Selezionare Luogo attuale e Mostra dettagli su una mappa
Questo tutorial mostra come creare un'app per iOS che recupera la posizione attuale del dispositivo, identifica le posizioni probabili, chiede all'utente di selezionare la corrispondenza migliore e mostra un indicatore sulla mappa per la posizione scelta.
È adatto a chi ha una conoscenza di base o intermedia di Swift o Objective-C e una conoscenza generale di Xcode. Per una guida avanzata alla creazione di mappe, leggi la guida per gli sviluppatori.
In questo tutorial creerai la seguente mappa. Il marcatore sulla mappa si trova a San Francisco, California, ma si sposterà ovunque si trovi il dispositivo o il simulatore.
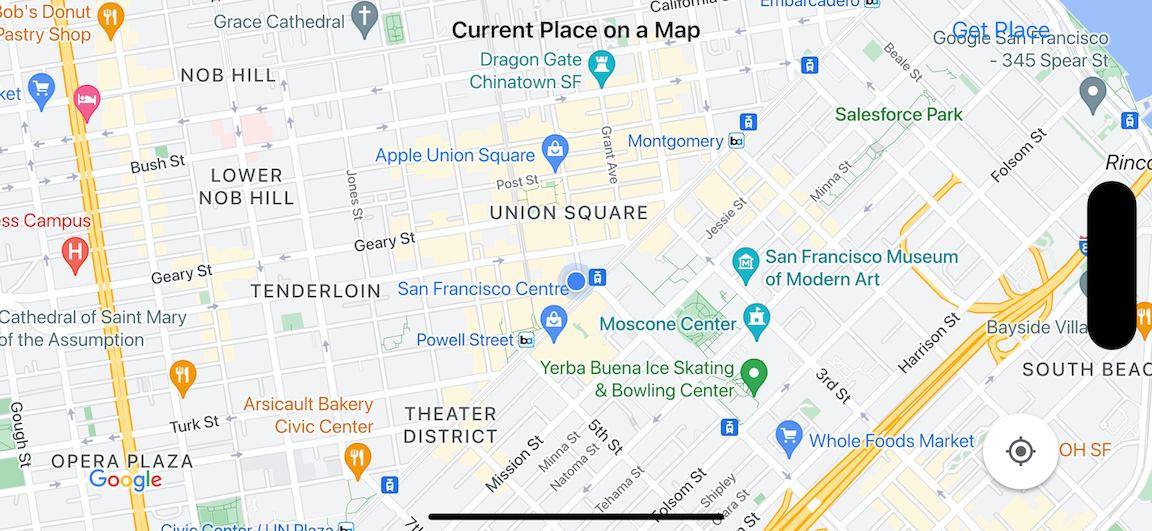
Questo tutorial utilizza l'SDK Places per iOS, l'SDK Maps per iOS e il framework Apple Core Location.
Ottieni il codice
Clona o scarica il repository di esempi di Google Maps per iOS da GitHub.In alternativa, fai clic sul pulsante seguente per scaricare il codice sorgente:
MapViewController
Swift
import UIKit import GoogleMaps import GooglePlaces class MapViewController: UIViewController { var locationManager: CLLocationManager! var currentLocation: CLLocation? var mapView: GMSMapView! var placesClient: GMSPlacesClient! var preciseLocationZoomLevel: Float = 15.0 var approximateLocationZoomLevel: Float = 10.0 // An array to hold the list of likely places. var likelyPlaces: [GMSPlace] = [] // The currently selected place. var selectedPlace: GMSPlace? // Update the map once the user has made their selection. @IBAction func unwindToMain(segue: UIStoryboardSegue) { // Clear the map. mapView.clear() // Add a marker to the map. if let place = selectedPlace { let marker = GMSMarker(position: place.coordinate) marker.title = selectedPlace?.name marker.snippet = selectedPlace?.formattedAddress marker.map = mapView } listLikelyPlaces() } override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() // Initialize the location manager. locationManager = CLLocationManager() locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization() locationManager.distanceFilter = 50 locationManager.startUpdatingLocation() locationManager.delegate = self placesClient = GMSPlacesClient.shared() // A default location to use when location permission is not granted. let defaultLocation = CLLocation(latitude: -33.869405, longitude: 151.199) // Create a map. let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.latitude, longitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: view.bounds, camera: camera) mapView.settings.myLocationButton = true mapView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight] mapView.isMyLocationEnabled = true // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. view.addSubview(mapView) mapView.isHidden = true listLikelyPlaces() } // Populate the array with the list of likely places. func listLikelyPlaces() { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces.removeAll() let placeFields: GMSPlaceField = [.name, .coordinate] placesClient.findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocation(withPlaceFields: placeFields) { (placeLikelihoods, error) in guard error == nil else { // TODO: Handle the error. print("Current Place error: \(error!.localizedDescription)") return } guard let placeLikelihoods = placeLikelihoods else { print("No places found.") return } // Get likely places and add to the list. for likelihood in placeLikelihoods { let place = likelihood.place self.likelyPlaces.append(place) } } } // Prepare the segue. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "segueToSelect" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? PlacesViewController { nextViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces } } } } // Delegates to handle events for the location manager. extension MapViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate { // Handle incoming location events. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) { let location: CLLocation = locations.last! print("Location: \(location)") let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: location.coordinate.latitude, longitude: location.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) if mapView.isHidden { mapView.isHidden = false mapView.camera = camera } else { mapView.animate(to: camera) } listLikelyPlaces() } // Handle authorization for the location manager. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didChangeAuthorization status: CLAuthorizationStatus) { // Check accuracy authorization let accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization switch accuracy { case .fullAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is precise.") case .reducedAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is not precise.") @unknown default: fatalError() } // Handle authorization status switch status { case .restricted: print("Location access was restricted.") case .denied: print("User denied access to location.") // Display the map using the default location. mapView.isHidden = false case .notDetermined: print("Location status not determined.") case .authorizedAlways: fallthrough case .authorizedWhenInUse: print("Location status is OK.") @unknown default: fatalError() } } // Handle location manager errors. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: Error) { locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation() print("Error: \(error)") } }
Objective-C
#import "MapViewController.h" #import "PlacesViewController.h" @import CoreLocation; @import GooglePlaces; @import GoogleMaps; @interface MapViewController () <CLLocationManagerDelegate> @end @implementation MapViewController { CLLocationManager *locationManager; CLLocation * _Nullable currentLocation; GMSMapView *mapView; GMSPlacesClient *placesClient; float preciseLocationZoomLevel; float approximateLocationZoomLevel; // An array to hold the list of likely places. NSMutableArray<GMSPlace *> *likelyPlaces; // The currently selected place. GMSPlace * _Nullable selectedPlace; } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; preciseLocationZoomLevel = 15.0; approximateLocationZoomLevel = 15.0; // Initialize the location manager. locationManager = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init]; locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest; [locationManager requestWhenInUseAuthorization]; locationManager.distanceFilter = 50; [locationManager startUpdatingLocation]; locationManager.delegate = self; placesClient = [GMSPlacesClient sharedClient]; // A default location to use when location permission is not granted. CLLocationCoordinate2D defaultLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.869405, 151.199); // Create a map. float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition *camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:defaultLocation.latitude longitude:defaultLocation.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; mapView = [GMSMapView mapWithFrame:self.view.bounds camera:camera]; mapView.settings.myLocationButton = YES; mapView.autoresizingMask = UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth | UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight; mapView.myLocationEnabled = YES; // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. [self.view addSubview:mapView]; mapView.hidden = YES; [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Populate the array with the list of likely places. - (void) listLikelyPlaces { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces = [NSMutableArray array]; GMSPlaceField placeFields = GMSPlaceFieldName | GMSPlaceFieldCoordinate; [placesClient findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocationWithPlaceFields:placeFields callback:^(NSArray<GMSPlaceLikelihood *> * _Nullable likelihoods, NSError * _Nullable error) { if (error != nil) { // TODO: Handle the error. NSLog(@"Current Place error: %@", error.localizedDescription); return; } if (likelihoods == nil) { NSLog(@"No places found."); return; } for (GMSPlaceLikelihood *likelihood in likelihoods) { GMSPlace *place = likelihood.place; [likelyPlaces addObject:place]; } }]; } // Update the map once the user has made their selection. - (void) unwindToMain:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue { // Clear the map. [mapView clear]; // Add a marker to the map. if (selectedPlace != nil) { GMSMarker *marker = [GMSMarker markerWithPosition:selectedPlace.coordinate]; marker.title = selectedPlace.name; marker.snippet = selectedPlace.formattedAddress; marker.map = mapView; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Prepare the segue. - (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { if ([segue.identifier isEqualToString:@"segueToSelect"]) { if ([segue.destinationViewController isKindOfClass:[PlacesViewController class]]) { PlacesViewController *placesViewController = (PlacesViewController *)segue.destinationViewController; placesViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces; } } } // Delegates to handle events for the location manager. #pragma mark - CLLocationManagerDelegate // Handle incoming location events. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray<CLLocation *> *)locations { CLLocation *location = locations.lastObject; NSLog(@"Location: %@", location); float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition * camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:location.coordinate.latitude longitude:location.coordinate.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; if (mapView.isHidden) { mapView.hidden = NO; mapView.camera = camera; } else { [mapView animateToCameraPosition:camera]; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Handle authorization for the location manager. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didChangeAuthorizationStatus:(CLAuthorizationStatus)status { // Check accuracy authorization CLAccuracyAuthorization accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization; switch (accuracy) { case CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is precise."); break; case CLAccuracyAuthorizationReducedAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is not precise."); break; } // Handle authorization status switch (status) { case kCLAuthorizationStatusRestricted: NSLog(@"Location access was restricted."); break; case kCLAuthorizationStatusDenied: NSLog(@"User denied access to location."); // Display the map using the default location. mapView.hidden = NO; case kCLAuthorizationStatusNotDetermined: NSLog(@"Location status not determined."); case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedAlways: case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedWhenInUse: NSLog(@"Location status is OK."); } } // Handle location manager errors. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didFailWithError:(NSError *)error { [manager stopUpdatingLocation]; NSLog(@"Error: %@", error.localizedDescription); } @end
PlacesViewController
Swift
import UIKit import GooglePlaces class PlacesViewController: UIViewController { // ... // Pass the selected place to the new view controller. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "unwindToMain" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? MapViewController { nextViewController.selectedPlace = selectedPlace } } } } // Respond when a user selects a place. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDelegate { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) { selectedPlace = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] performSegue(withIdentifier: "unwindToMain", sender: self) } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5 } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForFooterInSection section: Int) -> CGFloat { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1 } return 0 } } // Populate the table with the list of most likely places. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDataSource { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int { return likelyPlaces.count } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: cellReuseIdentifier, for: indexPath) let collectionItem = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] cell.textLabel?.text = collectionItem.name return cell } }
Objective-C
#import "PlacesViewController.h" @interface PlacesViewController () <UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate> // ... -(void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { } #pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate // Respond when a user selects a place. -(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { self.selectedPlace = [self.likelyPlaces objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; [self performSegueWithIdentifier:@"unwindToMain" sender:self]; } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5; } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForFooterInSection:(NSInteger)section { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1; } return 0; } #pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource - (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section { return self.likelyPlaces.count; } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:cellReuseIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; } @end
Inizia
Swift Package Manager
Maps SDK for iOS può essere installato utilizzando Swift Package Manager.
- Rimuovi tutte le dipendenze esistenti di Maps SDK for iOS.
- Apri una finestra del terminale e vai alla directory
tutorials/current-place-on-map. -
Chiudi lo spazio di lavoro Xcode ed esegui i seguenti comandi:
sudo gem install cocoapods-deintegrate cocoapods-clean pod deintegrate pod cache clean --all rm Podfile rm current-place-on-map.xcworkspace
- Apri il progetto Xcode ed elimina il podfile.
- Aggiungi gli SDK Places e Maps:
- Vai a File > Add Package Dependencies (File > Aggiungi dipendenze pacchetto).
- Inserisci https://github.com/googlemaps/ios-places-sdk come URL, premi Invio per importare il pacchetto e fai clic su Aggiungi pacchetto.
- Inserisci https://github.com/googlemaps/ios-maps-sdk come URL, premi Invio per importare il pacchetto e fai clic su Aggiungi pacchetto.
- Potresti dover reimpostare la cache dei pacchetti utilizzando File > Packages > Reset Package Cache (File > Pacchetti > Reimposta cache pacchetti).
Utilizzare CocoaPods
- Scarica e installa Xcode versione 26.0 o successive.
- Se non hai ancora CocoaPods,
installalo su macOS eseguendo il seguente comando dal terminale:
sudo gem install cocoapods
- Vai alla directory
tutorials/current-place-on-map. - Esegui il comando
pod install. In questo modo verranno installati gli SDK Maps e Places specificati inPodfile, insieme a eventuali dipendenze. - Esegui
pod outdatedper confrontare la versione del pod installata con eventuali nuovi aggiornamenti. Se viene rilevata una nuova versione, eseguipod updateper aggiornarePodfilee installare l'SDK più recente. Per maggiori dettagli, consulta la guida di CocoaPods. - Apri (fai doppio clic) il file current-place-on-map.xcworkspace
del progetto per aprirlo in Xcode. Per aprire il progetto, devi utilizzare il file
.xcworkspace.
Ottenere una chiave API e abilitare le API necessarie
Per completare questo tutorial, devi disporre di una chiave API di Google autorizzata a utilizzare l'Maps SDK for iOS e l'API Places.
- Segui le istruzioni riportate in Inizia a utilizzare Google Maps Platform per configurare un account di fatturazione e un progetto abilitato per entrambi i prodotti.
- Segui le istruzioni riportate in Recupera una chiave API per creare una chiave API per il progetto di sviluppo che hai configurato in precedenza.
Aggiungere la chiave API all'applicazione
Aggiungi la chiave API al tuo AppDelegate.swift nel seguente modo:
- Tieni presente che al file è stata aggiunta la seguente istruzione di importazione:
import GooglePlaces import GoogleMaps
- Modifica la seguente riga nel metodo
application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:), sostituendo YOUR_API_KEY con la tua chiave API:GMSPlacesClient.provideAPIKey("YOUR_API_KEY") GMSServices.provideAPIKey("YOUR_API_KEY")
Crea ed esegui la tua app
- Collega un dispositivo iOS al computer o seleziona un simulatore dal menu dello schema Xcode.
- Se utilizzi un dispositivo, assicurati che i servizi di localizzazione siano attivi. Se utilizzi un simulatore, seleziona una posizione dal menu Funzionalità.
- In Xcode, fai clic sull'opzione di menu Product/Run (Prodotto/Esegui) (o sull'icona del pulsante di riproduzione).
- Xcode crea l'app, quindi la esegue sul dispositivo o sul simulatore.
- Dovresti visualizzare una mappa con una serie di indicatori centrati sulla tua posizione attuale.
Risoluzione dei problemi:
- Se non vedi una mappa, verifica di aver ottenuto una chiave API e di averla aggiunta all'app, come descritto sopra. Controlla la console di debug di Xcode per i messaggi di errore relativi alla chiave API.
- Se hai limitato la chiave API in base all'identificatore bundle iOS, modifica la
chiave per aggiungere l'identificatore bundle per l'app:
com.google.examples.current-place-on-map. - La mappa non verrà visualizzata correttamente se la richiesta di autorizzazione per
i servizi di localizzazione viene rifiutata.
- Se utilizzi un dispositivo, vai a Impostazioni/Generali/Privacy/Servizi di localizzazione e riattiva i servizi di localizzazione.
- Se utilizzi un simulatore, vai a Simulatore/Reimposta contenuti e impostazioni…
- Assicurati di avere una buona connessione Wi-Fi o GPS.
- Se l'app viene avviata ma non viene visualizzata alcuna mappa, assicurati di aver aggiornato il file Info.plist per il tuo progetto con le autorizzazioni di accesso alla posizione appropriate. Per ulteriori informazioni sulla gestione delle autorizzazioni, consulta la guida alla richiesta dell'autorizzazione alla posizione nella tua app di seguito.
- Utilizza gli strumenti di debug di Xcode per visualizzare i log ed eseguire il debug dell'app.
comprendi il codice
Questa parte del tutorial spiega le sezioni più importanti dell'app current-place-on-map, per aiutarti a capire come creare un'app simile.
L'app current-place-on-map include due controller di visualizzazione:
uno per mostrare una mappa che indica il luogo selezionato dall'utente e uno
per presentare all'utente un elenco di luoghi probabili tra cui scegliere. Tieni presente che
ogni controller di visualizzazione ha le stesse variabili per il monitoraggio dell'elenco dei
luoghi probabili (likelyPlaces) e per indicare la selezione dell'utente (selectedPlace). La navigazione tra le visualizzazioni avviene
utilizzando i segway.
Richiesta dell'autorizzazione di accesso alla posizione
La tua app deve richiedere all'utente il consenso all'utilizzo dei servizi di localizzazione. Per farlo, includi la chiave NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription nel file Info.plist dell'app e imposta il valore di ogni chiave su una stringa che descrive come l'app intende utilizzare i dati sulla posizione.
Configurare il gestore della posizione
Utilizza CLLocationManager per trovare la posizione attuale del dispositivo e richiedere aggiornamenti regolari quando il dispositivo si sposta in una nuova posizione. Questo tutorial fornisce il codice necessario per ottenere la posizione del dispositivo. Per maggiori dettagli, consulta la guida su Come ottenere la posizione dell'utente nella documentazione per gli sviluppatori Apple.
- Dichiara il gestore della posizione, la posizione attuale, la visualizzazione della mappa, il client Places e il livello di zoom predefinito a livello di classe.
- Inizializza il gestore della posizione e
GMSPlacesClientinviewDidLoad(). - Dichiara le variabili per contenere l'elenco dei luoghi probabili e il luogo selezionato dall'utente.
- Aggiungi delegati per gestire gli eventi per il responsabile della sede utilizzando una clausola di estensione.
Swift
var locationManager: CLLocationManager! var currentLocation: CLLocation? var mapView: GMSMapView! var placesClient: GMSPlacesClient! var preciseLocationZoomLevel: Float = 15.0 var approximateLocationZoomLevel: Float = 10.0
Objective-C
CLLocationManager *locationManager; CLLocation * _Nullable currentLocation; GMSMapView *mapView; GMSPlacesClient *placesClient; float preciseLocationZoomLevel; float approximateLocationZoomLevel;
Swift
// Initialize the location manager. locationManager = CLLocationManager() locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization() locationManager.distanceFilter = 50 locationManager.startUpdatingLocation() locationManager.delegate = self placesClient = GMSPlacesClient.shared()
Objective-C
// Initialize the location manager. locationManager = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init]; locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest; [locationManager requestWhenInUseAuthorization]; locationManager.distanceFilter = 50; [locationManager startUpdatingLocation]; locationManager.delegate = self; placesClient = [GMSPlacesClient sharedClient];
Swift
// An array to hold the list of likely places. var likelyPlaces: [GMSPlace] = [] // The currently selected place. var selectedPlace: GMSPlace?
Objective-C
// An array to hold the list of likely places. NSMutableArray<GMSPlace *> *likelyPlaces; // The currently selected place. GMSPlace * _Nullable selectedPlace;
Swift
// Delegates to handle events for the location manager. extension MapViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate { // Handle incoming location events. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) { let location: CLLocation = locations.last! print("Location: \(location)") let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: location.coordinate.latitude, longitude: location.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) if mapView.isHidden { mapView.isHidden = false mapView.camera = camera } else { mapView.animate(to: camera) } listLikelyPlaces() } // Handle authorization for the location manager. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didChangeAuthorization status: CLAuthorizationStatus) { // Check accuracy authorization let accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization switch accuracy { case .fullAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is precise.") case .reducedAccuracy: print("Location accuracy is not precise.") @unknown default: fatalError() } // Handle authorization status switch status { case .restricted: print("Location access was restricted.") case .denied: print("User denied access to location.") // Display the map using the default location. mapView.isHidden = false case .notDetermined: print("Location status not determined.") case .authorizedAlways: fallthrough case .authorizedWhenInUse: print("Location status is OK.") @unknown default: fatalError() } } // Handle location manager errors. func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: Error) { locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation() print("Error: \(error)") } }
Objective-C
// Delegates to handle events for the location manager. #pragma mark - CLLocationManagerDelegate // Handle incoming location events. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray<CLLocation *> *)locations { CLLocation *location = locations.lastObject; NSLog(@"Location: %@", location); float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition * camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:location.coordinate.latitude longitude:location.coordinate.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; if (mapView.isHidden) { mapView.hidden = NO; mapView.camera = camera; } else { [mapView animateToCameraPosition:camera]; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; } // Handle authorization for the location manager. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didChangeAuthorizationStatus:(CLAuthorizationStatus)status { // Check accuracy authorization CLAccuracyAuthorization accuracy = manager.accuracyAuthorization; switch (accuracy) { case CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is precise."); break; case CLAccuracyAuthorizationReducedAccuracy: NSLog(@"Location accuracy is not precise."); break; } // Handle authorization status switch (status) { case kCLAuthorizationStatusRestricted: NSLog(@"Location access was restricted."); break; case kCLAuthorizationStatusDenied: NSLog(@"User denied access to location."); // Display the map using the default location. mapView.hidden = NO; case kCLAuthorizationStatusNotDetermined: NSLog(@"Location status not determined."); case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedAlways: case kCLAuthorizationStatusAuthorizedWhenInUse: NSLog(@"Location status is OK."); } } // Handle location manager errors. - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didFailWithError:(NSError *)error { [manager stopUpdatingLocation]; NSLog(@"Error: %@", error.localizedDescription); }
Aggiungere una mappa
Crea una mappa e aggiungila alla visualizzazione in viewDidLoad() nel
controller della visualizzazione principale. La mappa rimane nascosta finché non viene ricevuto un aggiornamento della posizione
(gli aggiornamenti della posizione vengono gestiti nell'estensione CLLocationManagerDelegate).
Swift
// A default location to use when location permission is not granted. let defaultLocation = CLLocation(latitude: -33.869405, longitude: 151.199) // Create a map. let zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == .fullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.latitude, longitude: defaultLocation.coordinate.longitude, zoom: zoomLevel) mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: view.bounds, camera: camera) mapView.settings.myLocationButton = true mapView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight] mapView.isMyLocationEnabled = true // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. view.addSubview(mapView) mapView.isHidden = true
Objective-C
// A default location to use when location permission is not granted. CLLocationCoordinate2D defaultLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.869405, 151.199); // Create a map. float zoomLevel = locationManager.accuracyAuthorization == CLAccuracyAuthorizationFullAccuracy ? preciseLocationZoomLevel : approximateLocationZoomLevel; GMSCameraPosition *camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithLatitude:defaultLocation.latitude longitude:defaultLocation.longitude zoom:zoomLevel]; mapView = [GMSMapView mapWithFrame:self.view.bounds camera:camera]; mapView.settings.myLocationButton = YES; mapView.autoresizingMask = UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth | UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight; mapView.myLocationEnabled = YES; // Add the map to the view, hide it until we've got a location update. [self.view addSubview:mapView]; mapView.hidden = YES;
Chiedere all'utente di selezionare il luogo in cui si trova
Utilizza Places SDK for iOS per ottenere le cinque probabilità
più alte per i luoghi in base alla posizione attuale dell'utente e presenta l'elenco in un
UITableView. Quando l'utente seleziona un luogo, aggiungi un indicatore alla
mappa.
- Ricevi un elenco di luoghi probabili per compilare un
UITableView, da cui l'utente può selezionare il luogo in cui si trova. - Apri una nuova visualizzazione per mostrare all'utente i luoghi più probabili. Quando l'utente
tocca "Ottieni luogo", viene visualizzata una nuova schermata e viene mostrato un elenco di possibili
luoghi tra cui scegliere. La funzione
prepareaggiornaPlacesViewControllercon l'elenco dei luoghi attuali più probabili e viene chiamata automaticamente quando viene eseguito un segue. - In
PlacesViewController, compila la tabella utilizzando l'elenco dei luoghi più probabili, utilizzando l'estensioneUITableViewDataSourcedelegate. - Gestisci la selezione dell'utente utilizzando l'estensione delegata
UITableViewDelegate.
Swift
// Populate the array with the list of likely places. func listLikelyPlaces() { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces.removeAll() let placeFields: GMSPlaceField = [.name, .coordinate] placesClient.findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocation(withPlaceFields: placeFields) { (placeLikelihoods, error) in guard error == nil else { // TODO: Handle the error. print("Current Place error: \(error!.localizedDescription)") return } guard let placeLikelihoods = placeLikelihoods else { print("No places found.") return } // Get likely places and add to the list. for likelihood in placeLikelihoods { let place = likelihood.place self.likelyPlaces.append(place) } } }
Objective-C
// Populate the array with the list of likely places. - (void) listLikelyPlaces { // Clean up from previous sessions. likelyPlaces = [NSMutableArray array]; GMSPlaceField placeFields = GMSPlaceFieldName | GMSPlaceFieldCoordinate; [placesClient findPlaceLikelihoodsFromCurrentLocationWithPlaceFields:placeFields callback:^(NSArray<GMSPlaceLikelihood *> * _Nullable likelihoods, NSError * _Nullable error) { if (error != nil) { // TODO: Handle the error. NSLog(@"Current Place error: %@", error.localizedDescription); return; } if (likelihoods == nil) { NSLog(@"No places found."); return; } for (GMSPlaceLikelihood *likelihood in likelihoods) { GMSPlace *place = likelihood.place; [likelyPlaces addObject:place]; } }]; }
Swift
// Prepare the segue. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "segueToSelect" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? PlacesViewController { nextViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces } } }
Objective-C
// Prepare the segue. - (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { if ([segue.identifier isEqualToString:@"segueToSelect"]) { if ([segue.destinationViewController isKindOfClass:[PlacesViewController class]]) { PlacesViewController *placesViewController = (PlacesViewController *)segue.destinationViewController; placesViewController.likelyPlaces = likelyPlaces; } } }
Swift
// Populate the table with the list of most likely places. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDataSource { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int { return likelyPlaces.count } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: cellReuseIdentifier, for: indexPath) let collectionItem = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] cell.textLabel?.text = collectionItem.name return cell } }
Objective-C
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource - (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section { return self.likelyPlaces.count; } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:cellReuseIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath]; } @end
Swift
class PlacesViewController: UIViewController { // ... // Pass the selected place to the new view controller. override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { if segue.identifier == "unwindToMain" { if let nextViewController = segue.destination as? MapViewController { nextViewController.selectedPlace = selectedPlace } } } } // Respond when a user selects a place. extension PlacesViewController: UITableViewDelegate { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) { selectedPlace = likelyPlaces[indexPath.row] performSegue(withIdentifier: "unwindToMain", sender: self) } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5 } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForFooterInSection section: Int) -> CGFloat { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1 } return 0 } }
Objective-C
@interface PlacesViewController () <UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate> // ... -(void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender { } #pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate // Respond when a user selects a place. -(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { self.selectedPlace = [self.likelyPlaces objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; [self performSegueWithIdentifier:@"unwindToMain" sender:self]; } // Adjust cell height to only show the first five items in the table // (scrolling is disabled in IB). -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { return self.tableView.frame.size.height/5; } // Make table rows display at proper height if there are less than 5 items. -(CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForFooterInSection:(NSInteger)section { if (section == tableView.numberOfSections - 1) { return 1; } return 0; }
Aggiungere un indicatore alla mappa
Quando l'utente effettua una selezione, utilizza un unwind segue per tornare alla
visualizzazione precedente e aggiungi il marcatore alla mappa. L'unwindToMain
IBAction viene chiamato automaticamente al ritorno al controller di visualizzazione principale.
Swift
// Update the map once the user has made their selection. @IBAction func unwindToMain(segue: UIStoryboardSegue) { // Clear the map. mapView.clear() // Add a marker to the map. if let place = selectedPlace { let marker = GMSMarker(position: place.coordinate) marker.title = selectedPlace?.name marker.snippet = selectedPlace?.formattedAddress marker.map = mapView } listLikelyPlaces() }
Objective-C
// Update the map once the user has made their selection. - (void) unwindToMain:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue { // Clear the map. [mapView clear]; // Add a marker to the map. if (selectedPlace != nil) { GMSMarker *marker = [GMSMarker markerWithPosition:selectedPlace.coordinate]; marker.title = selectedPlace.name; marker.snippet = selectedPlace.formattedAddress; marker.map = mapView; } [self listLikelyPlaces]; }
Complimenti! Hai creato un'app per iOS che consente all'utente di scegliere il luogo in cui si trova e mostra il risultato su una mappa di Google. Nel corso di questa operazione, hai imparato a utilizzare l'SDK Places per iOS, l'SDK Maps per iOS e il framework Apple Core Location.
