במדריך הזה מוסבר איך להוסיף מפה של Google לאפליקציית Android. המפה כוללת סמן, שנקרא גם סיכה, שמציין מיקום ספציפי.
פועלים לפי ההוראות במדריך כדי לפתח אפליקציית Android באמצעות Maps SDK ל-Android. סביבת הפיתוח המומלצת היא Android Studio.
קבל את הקוד
משכפלים או מורידים את מאגר הדוגמאות של Google Maps Android API v2 מ-GitHub.
כדי לראות את גרסת ה-Java של הפעילות:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapwithmarker; import android.os.Bundle; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with a marker (pin) to indicate a particular location. */ public class MapsMarkerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. In this case, * we just add a marker near Sydney, Australia. * If Google Play services is not installed on the device, the user receives a prompt to install * Play services inside the SupportMapFragment. The API invokes this method after the user has * installed Google Play services and returned to the app. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add a marker in Sydney, Australia, // and move the map's camera to the same location. LatLng sydney = new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211); googleMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney")); googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney)); } }
כדי לראות את גרסת הפעילות ב-Kotlin:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapwithmarker import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions /** * An activity that displays a Google map with a marker (pin) to indicate a particular location. */ class MapsMarkerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as? SupportMapFragment mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { val sydney = LatLng(-33.852, 151.211) googleMap.addMarker( MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney") ) googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney)) } }
הגדרת פרויקט הפיתוח
כדי ליצור את פרויקט ההדרכה ב-Android Studio, פועלים לפי השלבים הבאים.
- מורידים את Android Studio ומתקינים אותו.
- מוסיפים את חבילת Google Play services ל-Android Studio.
- משכפלים או מורידים את מאגר הדוגמאות של Google Maps Android API v2 אם לא עשיתם את זה כשקראתם את המדריך הזה.
מייבאים את פרויקט המדריך:
- ב-Android Studio, בוחרים באפשרות File > New > Import Project (קובץ > חדש > ייבוא פרויקט).
- עוברים למיקום שבו שמרתם את מאגר הדוגמאות של Google Maps Android API v2 אחרי שהורדתם אותו.
- מאתרים את הפרויקט MapWithMarker במיקום הבא:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/MapWithMarker(Java) או
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/MapWithMarker(Kotlin) - בוחרים את ספריית הפרויקט ולוחצים על פתיחה. מערכת Android Studio תבצע עכשיו build של הפרויקט באמצעות כלי ה-build של Gradle.
הפעלת ממשקי ה-API הנדרשים וקבלת מפתח API
כדי להשלים את המדריך הזה, אתם צריכים פרויקט ב-Google Cloud עם ממשקי ה-API הדרושים שמופעלים בו, ומפתח API שמאושר לשימוש ב-SDK של מפות ל-Android. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמרים הבאים:
הוספת מפתח ה-API לאפליקציה
- פותחים את הקובץ
local.propertiesשל הפרויקט. מוסיפים את המחרוזת הבאה ומחליפים את הערך
YOUR_API_KEYבערך של מפתח ה-API:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYכשאתם בונים את האפליקציה, הפלאגין של Secrets Gradle ל-Android מעתיק את מפתח ה-API והופך אותו לזמין כמשתנה build במניפסט של Android, כמו שמוסבר בהמשך.
איך יוצרים ומריצים את האפליקציה
כדי לבנות ולהריץ את האפליקציה:
מחברים מכשיר Android למחשב. פועלים לפי ההוראות כדי להפעיל את האפשרויות למפתחים במכשיר Android ולהגדיר את המערכת כך שתזהה את המכשיר.
אפשרות נוספת היא להשתמש במנהל המכשירים הווירטואליים (AVD) של Android כדי להגדיר מכשיר וירטואלי. כשבוחרים אמולטור, חשוב לבחור תמונה שכוללת את Google APIs. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר הגדרת פרויקט ב-Android Studio .
ב-Android Studio, לוחצים על האפשרות Run בתפריט (או על סמל לחצן ההפעלה). בוחרים מכשיר לפי ההנחיות.
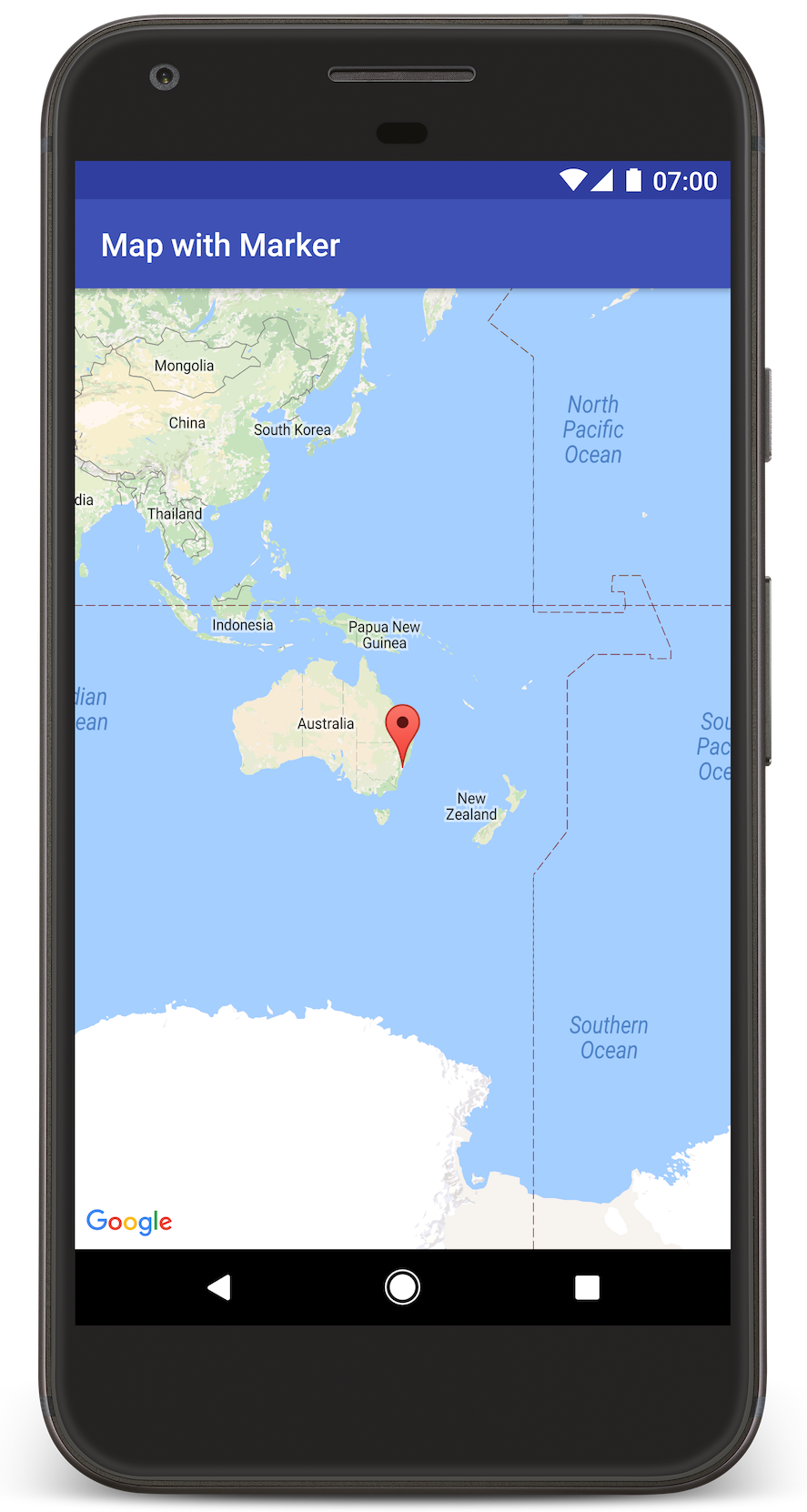
Android Studio מפעיל את Gradle כדי לבנות את האפליקציה, ואז מריץ את האפליקציה במכשיר או באמולטור. אמורה להופיע מפה עם סמן שמצביע על סידני בחוף המזרחי של אוסטרליה, כמו בתמונה שבדף הזה.
פתרון בעיות:
- אם לא רואים מפה, צריך לוודא שהשגתם מפתח API והוספתם אותו לאפליקציה, כמו שמתואר למעלה. בודקים את היומן בAndroid Monitor ב-Android Studio כדי לראות הודעות שגיאה לגבי מפתח ה-API.
- אפשר להשתמש בכלים לניפוי באגים ב-Android Studio כדי לראות את היומנים ולנפות באגים באפליקציה.
הסבר על הקוד
בחלק הזה של המדריך מוסבר על החלקים הכי חשובים באפליקציית MapWithMarker, כדי לעזור לכם להבין איך לבנות אפליקציה דומה.
בדיקת מניפסט Android
שימו לב לרכיבים הבאים בקובץ AndroidManifest.xml של האפליקציה:
מוסיפים רכיב
meta-dataכדי להטמיע את הגרסה של Google Play Services שהאפליקציה קומפלה איתה.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />מוסיפים רכיב
meta-dataשמציין את מפתח ה-API. בדוגמה שמצורפת למדריך הזה, הערך של מפתח ה-API ממופה למשתנה build שתואם לשם המפתח שהגדרתם קודם,MAPS_API_KEY. כשמבצעים build לאפליקציה, הפלאגין Secrets Gradle ל-Android הופך את המפתחות בקובץlocal.propertiesלזמינים כמשתני build של המניפסט.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />בקובץ
build.gradle, השורה הבאה מעבירה את מפתח ה-API למניפסט של Android.id 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
דוגמה למניפסט מלא:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name=".MapsMarkerActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps" android:exported="true"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
הוספת מפה
הצגת מפה באמצעות SDK של מפות ל-Android.
מוסיפים רכיב
<fragment>לקובץ הפריסה של הפעילות,activity_maps.xml. הרכיב הזה מגדירSupportMapFragmentשישמש כקונטיינר למפה ויספק גישה לאובייקטGoogleMap. במדריך נעשה שימוש בגרסת ספריית התמיכה של Android של קטע המפה, כדי להבטיח תאימות לדור קודם עם גרסאות קודמות של מסגרת Android.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.mapwithmarker.MapsMarkerActivity" />
ב-method
onCreate()של הפעילות, מגדירים את קובץ הפריסה כתצוגת התוכן. כדי לקבל נקודת אחיזה לשבר המפה, קוראים ל-FragmentManager.findFragmentById(). לאחר מכן משתמשים ב-getMapAsync()כדי להירשם לקריאה חוזרת של המפה:Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as? SupportMapFragment mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
מטמיעים את הממשק
OnMapReadyCallbackומבטלים את השיטהonMapReady()כדי להגדיר את המפה כשהאובייקטGoogleMapזמין:Java
public class MapsMarkerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { // ... @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { LatLng sydney = new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211); googleMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney")); } }
Kotlin
class MapsMarkerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { // ... override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { val sydney = LatLng(-33.852, 151.211) googleMap.addMarker( MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney") ) } }
כברירת מחדל, Maps SDK for Android מציג את התוכן של חלון המידע כשהמשתמש מקיש על סמן. אם אתם רוצים להשתמש בהתנהגות ברירת המחדל, אין צורך להוסיף listener ללחיצות על הסמן.
השלבים הבאים
מידע נוסף על אובייקט המפה ועל מה שאפשר לעשות עם סמנים.
