_VALUE) { final MenuInflater inflater = getMenuInflater(); inflater.inflate(menuResource, menu); for (int i = 0; i < menu.size(); i++) { final MenuItem menuItem = menu.getItem(i); menuItems.add( new GlassMenuItem(menuItem.getItemId(), menuItem.getIcon(), menuItem.getTitle().toString())); adapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); } } return super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu); } - Aby określić, która opcja została wybrana, użyj właściwości
OnScrollListenerw połączeniu z właściwościamiLayoutManageriSnapHelper. - Wykrywaj gest
TAP, by obsługiwać zdarzenie wyboru elementu menu. - Utwórz
Intentz informacjami o wybranym elemencie menu. - Ustaw wynik dla tej aktywności i zakończ ją.
- Wywołaj
startActivityForResultz fragmentu lub działania, dla którego chcesz utworzyć menu. W tym celu użyj gestuTAP. - Zastąp
onActivityResultwe fragmencie połączenia lub działaniu, które obsługuje wybrany element menu.
Wskazówki
Oto lista sugestii dotyczących konfiguracji układu menu:
- Rozmiar tekstu:
64sp - Kolor tła:
#96000000 - Użyj ikonę materiału o rozmiarze
64dpx64dp - Ustaw flagę motywu
windowIsTranslucentnatrue
Oto przykład niestandardowego układu menu:

Szczegóły implementacji znajdziesz w przykładowej aplikacji Card.
Strony przesuwane
Ekran Glass i touchpad działają razem, by wygodnie wyświetlać karty przesuwane. Na podstawie swojej aktywności możesz też tworzyć strony przesuwane za pomocą standardowego interfejsu API ViewPager na Androida.
Więcej informacji o korzystaniu z Androida ViewPager do przewijania kart i ekranów znajdziesz w dokumentacji szkoleniowej dotyczącej slajdu ekranu.
