Sélectionner le lieu actuel et afficher les détails sur une carte
Ce tutoriel explique comment créer une application iOS qui récupère la position actuelle de l'appareil, identifie les lieux probables, invite l'utilisateur à sélectionner le lieu le plus pertinent et affiche un repère sur la carte pour le lieu choisi.
Il convient aux personnes ayant des connaissances de base ou intermédiaires en Swift ou Objective-C, et des connaissances générales sur Xcode. Pour en savoir plus sur la création de cartes, consultez le guide du développeur.
À l'aide de ce tutoriel, vous allez créer la carte suivante. Le repère de la carte est positionné à San Francisco, en Californie, mais il se déplacera vers l'emplacement de l'appareil ou du simulateur.
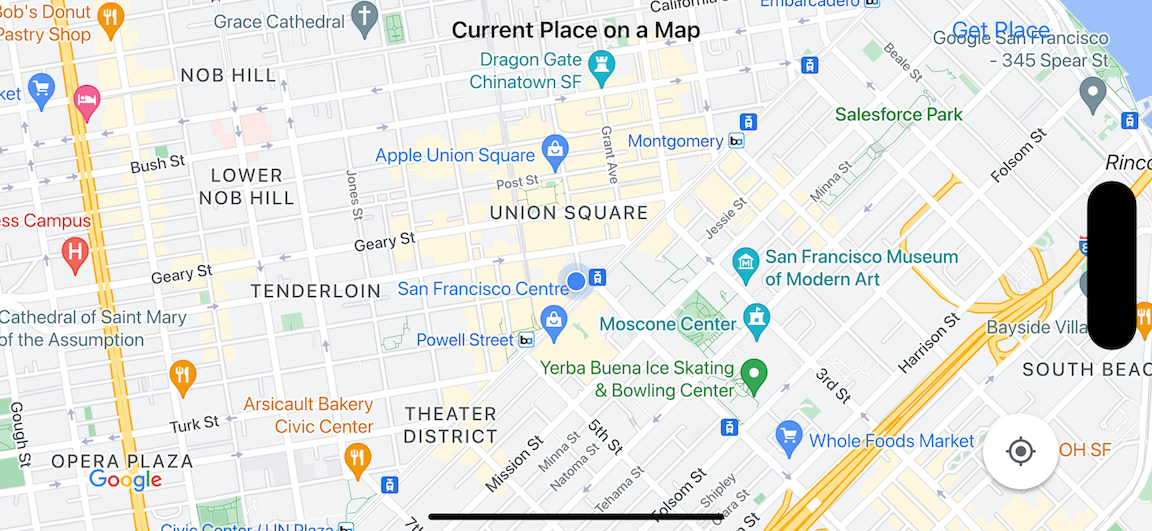
Ce tutoriel utilise le SDK Places pour iOS, le SDK Maps pour iOS et le framework Apple Core Location.
Obtenir le code
Clonez ou téléchargez le dépôt d'exemples Google Maps pour iOS à partir de GitHub.Vous pouvez également cliquer sur le bouton suivant pour télécharger le code source :
MapViewController
Swift
import UIKit import GoogleMaps import GooglePlaces class MapViewController: UIViewController { var locationManager: CLLocationManager! var currentLocation: CLLocation? var mapView: GMSMapView! var placesClient: GMSPlacesClient! var preciseLocationZoomLevel: Float = 15.0 var approximateLocationZoomLevel: Float = 10.0 // An array to hold the list of likely places. var likelyPlaces: [GMSPlace] = [] // The currently selected place. var selectedPlace: GMSPlace? // Update the map once the user has made their selection. @IBAction func unwindToMain(segue: UIStoryboardSegue) { // Clear the map. mapView.clear() // Add a marker to the map. if let place = selectedPlace { let marker = GMSMarker(position: place.coordinate) marker.title = selectedPlace?.name marker.snippet = selectedPlace?.formattedAddress marker.map = mapView } listLikelyPlaces() } override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() // Initialize the location manager. locationManager = CLLocationManager() locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization() locationManager.distanceFilter = 50 locationManager.startUpdatingLocation() locationManager.delegate = self placesClient = GMSPlacesClient.shared() // A default location to use when location permission is not granted. let defaultLocation = CLLocation(latitude: -33.869405, longitude: 151.199) // Create a map. let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.latitude, longitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: view.bounds, camera: camera) mapView.settings.myLocationButton = true mapView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight] mapView.isMyLocationEnabled = true // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. view.addSubview(mapView) mapView.isHidden = true listLikelyPlaces() } // Populate the array with the list of likely places. func listLikelyPlaces() { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces.removeAll() let placeFields: GMSPlaceField = [.name, .coordinate] placesClient.findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocation(withPlaceFields: placeFields) { (placeLikelihoods, error) in guard error == nil else { // TODO: Handle the error. print("Current Place error: \(error!.localizedDescription)") return } guard let placeLikelihoods = placeLikelihoods else { print("No places found.") return } // Get likely places and add to the list. for likelihood in placeLikelihoods { let place = likelihood.place self.likelyPlaces.append(place) } } } // Prepare the segue. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "segueToSelect" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? PlacesViewController { nextViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces } } } } // Delegates to handle events for the location manager. extension MapViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate { // Handle incoming location events. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) { let location: CLLocation = locations.last! print("Location: \(location)") let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: location.coordinate.latitude, longitude: location.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) if mapView.isHidden { mapView.isHidden = false mapView.camera = camera } else { mapView.animate(to: camera) } listLikelyPlaces() } // Handle authorization for the location manager. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didChangeAuthorization status: CLAuthorizationStatus) { // Check accuracy authorization let accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization switch accuracy { case .fullAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is precise.") case .reducedAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is not precise.") @unknown default: fatalError() } // Handle authorization status switch status { case .restricted: print("Location access was restricted.") case .denied: print("User denied access to location.") // Display the map using the default location. mapView.isHidden = false case .notDetermined: print("Location status not determined.") case .authorizedAlways: fallthrough case .authorizedWhenInUse: print("Location status is OK.") @unknown default: fatalError() } } // Handle location manager errors. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: Error) { locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation() print("Error: \(error)") } }
Objective-C
#import "MapViewController.h" #import "PlacesViewController.h" @import CoreLocation; @import GooglePlaces; @import GoogleMaps; @interface MapViewController () <CLLocationManagerDelegate> @end @implementation MapViewController { CLLocationManager *locationManager; CLLocation * _Nullable currentLocation; GMSMapView *mapView; GMSPlacesClient *placesClient; float preciseLocationZoomLevel; float approximateLocationZoomLevel; // An array to hold the list of likely places. NSMutableArray<GMSPlace *> *likelyPlaces; // The currently selected place. GMSPlace * _Nullable selectedPlace; } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; preciseLocationZoomLevel = 15.0; approximateLocationZoomLevel = 15.0; // Initialize the location manager. locationManager = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init]; locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest; [locationManager requestWhenInUseAuthorization]; locationManager.distanceFilter = 50; [locationManager startUpdatingLocation]; locationManager.delegate = self; placesClient = [GMSPlacesClient sharedClient]; // A default location to use when location permission is not granted. CLLocationCoordinate2D defaultLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.869405, 151.199); // Create a map. float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition *camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:defaultLocation.latitude longitude:defaultLocation.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; mapView = [GMSMapView mapWithFrame:self.view.bounds camera:camera]; mapView.settings.myLocationButton = YES; mapView.autoresizingMask = UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth | UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight; mapView.myLocationEnabled = YES; // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. [self.view addSubview:mapView]; mapView.hidden = YES; [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Populate the array with the list of likely places. - (void) listLikelyPlaces { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces = [NSMutableArray array]; GMSPlaceField placeFields = GMSPlaceFieldName | GMSPlaceFieldCoordinate; [placesClient findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocationWithPlaceFields:placeFields callback:^(NSArray<GMSPlaceLikelihood *> * _Nullable likelihoods, NSError * _Nullable error) { if (error != nil) { // TODO: Handle the error. NSLog(@"Current Place error: %@", error.localizedDescription); return; } if (likelihoods == nil) { NSLog(@"No places found."); return; } for (GMSPlaceLikelihood *likelihood in likelihoods) { GMSPlace *place = likelihood.place; [likelyPlaces addObject:place]; } }]; } // Update the map once the user has made their selection. - (void) unwindToMain:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue { // Clear the map. [mapView clear]; // Add a marker to the map. if (selectedPlace != nil) { GMSMarker *marker = [GMSMarker markerWithPosition:selectedPlace.coordinate]; marker.title = selectedPlace.name; marker.snippet = selectedPlace.formattedAddress; marker.map = mapView; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Prepare the segue. - (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { if ([segue.identifier isEqualToString:@"segueToSelect"]) { if ([segue.destinationViewController isKindOfClass:[PlacesViewController class]]) { PlacesViewController *placesViewController = (PlacesViewController *)segue.destinationViewController; placesViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces; } } } // Delegates to handle events for the location manager. #pragma mark - CLLocationManagerDelegate // Handle incoming location events. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray<CLLocation *> *)locations { CLLocation *location = locations.lastObject; NSLog(@"Location: %@", location); float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition * camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:location.coordinate.latitude longitude:location.coordinate.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; if (mapView.isHidden) { mapView.hidden = NO; mapView.camera = camera; } else { [mapView animateToCameraPosition:camera]; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Handle authorization for the location manager. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didChangeAuthorizationStatus:(CLAuthorizationStatus)status { // Check accuracy authorization CLAccuracyAuthorization accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization; switch (accuracy) { case CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is precise."); break; case CLAccuracyAuthorizationReducedAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is not precise."); break; } // Handle authorization status switch (status) { case kCLAuthorizationStatusRestricted: NSLog(@"Location access was restricted."); break; case kCLAuthorizationStatusDenied: NSLog(@"User denied access to location."); // Display the map using the default location. mapView.hidden = NO; case kCLAuthorizationStatusNotDetermined: NSLog(@"Location status not determined."); case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedAlways: case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedWhenInUse: NSLog(@"Location status is OK."); } } // Handle location manager errors. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didFailWithError:(NSError *)error { [manager stopUpdatingLocation]; NSLog(@"Error: %@", error.localizedDescription); } @end
PlacesViewController
Swift
import UIKit import GooglePlaces class PlacesViewController: UIViewController { // ... // Pass the selected place to the new view controller. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "unwindToMain" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? MapViewController { nextViewController.selectedPlace = selectedPlace } } } } // Respond when a user selects a place. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDelegate { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) { selectedPlace = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] performSegue(withIdentifier: "unwindToMain", sender: self) } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5 } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForFooterInSection section: Int) -> CGFloat { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1 } return 0 } } // Populate the table with the list of most likely places. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDataSource { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int { return likelyPlaces.count } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: cellReuseIdentifier, for: indexPath) let collectionItem = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] cell.textLabel?.text = collectionItem.name return cell } }
Objective-C
#import "PlacesViewController.h" @interface PlacesViewController () <UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate> // ... -(void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { } #pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate // Respond when a user selects a place. -(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { self.selectedPlace = [self.likelyPlaces objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; [self performSegueWithIdentifier:@"unwindToMain" sender:self]; } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5; } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForFooterInSection:(NSInteger)section { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1; } return 0; } #pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource - (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section { return self.likelyPlaces.count; } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:cellReuseIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; } @end
Commencer
Swift Package Manager
Le SDK Maps pour iOS peut être installé à l'aide de Swift Package Manager.
- Supprimez toutes les dépendances existantes du SDK Maps pour iOS.
- Ouvrez une fenêtre de terminal et accédez au répertoire
tutorials/current-place-on-map. -
Fermez votre espace de travail Xcode et exécutez les commandes suivantes :
sudo gem install cocoapods-deintegrate cocoapods-clean pod deintegrate pod cache clean --all rm Podfile rm current-place-on-map.xcworkspace
- Ouvrez votre projet Xcode et supprimez le fichier Podfile.
- Ajoutez les SDK Places et Maps :
- Accédez à File > Add Package Dependencies (Fichier > Ajouter des dépendances de package).
- Saisissez l'URL https://github.com/googlemaps/ios-places-sdk, appuyez sur Entrée pour importer le package, puis cliquez sur Add Package (Ajouter le package).
- Saisissez l'URL https://github.com/googlemaps/ios-maps-sdk, appuyez sur Entrée pour importer le package, puis cliquez sur Add Package (Ajouter le package).
- Vous devrez peut-être réinitialiser le cache des packages en utilisant File > Packages > Reset Package Cache (Fichier > Packages > Réinitialiser le cache des packages).
Utiliser CocoaPods
- Téléchargez et installez Xcode version 16.0 ou ultérieure.
- Si vous ne possédez pas encore CocoaPods, installez-le sur macOS en exécutant la commande ci-dessous à partir du terminal :
sudo gem install cocoapods
- Accédez au répertoire
tutorials/current-place-on-map. - Exécutez la commande
pod install. Cela installera les SDK Maps et Places spécifiés dans lePodfile, ainsi que toutes les éventuelles dépendances. - Exécutez
pod outdatedpour comparer la version du pod installé avec les nouvelles mises à jour. Si une nouvelle version est détectée, exécutezpod updatepour mettre à jourPodfileet installer le dernier SDK. Pour en savoir plus, consultez le guide CocoaPods. - Ouvrez (double-cliquez) le fichier current-place-on-map.xcworkspace du projet pour l'ouvrir dans Xcode. Vous devez utiliser le fichier
.xcworkspacepour ouvrir le projet.
Obtenir une clé API et activer les API nécessaires
Pour suivre ce tutoriel, vous devez disposer d'une clé API Google autorisée à utiliser le SDK Maps pour iOS et l'API Places.
- Suivez les instructions de Premiers pas avec Google Maps Platform pour configurer un compte de facturation et un projet activé avec ces deux produits.
- Suivez les instructions de la section Obtenir une clé API pour créer une clé API pour le projet de développement que vous avez configuré précédemment.
Ajouter la clé API à votre application
Ajoutez votre clé API à votre fichier AppDelegate.swift comme suit :
- Notez que l'instruction d'importation suivante a été ajoutée au fichier :
import GooglePlaces import GoogleMaps
- Modifiez la ligne suivante dans votre méthode
application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:), en remplaçant YOUR_API_KEY par votre clé API :GMSPlacesClient.provideAPIKey("YOUR_API_KEY") GMSServices.provideAPIKey("YOUR_API_KEY")
Compiler et exécuter votre application
- Connectez un appareil iOS à votre ordinateur ou sélectionnez un simulateur dans le menu du schéma Xcode.
- Si vous utilisez un appareil, assurez-vous que les services de localisation sont activés. Si vous utilisez un simulateur, sélectionnez un emplacement dans le menu Fonctionnalités.
- Dans Xcode, cliquez sur l'option de menu Product/Run (Produit/Exécuter) (ou sur l'icône du bouton de lecture).
- Xcode crée l'application, puis l'exécute sur l'appareil ou sur le simulateur.
- Vous devriez voir une carte avec un certain nombre de repères centrés autour de votre position actuelle.
Dépannage :
- Si aucune carte ne s'affiche, vérifiez que vous avez bien obtenu une clé API et que vous l'avez ajoutée à l'application, comme décrit ci-dessus. Consultez la console de débogage Xcode pour vérifier s'il contient des messages d'erreur concernant la clé API.
- Si vous avez restreint la clé API par l'identifiant du bundle iOS, modifiez-la afin d'ajouter l'identifiant du bundle pour l'application :
com.google.examples.current-place-on-map. - La carte ne s'affichera pas correctement si la demande d'autorisation pour les services de localisation est refusée.
- Si vous utilisez un appareil, accédez à Réglages/Général/Confidentialité/Service de localisation, puis réactivez les services de localisation.
- Si vous utilisez un simulateur, accédez à Simulateur/Réinitialiser le contenu et les paramètres….
- Assurez-vous d'avoir un bon signal Wi-Fi ou GPS.
- Si l'application se lance, mais qu'aucune carte n'est affichée, assurez-vous d'avoir mis à jour le fichier Info.plist de votre projet avec les autorisations de localisation appropriées. Pour en savoir plus sur la gestion des autorisations, consultez le guide Demander l'autorisation d'accéder à la position dans votre application ci-dessous.
- Utilisez les outils de débogage Xcode pour afficher les journaux et déboguer l'application.
Comprendre le code
Cette partie du tutoriel décrit les principales composantes de l'application current-place-on-map pour vous aider à comprendre comment créer une application similaire.
L'application current-place-on-map comporte deux contrôleurs de vue :
l'un pour afficher une carte indiquant le lieu sélectionné par l'utilisateur et l'autre pour lui présenter une liste de lieux probables parmi lesquels choisir. Notez que chaque contrôleur de vue possède les mêmes variables pour suivre la liste des lieux probables (likelyPlaces) et pour indiquer la sélection de l'utilisateur (selectedPlace). La navigation entre les vues s'effectue à l'aide de segues.
Demander l'autorisation d'accéder à la position
Votre application doit demander à l'utilisateur son consentement pour utiliser les services de localisation. Pour ce faire, incluez la clé NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription dans le fichier Info.plist de l'application et définissez la valeur de chaque clé sur une chaîne décrivant comment l'application prévoit d'utiliser les données de localisation.
Configurer le gestionnaire de localisation
Utilisez CLLocationManager pour trouver la position actuelle de l'appareil et demander des mises à jour régulières lorsque l'appareil se déplace vers un nouvel emplacement. Ce tutoriel fournit le code nécessaire pour obtenir la position de l'appareil. Pour en savoir plus, consultez le guide Obtenir la position de l'utilisateur dans la documentation Apple Developer.
- Déclarez le gestionnaire de localisation, la position actuelle, la vue de la carte, le client Places et le niveau de zoom par défaut au niveau de la classe.
- Initialisez le gestionnaire de localisation et
GMSPlacesClientdansviewDidLoad(). - Déclarez des variables pour contenir la liste des lieux probables et le lieu sélectionné par l'utilisateur.
- Ajoutez des délégués pour gérer les événements du gestionnaire de localisation à l'aide d'une clause d'extension.
Swift
var locationManager: CLLocationManager! var currentLocation: CLLocation? var mapView: GMSMapView! var placesClient: GMSPlacesClient! var preciseLocationZoomLevel: Float = 15.0 var approximateLocationZoomLevel: Float = 10.0
Objective-C
CLLocationManager *locationManager; CLLocation * _Nullable currentLocation; GMSMapView *mapView; GMSPlacesClient *placesClient; float preciseLocationZoomLevel; float approximateLocationZoomLevel;
Swift
// Initialize the location manager. locationManager = CLLocationManager() locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization() locationManager.distanceFilter = 50 locationManager.startUpdatingLocation() locationManager.delegate = self placesClient = GMSPlacesClient.shared()
Objective-C
// Initialize the location manager. locationManager = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init]; locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest; [locationManager requestWhenInUseAuthorization]; locationManager.distanceFilter = 50; [locationManager startUpdatingLocation]; locationManager.delegate = self; placesClient = [GMSPlacesClient sharedClient];
Swift
// An array to hold the list of likely places. var likelyPlaces: [GMSPlace] = [] // The currently selected place. var selectedPlace: GMSPlace?
Objective-C
// An array to hold the list of likely places. NSMutableArray<GMSPlace *> *likelyPlaces; // The currently selected place. GMSPlace * _Nullable selectedPlace;
Swift
// Delegates to handle events for the location manager. extension MapViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate { // Handle incoming location events. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) { let location: CLLocation = locations.last! print("Location: \(location)") let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: location.coordinate.latitude, longitude: location.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) if mapView.isHidden { mapView.isHidden = false mapView.camera = camera } else { mapView.animate(to: camera) } listLikelyPlaces() } // Handle authorization for the location manager. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didChangeAuthorization status: CLAuthorizationStatus) { // Check accuracy authorization let accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization switch accuracy { case .fullAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is precise.") case .reducedAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is not precise.") @unknown default: fatalError() } // Handle authorization status switch status { case .restricted: print("Location access was restricted.") case .denied: print("User denied access to location.") // Display the map using the default location. mapView.isHidden = false case .notDetermined: print("Location status not determined.") case .authorizedAlways: fallthrough case .authorizedWhenInUse: print("Location status is OK.") @unknown default: fatalError() } } // Handle location manager errors. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: Error) { locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation() print("Error: \(error)") } }
Objective-C
// Delegates to handle events for the location manager. #pragma mark - CLLocationManagerDelegate // Handle incoming location events. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray<CLLocation *> *)locations { CLLocation *location = locations.lastObject; NSLog(@"Location: %@", location); float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition * camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:location.coordinate.latitude longitude:location.coordinate.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; if (mapView.isHidden) { mapView.hidden = NO; mapView.camera = camera; } else { [mapView animateToCameraPosition:camera]; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Handle authorization for the location manager. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didChangeAuthorizationStatus:(CLAuthorizationStatus)status { // Check accuracy authorization CLAccuracyAuthorization accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization; switch (accuracy) { case CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is precise."); break; case CLAccuracyAuthorizationReducedAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is not precise."); break; } // Handle authorization status switch (status) { case kCLAuthorizationStatusRestricted: NSLog(@"Location access was restricted."); break; case kCLAuthorizationStatusDenied: NSLog(@"User denied access to location."); // Display the map using the default location. mapView.hidden = NO; case kCLAuthorizationStatusNotDetermined: NSLog(@"Location status not determined."); case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedAlways: case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedWhenInUse: NSLog(@"Location status is OK."); } } // Handle location manager errors. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didFailWithError:(NSError *)error { [manager stopUpdatingLocation]; NSLog(@"Error: %@", error.localizedDescription); }
Ajouter une carte
Créez une carte et ajoutez-la à la vue dans viewDidLoad() dans le contrôleur de vue principal. La carte reste masquée jusqu'à ce qu'une mise à jour de la position soit reçue (les mises à jour de la position sont gérées dans l'extension CLLocationManagerDelegate).
Swift
// A default location to use when location permission is not granted. let defaultLocation = CLLocation(latitude: -33.869405, longitude: 151.199) // Create a map. let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.latitude, longitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: view.bounds, camera: camera) mapView.settings.myLocationButton = true mapView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight] mapView.isMyLocationEnabled = true // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. view.addSubview(mapView) mapView.isHidden = true
Objective-C
// A default location to use when location permission is not granted. CLLocationCoordinate2D defaultLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.869405, 151.199); // Create a map. float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition *camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:defaultLocation.latitude longitude:defaultLocation.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; mapView = [GMSMapView mapWithFrame:self.view.bounds camera:camera]; mapView.settings.myLocationButton = YES; mapView.autoresizingMask = UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth | UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight; mapView.myLocationEnabled = YES; // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. [self.view addSubview:mapView]; mapView.hidden = YES;
Inviter l'utilisateur à sélectionner son lieu actuel
Utilisez le SDK Places pour iOS afin d'obtenir les cinq lieux les plus probables en fonction de la position actuelle de l'utilisateur, puis présentez la liste dans un UITableView. Lorsque l'utilisateur sélectionne un lieu, ajoutez un repère sur la carte.
- Obtenez une liste de lieux probables pour remplir un
UITableView, à partir duquel l'utilisateur peut sélectionner le lieu où il se trouve. - Ouvrez une nouvelle vue pour présenter à l'utilisateur des lieux susceptibles d'identifier sa position actuelle. Lorsque l'utilisateur appuie sur "Obtenir le lieu", nous passons à une nouvelle vue et lui présentons une liste de lieux possibles parmi lesquels choisir. La fonction
preparemet à jourPlacesViewControlleravec la liste des lieux probables actuels et est appelée automatiquement lorsqu'un segue est effectué. - Dans
PlacesViewController, remplissez le tableau à l'aide de la liste des lieux les plus probables, en utilisant l'extension de déléguéUITableViewDataSource. - Gérez la sélection de l'utilisateur à l'aide de l'extension de délégué
UITableViewDelegate.
Swift
// Populate the array with the list of likely places. func listLikelyPlaces() { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces.removeAll() let placeFields: GMSPlaceField = [.name, .coordinate] placesClient.findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocation(withPlaceFields: placeFields) { (placeLikelihoods, error) in guard error == nil else { // TODO: Handle the error. print("Current Place error: \(error!.localizedDescription)") return } guard let placeLikelihoods = placeLikelihoods else { print("No places found.") return } // Get likely places and add to the list. for likelihood in placeLikelihoods { let place = likelihood.place self.likelyPlaces.append(place) } } }
Objective-C
// Populate the array with the list of likely places. - (void) listLikelyPlaces { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces = [NSMutableArray array]; GMSPlaceField placeFields = GMSPlaceFieldName | GMSPlaceFieldCoordinate; [placesClient findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocationWithPlaceFields:placeFields callback:^(NSArray<GMSPlaceLikelihood *> * _Nullable likelihoods, NSError * _Nullable error) { if (error != nil) { // TODO: Handle the error. NSLog(@"Current Place error: %@", error.localizedDescription); return; } if (likelihoods == nil) { NSLog(@"No places found."); return; } for (GMSPlaceLikelihood *likelihood in likelihoods) { GMSPlace *place = likelihood.place; [likelyPlaces addObject:place]; } }]; }
Swift
// Prepare the segue. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "segueToSelect" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? PlacesViewController { nextViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces } } }
Objective-C
// Prepare the segue. - (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { if ([segue.identifier isEqualToString:@"segueToSelect"]) { if ([segue.destinationViewController isKindOfClass:[PlacesViewController class]]) { PlacesViewController *placesViewController = (PlacesViewController *)segue.destinationViewController; placesViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces; } } }
Swift
// Populate the table with the list of most likely places. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDataSource { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int { return likelyPlaces.count } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: cellReuseIdentifier, for: indexPath) let collectionItem = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] cell.textLabel?.text = collectionItem.name return cell } }
Objective-C
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource - (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section { return self.likelyPlaces.count; } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:cellReuseIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; } @end
Swift
class PlacesViewController: UIViewController { // ... // Pass the selected place to the new view controller. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "unwindToMain" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? MapViewController { nextViewController.selectedPlace = selectedPlace } } } } // Respond when a user selects a place. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDelegate { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) { selectedPlace = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] performSegue(withIdentifier: "unwindToMain", sender: self) } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5 } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForFooterInSection section: Int) -> CGFloat { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1 } return 0 } }
Objective-C
@interface PlacesViewController () <UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate> // ... -(void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { } #pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate // Respond when a user selects a place. -(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { self.selectedPlace = [self.likelyPlaces objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; [self performSegueWithIdentifier:@"unwindToMain" sender:self]; } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5; } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForFooterInSection:(NSInteger)section { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1; } return 0; }
Ajouter un repère à la carte
Lorsque l'utilisateur effectue une sélection, utilisez un segue de retour pour revenir à la vue précédente et ajoutez le repère à la carte. L'IBAction unwindToMain est appelé automatiquement lors du retour au contrôleur de vue principal.
Swift
// Update the map once the user has made their selection. @IBAction func unwindToMain(segue: UIStoryboardSegue) { // Clear the map. mapView.clear() // Add a marker to the map. if let place = selectedPlace { let marker = GMSMarker(position: place.coordinate) marker.title = selectedPlace?.name marker.snippet = selectedPlace?.formattedAddress marker.map = mapView } listLikelyPlaces() }
Objective-C
// Update the map once the user has made their selection. - (void) unwindToMain:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue { // Clear the map. [mapView clear]; // Add a marker to the map. if (selectedPlace != nil) { GMSMarker *marker = [GMSMarker markerWithPosition:selectedPlace.coordinate]; marker.title = selectedPlace.name; marker.snippet = selectedPlace.formattedAddress; marker.map = mapView; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; }
Félicitations ! Vous avez créé une application iOS qui permet à l'utilisateur de choisir son lieu actuel et d'afficher le résultat sur une carte Google. Au cours de cet atelier, vous avez appris à utiliser le SDK Places pour iOS, le SDK Maps pour iOS et le framework Apple Core Location.

