บทแนะนำนี้จะแสดงวิธีเพิ่มแผนที่ Google ลงในแอป Android และใช้ เส้นหลายเส้นและรูปหลายเหลี่ยมเพื่อแสดงเส้นทางและพื้นที่บนแผนที่
ทำตามบทแนะนำเพื่อสร้างแอป Android โดยใช้ Maps SDK สำหรับ Android สภาพแวดล้อมในการพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ที่แนะนำคือ Android Studio
รับโค้ด
โคลนหรือดาวน์โหลดที่เก็บตัวอย่าง Google Maps Android API v2 จาก GitHub
ดูเวอร์ชัน Java ของกิจกรรม
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A"); // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1); Polyline polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), new LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), new LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), new LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), new LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), new LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))); polyline2.setTag("B"); stylePolyline(polyline2); // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha"); // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1); Polygon polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), new LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), new LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), new LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))); polygon2.setTag("beta"); stylePolygon(polygon2); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); } private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); } private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolygonClick(Polygon polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. int color = polygon.getStrokeColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setStrokeColor(color); color = polygon.getFillColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setFillColor(color); Toast.makeText(this, "Area type " + polygon.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); } }
ดูเวอร์ชัน Kotlin ของกิจกรรม
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A" // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1) val polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))) polyline2.tag = "B" stylePolyline(polyline2) // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1) val polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))) polygon2.tag = "beta" stylePolygon(polygon2) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) } private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND } private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolygonClick(polygon: Polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. var color = polygon.strokeColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.strokeColor = color color = polygon.fillColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.fillColor = color Toast.makeText(this, "Area type ${polygon.tag?.toString()}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor } }
สร้างโปรเจ็กต์การพัฒนา
ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อสร้างโปรเจ็กต์บทแนะนำใน Android Studio
- ดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้ง Android Studio
- เพิ่มแพ็กเกจ Google Play services ลงใน Android Studio
- โคลนหรือดาวน์โหลดที่เก็บตัวอย่าง Google Maps Android API v2 หากคุณไม่ได้ทำเมื่อเริ่มอ่านบทแนะนำนี้
นำเข้าโปรเจ็กต์บทแนะนำ
- ใน Android Studio ให้เลือก File > New > Import Project
- ไปที่ตำแหน่งที่คุณบันทึกที่เก็บตัวอย่าง Google Maps Android API v2 หลังจากดาวน์โหลด
- ค้นหาโปรเจ็กต์ Polygons ได้ที่
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/Polygons(Java) หรือ
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/Polygons(Kotlin) - เลือกไดเรกทอรีโปรเจ็กต์ แล้วคลิกเปิด ตอนนี้ Android Studio จะสร้างโปรเจ็กต์โดยใช้เครื่องมือบิลด์ Gradle
เปิดใช้ API ที่จำเป็นและรับคีย์ API
หากต้องการทำตามบทแนะนำนี้ให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์ คุณต้องมีโปรเจ็กต์ Google Cloud ที่เปิดใช้ API ที่จำเป็นและคีย์ API ที่ได้รับอนุญาตให้ใช้ Maps SDK สำหรับ Android ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมได้ที่
เพิ่มคีย์ API ลงในแอป
- เปิดไฟล์
local.propertiesของโปรเจ็กต์ เพิ่มสตริงต่อไปนี้ แล้วแทนที่
YOUR_API_KEYด้วยค่าของ คีย์ API ของคุณMAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYเมื่อคุณสร้างแอป ปลั๊กอินข้อมูลลับ Gradle สำหรับ Android จะคัดลอกคีย์ API และทำให้พร้อมใช้งานเป็นตัวแปรบิลด์ใน ไฟล์ Manifest ของ Android ตามที่อธิบายด้านล่าง
สร้างและเรียกใช้แอป
วิธีสร้างและเรียกใช้แอป
เชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ Android กับคอมพิวเตอร์ ทำตามวิธีการเพื่อเปิดใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ในอุปกรณ์ Android และกำหนดค่าระบบให้ตรวจหาอุปกรณ์
หรือจะใช้ตัวจัดการอุปกรณ์เสมือน Android (AVD) เพื่อกำหนดค่าอุปกรณ์เสมือนก็ได้ เมื่อเลือกโปรแกรมจำลอง ให้เลือก อิมเมจที่มี Google API ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมได้ที่ ตั้งค่าโปรเจ็กต์ Android Studio
ใน Android Studio ให้คลิกตัวเลือกเมนูเรียกใช้ (หรือไอคอนปุ่มเล่น) เลือกอุปกรณ์ตามที่ได้รับแจ้ง
Android Studio จะเรียกใช้ Gradle เพื่อสร้างแอป แล้วเรียกใช้แอปใน อุปกรณ์หรือในโปรแกรมจำลอง
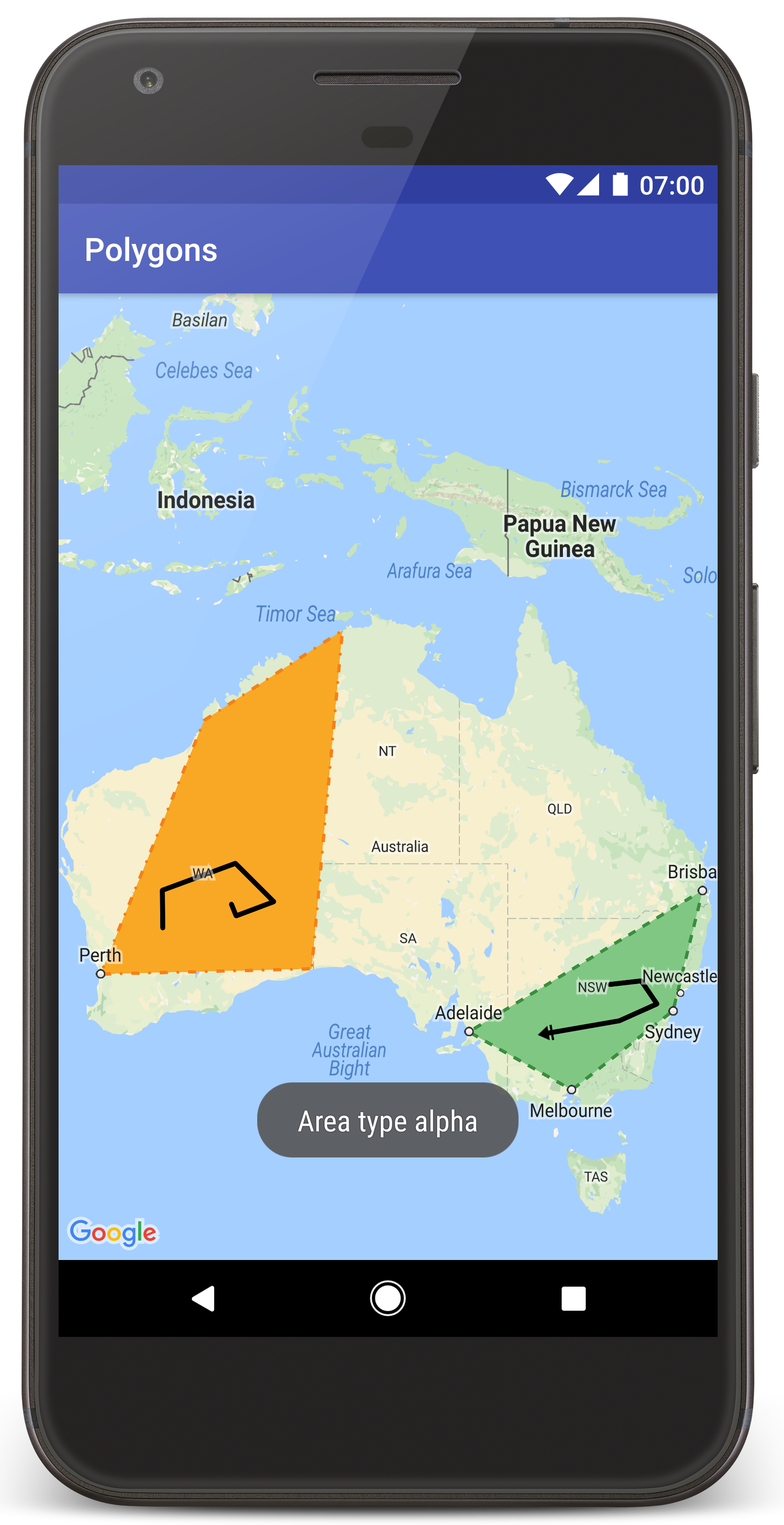
คุณควรเห็นแผนที่ที่มีรูปหลายเหลี่ยม 2 รูปซ้อนอยู่บนออสเตรเลีย คล้ายกับ รูปภาพในหน้านี้
การแก้ปัญหา:
- หากไม่เห็นแผนที่ ให้ตรวจสอบว่าคุณได้รับคีย์ API และเพิ่มคีย์ดังกล่าวลงในแอปแล้วตามที่อธิบายไว้ข้างต้น ตรวจสอบบันทึกใน Android Monitor ของ Android Studio เพื่อดูข้อความแสดงข้อผิดพลาดเกี่ยวกับคีย์ API
- ใช้เครื่องมือแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องของ Android Studio เพื่อดูบันทึกและแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องของแอป
ทำความเข้าใจโค้ด
ส่วนนี้ของบทแนะนำจะอธิบายส่วนที่สำคัญที่สุดของแอป Polygons เพื่อช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจวิธีสร้างแอปที่คล้ายกัน
ตรวจสอบไฟล์ Manifest ของ Android
โปรดสังเกตองค์ประกอบต่อไปนี้ในไฟล์ AndroidManifest.xml ของแอป
เพิ่มองค์ประกอบ
meta-dataเพื่อฝังเวอร์ชันของบริการ Google Play ที่ใช้คอมไพล์แอป<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />เพิ่มองค์ประกอบ
meta-dataที่ระบุคีย์ API ตัวอย่างที่มาพร้อมกับ บทแนะนำนี้จะแมปค่าสำหรับคีย์ API กับตัวแปรบิลด์ที่ตรงกับ ชื่อของคีย์ที่คุณกำหนดไว้ก่อนหน้านี้MAPS_API_KEYเมื่อคุณสร้างแอป Secrets Gradle Plugin สำหรับ Android จะทำให้คีย์ในไฟล์local.propertiesพร้อมใช้งานเป็นตัวแปรบิลด์ Manifest<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />ในไฟล์
build.gradleบรรทัดต่อไปนี้จะส่งคีย์ API ไปยัง Manifest ของ Androidid 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
ด้านล่างนี้คือตัวอย่างไฟล์ Manifest ที่สมบูรณ์
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
เพิ่มแผนที่
แสดงแผนที่โดยใช้ Maps SDK สำหรับ Android
เพิ่มองค์ประกอบ
<fragment>ลงในไฟล์เลย์เอาต์ของกิจกรรมactivity_maps.xmlองค์ประกอบนี้กำหนดSupportMapFragmentให้ทำหน้าที่เป็นคอนเทนเนอร์สำหรับแผนที่ และให้สิทธิ์เข้าถึงออบเจ็กต์GoogleMapบทแนะนำ ใช้ MapFragment เวอร์ชันไลบรารีการสนับสนุน Android เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่า จะเข้ากันได้กับเฟรมเวิร์ก Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้า<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" />
ในเมธอด
onCreate()ของกิจกรรม ให้ตั้งค่าไฟล์เลย์เอาต์ เป็นมุมมองเนื้อหา รับแฮนเดิลไปยัง MapFragment โดยการเรียกใช้FragmentManager.findFragmentById()จากนั้นใช้getMapAsync()เพื่อลงทะเบียนสำหรับการเรียกกลับของแผนที่Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
ใช้
OnMapReadyCallbackอินเทอร์เฟซและ ลบล้างเมธอดonMapReady()API จะเรียกใช้ การเรียกกลับนี้เมื่อออบเจ็กต์GoogleMapพร้อมใช้งาน เพื่อให้คุณเพิ่มออบเจ็กต์ลงในแผนที่และปรับแต่งเพิ่มเติมสำหรับแอปได้Java
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
Kotlin
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
เพิ่มเส้นหลายส่วนเพื่อวาดเส้นบนแผนที่
Polyline คือชุดของส่วนของเส้นที่เชื่อมต่อกัน Polyline มีประโยชน์ในการแสดงเส้นทาง ทางเดิน หรือการเชื่อมต่ออื่นๆ ระหว่างสถานที่ต่างๆ บนแผนที่
สร้างออบเจ็กต์
PolylineOptionsแล้วเพิ่มจุดลงในออบเจ็กต์ แต่ละจุดแสดงถึงตำแหน่งบนแผนที่ ซึ่งคุณกำหนดได้ด้วยออบเจ็กต์LatLngที่มีค่าละติจูดและลองจิจูด ตัวอย่างโค้ดด้านล่างสร้างเส้นหลายเส้นที่มี 6 จุดโทรหา
GoogleMap.addPolyline()เพื่อเพิ่มเส้นหลายส่วนลงในแผนที่Java
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)));
Kotlin
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)))
ตั้งค่าตัวเลือก clickable ของ Polyline เป็น true หากต้องการจัดการเหตุการณ์คลิก
ใน Polyline ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการจัดการเหตุการณ์ได้ในภายหลังในบทแนะนำนี้
จัดเก็บข้อมูลที่กำหนดเองด้วย Polyline
คุณสามารถจัดเก็บออบเจ็กต์ข้อมูลที่กำหนดเองด้วยเส้นหลายเส้นและออบเจ็กต์เรขาคณิตอื่นๆ
เรียกใช้
Polyline.setTag()เพื่อจัดเก็บออบเจ็กต์ข้อมูลที่มี เส้นหลายเส้น โค้ดด้านล่างกำหนดแท็กแบบสุ่ม (A) ที่ระบุประเภทของ เส้นหลายเส้นJava
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A");
Kotlin
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A
เรียกข้อมูลโดยใช้
Polyline.getTag()ดังที่ส่วนถัดไปแสดง
เพิ่มสไตล์ที่กำหนดเองให้กับเส้นหลายส่วน
คุณระบุพร็อพเพอร์ตี้การจัดรูปแบบต่างๆ ได้ในออบเจ็กต์
PolylineOptions ตัวเลือกการจัดรูปแบบประกอบด้วยสีเส้นขอบ
ความกว้างของเส้นขอบ รูปแบบเส้นขอบ ประเภทข้อต่อ และส่วนเริ่มต้นและส่วนสิ้นสุด หากคุณไม่ได้ระบุพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ใด พร็อพเพอร์ตี้นั้น API จะใช้ค่าเริ่มต้นสำหรับพร็อพเพอร์ตี้นั้น
โค้ดต่อไปนี้ใช้การปิดท้ายแบบกลมที่ส่วนท้ายของเส้น และการปิดต้นแบบอื่น ๆ โดยขึ้นอยู่กับประเภทของเส้นหลายเส้น ซึ่งประเภทคือพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ที่กำหนดเอง ซึ่งจัดเก็บไว้ในออบเจ็กต์ข้อมูลสำหรับเส้นหลายเส้น ตัวอย่างยังระบุ ความกว้างของเส้น สีของเส้น และประเภทการเชื่อมต่อด้วย
Java
private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); }
Kotlin
private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND }
โค้ดด้านบนระบุบิตแมปที่กำหนดเองสำหรับส่วนเริ่มต้นของเส้นโพลีไลน์ประเภท A และระบุความกว้างของเส้นอ้างอิงเป็น 10 พิกเซล API จะปรับขนาดบิตแมปตามความกว้างของเส้นอ้างอิง เมื่อระบุความกว้างของเส้นอ้างอิง ให้ระบุความกว้างที่คุณใช้เมื่อออกแบบรูปภาพบิตแมปที่ ขนาดเดิมของรูปภาพ เคล็ดลับ: เปิดรูปภาพบิตแมปที่ระดับการซูม 100% ในโปรแกรมแก้ไขรูปภาพ แล้วพล็อตความกว้างที่ต้องการของเส้นขีดเทียบกับ รูปภาพ
อ่านเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการปิดเส้นและตัวเลือกอื่นๆ สำหรับการปรับแต่งรูปร่าง
จัดการเหตุการณ์คลิกในเส้นหลายส่วน
ทำให้เส้นหลายเส้นคลิกได้โดยเรียกใช้
Polyline.setClickable()(โดยค่าเริ่มต้น โพลีไลน์จะ คลิกไม่ได้ และแอปจะไม่ได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเมื่อผู้ใช้ แตะโพลีไลน์)ใช้
OnPolylineClickListenerอินเทอร์เฟซ และเรียกใช้GoogleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener()เพื่อตั้งค่า Listener บนแผนที่Java
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
Kotlin
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
แทนที่เมธอดเรียกกลับ
onPolylineClick()ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้จะสลับรูปแบบเส้นของเส้นระหว่างเส้นทึบกับ เส้นประทุกครั้งที่ผู้ใช้คลิกเส้นหลายเส้นJava
private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }
Kotlin
private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() }
เพิ่มรูปหลายเหลี่ยมเพื่อแสดงพื้นที่บนแผนที่
Polygon คือรูปร่างที่ประกอบด้วยชุดพิกัดในลำดับที่เรียงตามลำดับ คล้ายกับ Polyline ความแตกต่างคือรูปหลายเหลี่ยมกำหนดพื้นที่ปิดที่มีการตกแต่งภายในที่เติมได้ ในขณะที่เส้นหลายเหลี่ยม
เป็นแบบเปิด
สร้างออบเจ็กต์
PolygonOptionsแล้วเพิ่มจุดลงในออบเจ็กต์ แต่ละจุดแสดงถึงตำแหน่งบนแผนที่ ซึ่งคุณกำหนดได้ด้วยออบเจ็กต์LatLngที่มีค่าละติจูดและลองจิจูด ตัวอย่างโค้ดด้านล่างสร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยมที่มี 4 จุดทำให้รูปหลายเหลี่ยมคลิกได้โดยเรียกใช้
Polygon.setClickable()(โดยค่าเริ่มต้น รูปหลายเหลี่ยมจะคลิกไม่ได้ และแอปจะไม่ได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะรูปหลายเหลี่ยม) การจัดการเหตุการณ์คลิกรูปหลายเหลี่ยมจะคล้ายกับการจัดการ เหตุการณ์ใน Polyline ซึ่งอธิบายไว้ก่อนหน้านี้ในบทแนะนำนี้โทรหา
GoogleMap.addPolygon()เพื่อเพิ่มรูปหลายเหลี่ยมลงในแผนที่เรียกใช้
Polygon.setTag()เพื่อจัดเก็บออบเจ็กต์ข้อมูลที่มี รูปหลายเหลี่ยม โค้ดด้านล่างกำหนดประเภทที่กำหนดเอง (alpha) สำหรับรูปหลายเหลี่ยมJava
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha");
Kotlin
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon.
เพิ่มสไตล์ที่กำหนดเองให้กับรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
คุณระบุพร็อพเพอร์ตี้การจัดรูปแบบได้หลายรายการในออบเจ็กต์
PolygonOptions ตัวเลือกการจัดรูปแบบ ได้แก่ สีเส้นขอบ
ความกว้างของเส้นขอบ รูปแบบเส้นขอบ ประเภทข้อต่อของเส้นขอบ และสีเติม หากคุณไม่ได้ระบุพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ใด พร็อพเพอร์ตี้นั้น API จะใช้ค่าเริ่มต้นสำหรับพร็อพเพอร์ตี้นั้น
โค้ดต่อไปนี้ใช้สีและรูปแบบเส้นที่เฉพาะเจาะจงตามประเภทของรูปหลายเหลี่ยม โดยประเภทคือพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ที่กำหนดเองซึ่งจัดเก็บไว้ในออบเจ็กต์ข้อมูลสำหรับรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
Java
private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); }
Kotlin
private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor }
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับรูปแบบเส้นและตัวเลือกอื่นๆ สำหรับ การปรับแต่งรูปร่าง
ขั้นตอนถัดไป
ดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับออบเจ็กต์วงกลม วงกลมคล้ายกับรูปหลายเหลี่ยม แต่มีคุณสมบัติที่แสดงถึงรูปร่างของวงกลม
