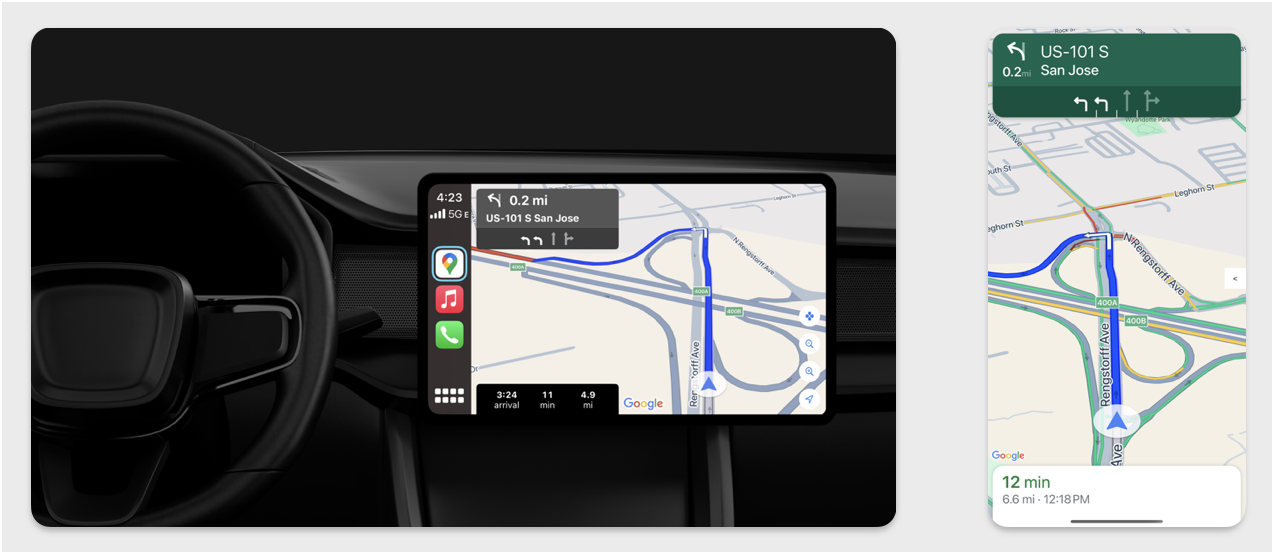
W tej sekcji opisujemy, jak używać pakietu Navigation SDK z biblioteką Apple CarPlay, aby wyświetlać nawigację w aplikacji na jednostkach głównych w samochodzie. Jeśli system na desce rozdzielczej kierowcy obsługuje CarPlay, kierowcy mogą korzystać z Twojej aplikacji bezpośrednio na wyświetlaczu samochodowym, podłączając telefon do urządzenia. Wskazówki głosowe są też odtwarzane przez głośniki w samochodzie.
Aplikację CarPlay tworzysz na podstawie zestawu szablonów interfejsu udostępnionych przez Apple. Twoja aplikacja odpowiada za wybór szablonu do wyświetlenia i za dostarczanie danych w jego obrębie.
System w samochodzie wyświetla zatwierdzone pod względem bezpieczeństwa elementy interaktywne, dzięki czemu kierowca może bezpiecznie dotrzeć do celu bez nadmiernego rozpraszania uwagi. Możesz też zaprogramować aplikację tak, aby kierowca mógł korzystać z jej funkcji, np. przyjmować lub odrzucać zamówienia albo wyświetlać lokalizację klienta na mapie. Aktualizacje stanu zamówienia można też zaprogramować tak, aby pojawiały się na urządzeniu w kokpicie.
Konfiguracja
Rozpocznij w CarPlay
Najpierw zapoznaj się z dokumentacją Apple:
Konfigurowanie pakietu Navigation SDK
- Po zapoznaniu się z dokumentacją Apple możesz zacząć korzystać z pakietu Navigation SDK.
- Skonfiguruj projekt, jeśli nie masz jeszcze zintegrowanego pakietu Navigation SDK z aplikacją.
- Włącz w aplikacji plik danych z instrukcjami krok po kroku.
- Opcjonalnie: Używaj wygenerowanych ikon z pakietu Navigation SDK.
- Narysuj mapę za pomocą klasy
GMSMapViewudostępnionej w klasie UIView. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Nawigowanie po trasie. Wypełnij poleCPNavigationSessiondanymi z biblioteki TurnByTurn.
Rysowanie interfejsu mapy i nawigacji
Klasa
GMSMapView
renderuje mapę, a klasa
CPMapTemplate
renderuje interfejs na ekranach CarPlay. Działa podobnie jak GMSMapView na telefonach, ale ma ograniczoną interaktywność.
Swift
init(window: CPWindow) {
super.init(nibName: nil, bundle: nil)
self.window = window
// More CPMapTemplate initialization
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let mapViewOptions = GMSMapViewOptions()
mapViewOptions.screen = window.screen
mapViewOptions.frame = self.view.bounds
mapView = GMSMapView(options: mapViewOptions)
mapView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleHeight, .flexibleWidth]
mapView.settings.isNavigationHeaderEnabled = false
mapView.settings.isNavigationFooterEnabled = false
// Disable buttons: in CarPlay, no part of the map is clickable.
// The app should instead place these buttons in the appropriate slots of the CarPlay template.
mapView.settings.compassButton = false
mapView.settings.isRecenterButtonEnabled = false
mapView.shouldDisplaySpeedometer = false
mapView.isMyLocationEnabled = true
self.view.addSubview(mapView)
}
Objective-C
- (instancetype)initWithWindow:(CPWindow *)window {
self = [super initWithNibName:nil bundle:nil];
if (self) {
_window = window;
// More CPMapTemplate initialization
}
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
GMSMapViewOptions *options = [[GMSMapViewOptions alloc] init];
options.screen = _window.screen;
options.frame = self.view.bounds;
_mapView = [[GMSMapView alloc] initWithOptions:options];
_mapView.autoresizingMask = UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight | UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth;
_mapView.settings.navigationHeaderEnabled = NO;
_mapView.settings.navigationFooterEnabled = NO;
// Disable buttons: in CarPlay, no part of the map is clickable.
// The app should instead place these buttons in the appropriate slots of the CarPlay template.
_mapView.settings.compassButton = NO;
_mapView.settings.recenterButtonEnabled = NO;
_mapView.shouldDisplaySpeedometer = NO;
_mapView.myLocationEnabled = YES;
[self.view addSubview:_mapView];
}
Włącz interakcję z mapą
Aby zapewnić bezpieczeństwo kierowcy, CarPlay ogranicza interakcję z ekranem do kilkuCPMapTemplateDelegate metod. Użyj tych wywołań zwrotnych, aby umożliwić kierowcy ograniczoną interakcję z mapą na ekranie w samochodzie.
Aby obsługiwać dodatkowe działania użytkowników, utwórz tablicę CPMapButton i przypisz ją doCPMapTemplate.mapButtons.
Poniższy kod tworzy interakcje przesuwania i przyciski do przesuwania, powiększania i pomniejszania oraz określania lokalizacji użytkownika.
Interakcje z przesuwaniem
Swift
// MARK: CPMapTemplateDelegate
func mapTemplate(_ mapTemplate: CPMapTemplate, panBeganWith direction: CPMapTemplate.PanDirection) {
}
func mapTemplate(_ mapTemplate: CPMapTemplate, panWith direction: CPMapTemplate.PanDirection) {
let scrollAmount = scrollAmount(for: direction)
let scroll = GMSCameraUpdate.scrollBy(x: scrollAmount.x, y: scrollAmount.y)
mapView.animate(with: scroll)
}
func mapTemplate(_ mapTemplate: CPMapTemplate, panEndedWith direction: CPMapTemplate.PanDirection) {
}
func scrollAmount(for panDirection: CPMapTemplate.PanDirection) -> CGPoint {
let scrollDistance = 80.0
var scrollAmount = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
switch panDirection {
case .left:
scrollAmount.x -= scrollDistance
break;
case .right:
scrollAmount.x += scrollDistance
break;
case .up:
scrollAmount.y += scrollDistance
break;
case .down:
scrollAmount.y -= scrollDistance
break;
default:
break;
}
if scrollAmount.x != 0 && scrollAmount.y != 0 {
// Adjust length if scrolling diagonally.
scrollAmount = CGPointMake(scrollAmount.x * sqrt(1.0/2.0), scrollAmount.y * sqrt(1.0/2.0))
}
return scrollAmount
}
Objective-C
#pragma mark - CPMapTemplateDelegate
- (void)mapTemplate:(CPMapTemplate *)mapTemplate panBeganWithDirection:(CPPanDirection)direction {
}
- (void)mapTemplate:(CPMapTemplate *)mapTemplate panWithDirection:(CPPanDirection)direction {
CGPoint scrollAmount = [self scrollAmountForPanDirection:direction];
GMSCameraUpdate *scroll = [GMSCameraUpdate scrollByX:scrollAmount.x Y:scrollAmount.y];
[_mapView animateWithCameraUpdate:scroll];
}
- (void)mapTemplate:(CPMapTemplate *)mapTemplate panEndedWithDirection:(CPPanDirection)direction {
}
- (CGPoint)scrollAmountForPanDirection:(CPPanDirection)direction {
static const CGFloat scrollDistance = 80.;
CGPoint scrollAmount = {0., 0.};
if (direction & CPPanDirectionLeft) {
scrollAmount.x = -scrollDistance;
}
if (direction & CPPanDirectionRight) {
scrollAmount.x = scrollDistance;
}
if (direction & CPPanDirectionUp) {
scrollAmount.y = -scrollDistance;
}
if (direction & CPPanDirectionDown) {
scrollAmount.y = scrollDistance;
}
if (scrollAmount.x != 0 && scrollAmount.y != 0) {
// Adjust length if scrolling diagonally.
scrollAmount =
CGPointMake(scrollAmount.x * (CGFloat)M_SQRT1_2, scrollAmount.y * (CGFloat)M_SQRT1_2);
}
return scrollAmount;
}
Typowe zastosowania przycisków
Swift
// MARK: Create Buttons
func createMapButtons() -> [CPMapButton] {
let panButton = mapButton(systemImageName: "dpad.fill") { [weak self] in
self?.didTapPanButton()
}
let zoomOutButton = mapButton(systemImageName: "minus.magnifyingglass") { [weak self] in
self?.didTapZoomOutButton()
}
let zoomInButton = mapButton(systemImageName: "plus.magnifyingglass") { [weak self] in
self?.didTapZoomInButton()
}
let myLocationButton = mapButton(systemImageName: "location") { [weak self] in
self?.didTapMyLocationButton()
}
let mapButtons = [panButton, zoomOutButton, zoomInButton, myLocationButton]
return mapButtons
}
func mapButton(systemImageName: String, handler: @escaping () -> Void) -> CPMapButton {
}
// MARK: Button callbacks
@objc func didTapPanButton() {
mapTemplate?.showPanningInterface(animated: true)
}
@objc func didTapZoomOutButton() {
mapView.animate(with: GMSCameraUpdate.zoomOut())
}
@objc func didTapZoomInButton() {
mapView.animate(with: GMSCameraUpdate.zoomIn())
}
@objc func didTapMyLocationButton() {
if let lastLocation = lastLocation {
let cameraPosition = GMSCameraPosition(target: lastLocation.coordinate, zoom: 15)
mapView.animate(to: cameraPosition)
}
}
Objective-C
#pragma mark - Create Buttons
- (NSArray<CPMapButton *>*)createMapButtons {
NSMutableArray<CPMapButton *> *mapButtons = [NSMutableArray<CPMapButton *> array];
__weak __typeof__(self) weakSelf = self;
CPMapButton *panButton = [self mapButtonWithSystemImageNamed:@"dpad.fill"
handler:^(CPMapButton *_) {
[weakSelf didTapPanButton];
}];
[mapButtons addObject:panButton];
CPMapButton *zoomOutButton =
[self mapButtonWithSystemImageNamed:@"minus.magnifyingglass"
handler:^(CPMapButton *_Nonnull mapButon) {
[weakSelf didTapZoomOutButton];
}];
[mapButtons addObject:zoomOutButton];
CPMapButton *zoomInButton =
[self mapButtonWithSystemImageNamed:@"plus.magnifyingglass"
handler:^(CPMapButton *_Nonnull mapButon) {
[weakSelf didTapZoomInButton];
}];
[mapButtons addObject:zoomInButton];
CPMapButton *myLocationButton =
[self mapButtonWithSystemImageNamed:@"location"
handler:^(CPMapButton *_Nonnull mapButton) {
[weakSelf didTapMyLocationButton];
}];
[mapButtons addObject:myLocationButton];
return mapButtons;
}
#pragma mark - Button Callbacks
- (void)didTapZoomOutButton {
[_mapView animateWithCameraUpdate:[GMSCameraUpdate zoomOut]];
}
- (void)didTapZoomInButton {
[_mapView animateWithCameraUpdate:[GMSCameraUpdate zoomIn]];
}
- (void)didTapMyLocationButton {
CLLocation *location = self.lastLocation;
if (location) {
GMSCameraPosition *position =
[[GMSCameraPosition alloc] initWithTarget:self.lastLocation.coordinate zoom:15.];
[_mapView animateToCameraPosition:position];
}
}
- (void)didTapPanButton {
[_mapTemplate showPanningInterfaceAnimated:YES];
_isPanningInterfaceEnabled = YES;
}
- (void)didTapStopPanningButton {
[_mapTemplate dismissPanningInterfaceAnimated:YES];
_isPanningInterfaceEnabled = NO;
}
Uwaga: na ekranie CarPlay nie można wybierać tras alternatywnych. Muszą być wybrane na telefonie przed uruchomieniem CarPlay.
Wyświetlanie wskazówek nawigacyjnych
Z tej sekcji dowiesz się, jak skonfigurować odbiornik pliku danych i jak wypełniać panele wskazówek i szacowania podróży wskazówkami nawigacyjnymi. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w sekcji „Tworzenie aplikacji do nawigacji w CarPlay” w przewodniku programowania aplikacji na CarPlay.

Panele wskazówek i szacowania czasu podróży zawierają kartę nawigacji, która wyświetla informacje o nawigacji związane z bieżącą podróżą. Biblioteka TurnByTurn w pakiecie SDK Navigation może pomóc w przekazywaniu niektórych z tych informacji, takich jak symbol, tekst i pozostały czas.
Konfigurowanie odbiornika
Postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami konfigurowania odbiornika zdarzeń w sekcji Szczegóły pliku danych z instrukcjami krok po kroku.
Wypełnianie informacji nawigacyjnych
Pierwsza część poniższego przykładowego kodu pokazuje, jak tworzyć szacunki czasu podróży w CarPlay, tłumacząc GMSNavigationNavInfo.timeToCurrentStepSeconds na CPTravelEstimate. Więcej informacji o tych i innych elementach wyświetlania znajdziesz w szczegółach dotyczących pliku danych z instrukcjami krok po kroku.
Druga część przykładu pokazuje, jak utworzyć obiekt i zapisać go w polu userInfo obiektu CPManuevers. Określa to CPManeuverDisplayStyle, która jest też używana do informacji o pasach ruchu. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w przewodniku po programowaniu aplikacji CarPlay firmy Apple.
Swift
// Get a CPTravelEstimate from GMSNavigationNavInfo
func getTravelEstimates(from navInfo:GMSNavigationNavInfo) -> CPTravelEstimates {
let distanceRemaining = navInfo.roundedDistance(navInfo.distanceToCurrentStepMeters)
let timeRemaining = navInfo.roundedTime(navInfo.timeToCurrentStepSeconds)
let travelEstimates = CPTravelEstimates(distanceRemaining: distanceRemaining, timeRemaining: timeRemaining)
return travelEstimates
}
// Create an object to be stored in the userInfo field of CPManeuver to determine the CPManeuverDisplayStyle.
/** An object to be stored in the userInfo field of a CPManeuver. */
struct ManeuverUserInfo {
var stepInfo: GMSNavigationStepInfo
var isLaneGuidance: Bool
}
func mapTemplate(_ mapTemplate: CPMapTemplate, displayStyleFor maneuver: CPManeuver) -> CPManeuverDisplayStyle {
let userInfo = maneuver.userInfo
if let maneuverUserInfo = userInfo as? ManeuverUserInfo {
return maneuverUserInfo.isLaneGuidance ? .symbolOnly : .leadingSymbol
}
return .leadingSymbol
}
// Get a CPManeuver with instructionVariants and symbolImage from GMSNavigationStepInfo
func getManeuver(for stepInfo: GMSNavigationStepInfo) -> CPManeuver {
let maneuver = CPManeuver()
maneuver.userInfo = ManeuverUserInfo(stepInfo: stepInfo, isLaneGuidance: false)
switch stepInfo.maneuver {
case .destination:
maneuver.instructionVariants = ["Your destination is ahead."]
break
case .destinationLeft:
maneuver.instructionVariants = ["Your destination is ahead on your left."]
break
case .destinationRight:
maneuver.instructionVariants = ["Your destination is ahead on your right."]
break
default:
maneuver.attributedInstructionVariants = currentNavInfo?.instructions(forStep: stepInfo, options: instructionOptions)
break
}
maneuver.symbolImage = stepInfo.maneuverImage(with: instructionOptions.imageOptions)
return maneuver
}
// Get the lane image for a CPManeuver from GMSNavigationStepInfo
func laneGuidanceManeuver(for stepInfo: GMSNavigationStepInfo) -> CPManeuver? {
let maneuver = CPManeuver()
maneuver.userInfo = ManeuverUserInfo(stepInfo: stepInfo, isLaneGuidance: true)
let lanesImage = stepInfo.lanesImage(with: imageOptions)
guard let lanesImage = lanesImage else { return nil }
maneuver.symbolImage = lanesImage
return maneuver
}
Objective-C
// Get a CPTravelEstimate from GMSNavigationNavInfo
- (nonull CPTravelEstimates *)travelEstimates:(GMSNavigationNavInfo *_Nonnull navInfo) {
NSMeasurement<NSUnitLength *> *distanceRemaining = [navInfo roundedDistance:navInfo.distanceToCurrentStepMeters];
NSTimeInterval timeRemaining = [navInfo roundedTime:navInfo.timeToCurrentStepSeconds];
CPTravelEstimate* travelEstimate = [[CPTravelEstimates alloc] initWithDistanceRemaining:distanceRemaining
timeRemaining:timeRemaining];
}
// Create an object to be stored in the userInfo field of CPManeuver to determine the CPManeuverDisplayStyle.
/** An object to be stored in the userInfo field of a CPManeuver. */
@interface ManeuverUserInfo : NSObject
@property(nonatomic, readonly, nonnull) GMSNavigationStepInfo *stepInfo;
@property(nonatomic, readonly, getter=isLaneGuidance) BOOL laneGuidance;
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithStepInfo:(GMSNavigationStepInfo *)stepInfo
isLaneGuidance:(BOOL)isLaneGuidance NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
- (instancetype)init NS_UNAVAILABLE;
@end
- (CPManeuverDisplayStyle)mapTemplate:(CPMapTemplate *)mapTemplate
displayStyleForManeuver:(nonnull CPManeuver *)maneuver {
ManeuverUserInfo *userInfo = maneuver.userInfo;
return userInfo.laneGuidance ? CPManeuverDisplayStyleSymbolOnly : CPManeuverDisplayStyleDefault;
}
// Get a CPManeuver with instructionVariants and symbolImage from GMSNavigationStepInfo
- (nonnull CPManeuver *)maneuverForStep:(nonnull GMSNavigationStepInfo *)stepInfo {
CPManeuver *maneuver = [[CPManeuver alloc] init];
maneuver.userInfo = [[ManeuverUserInfo alloc] initWithStepInfo:stepInfo isLaneGuidance:NO];
switch (stepInfo.maneuver) {
case GMSNavigationManeuverDestination:
maneuver.instructionVariants = @[ @"Your destination is ahead." ];
break;
case GMSNavigationManeuverDestinationLeft:
maneuver.instructionVariants = @[ @"Your destination is ahead on your left." ];
break;
case GMSNavigationManeuverDestinationRight:
maneuver.instructionVariants = @[ @"Your destination is ahead on your right." ];
break;
default: {
maneuver.attributedInstructionVariants =
[_currentNavInfo instructionsForStep:stepInfo options:_instructionOptions];
break;
}
}
maneuver.symbolImage = [stepInfo maneuverImageWithOptions:_instructionOptions.imageOptions];
return maneuver;
}
// Get the lane image for a CPManeuver from GMSNavigationStepInfo
- (nullable CPManeuver *)laneGuidanceManeuverForStep:(nonnull GMSNavigationStepInfo *)stepInfo {
CPManeuver *maneuver = [[CPManeuver alloc] init];
maneuver.userInfo = [[ManeuverUserInfo alloc] initWithStepInfo:stepInfo isLaneGuidance:YES];
UIImage *lanesImage = [stepInfo lanesImageWithOptions:_imageOptions];
if (!lanesImage) {
return nil;
}
maneuver.symbolImage = lanesImage;
return maneuver;
}
Manewry
CarPlay używa CPManeuverklasy, aby podawać wskazówki dojazdu krok po kroku. Więcej informacji o manewrach i wskazówkach dotyczących pasa ruchu znajdziesz w szczegółach dotyczących pliku danych z instrukcjami skrętu.
Powiązana dokumentacja
- https://developer.apple.com/carplay/
- https://developer.apple.com/carplay/documentation/CarPlay-App-Programming-Guide.pdf
- https://developer.apple.com/design/human-interface-guidelines/carplay
- Szczegóły pliku danych o nawigacji krok po kroku
- Nawigowanie po trasie

