جزء جزئیات مکان
جزء Place Details در Places UI Kit به شما امکان می دهد یک مؤلفه UI جداگانه اضافه کنید که جزئیات مکان را در برنامه شما نمایش می دهد. این جزء قابل تنظیم است.
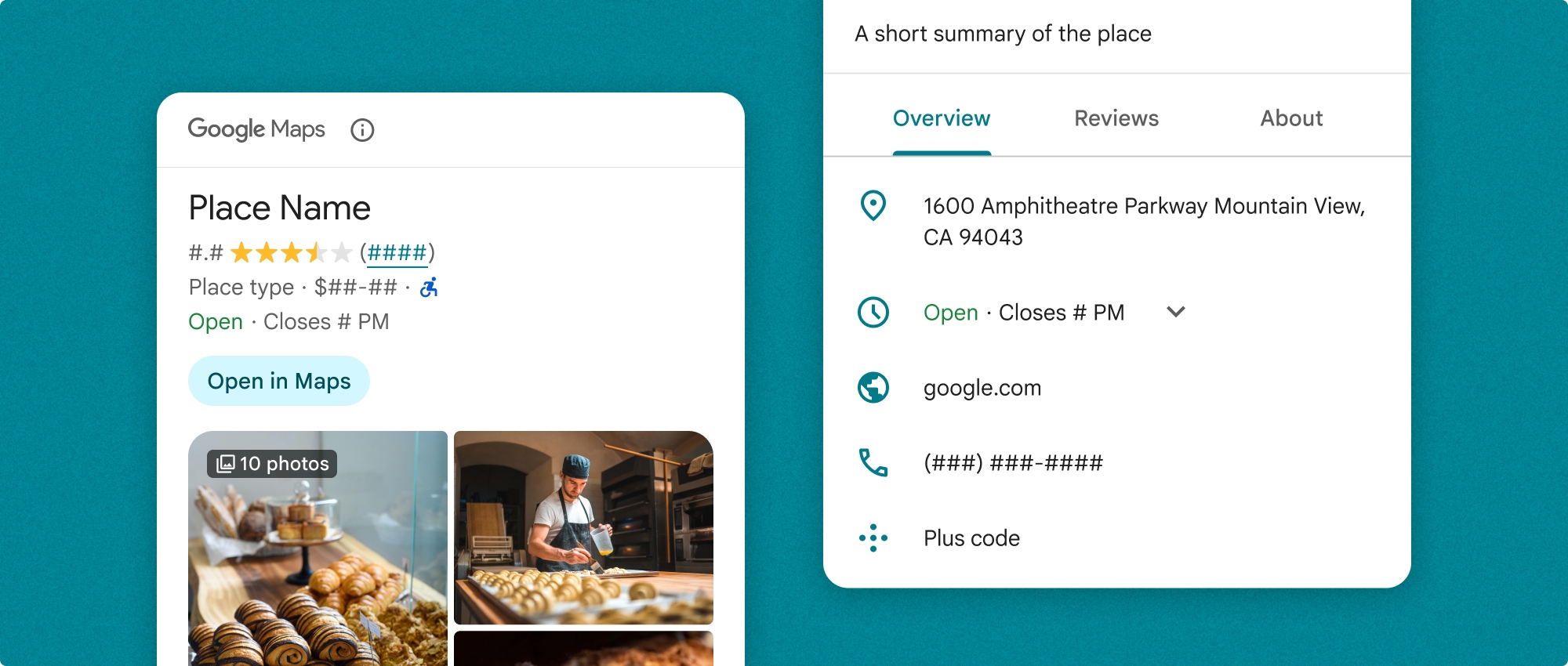
مولفه Place Details را می توان به طور مستقل یا همراه با سایر APIها و سرویس های پلتفرم Google Maps استفاده کرد. مؤلفه یا شناسه مکان ، نام منبع، یا مختصات طول و عرض جغرافیایی را می گیرد و اطلاعات جزئیات مکان ارائه شده را برمی گرداند.
مولفه Place Details کاملاً مضمونپذیر است و به شما این امکان را میدهد که فونتها، رنگها و شعاع گوشهها را مطابق با مورد استفاده و دستورالعملهای برند بصری خود سفارشی کنید. میتوانید ظاهر جزئیات مکان را با ایجاد تمی که PlacesMaterialTheme را گسترش میدهد و ویژگیهای موضوع را لغو میکند، سفارشی کنید. همچنین میتوانید با تعیین فهرستی از ورودیهای محتوا، که هر کدام مربوط به اطلاعاتی است که در مورد مکان نشان داده شده است، فیلدهای جزئیات مکان را سفارشی کنید.
انواع چیدمان
مولفه Place Details از دو نوع چیدمان اصلی پشتیبانی می کند:
- فشرده: طرحی برای پیش نمایش اطلاعات کلیدی.
- کامل: یک طرح جامع که تمام جزئیات مکان موجود را نمایش می دهد.
طرح فشرده می تواند در جهت عمودی یا افقی نمایش داده شود. این به شما امکان می دهد کامپوننت را در طرح بندی های مختلف طراحی و اندازه های صفحه ادغام کنید. طرح کامل فقط می تواند به صورت عمودی نمایش داده شود.
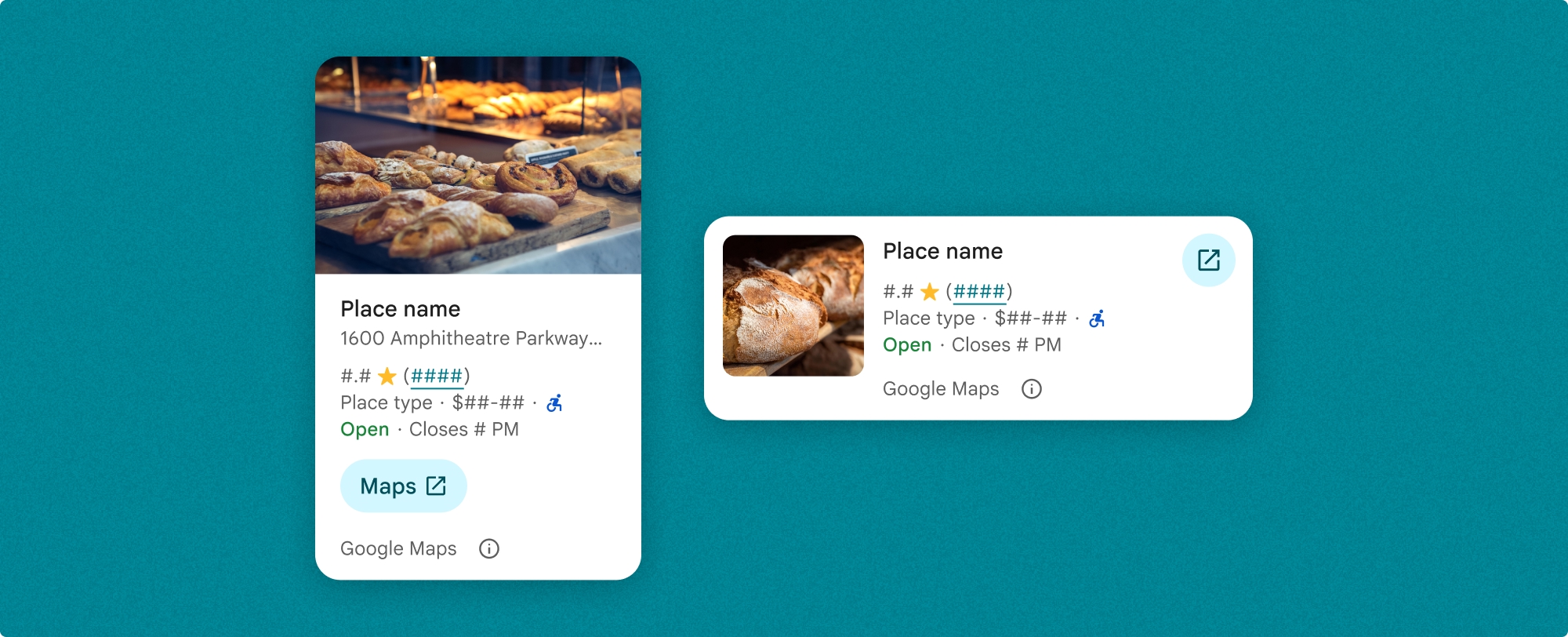
مؤلفه Place Details به شما کنترل دقیقی بر محتوای نمایش داده شده در مؤلفه می دهد. هر عنصر (مانند عکسها، نظرات، و اطلاعات تماس) میتواند بهصورت جداگانه نشان داده یا پنهان شود، که امکان سفارشیسازی دقیق ظاهر اجزا و چگالی اطلاعات را فراهم میکند.

نمای فشرده مکان جزئیات
قطعه فشرده Place Details ( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment ) جزئیات یک مکان انتخاب شده را با استفاده از حداقل فضا ارائه می دهد. این ممکن است در یک پنجره اطلاعاتی که مکان را روی نقشه برجسته میکند، در یک تجربه رسانههای اجتماعی مانند اشتراکگذاری یک مکان در چت، به عنوان پیشنهادی برای انتخاب مکان فعلیتان، یا در یک مقاله رسانهای برای ارجاع به مکان در Google Maps مفید باشد.
جزئیات مکان نمای کامل
نمای کامل جزئیات مکان ( PlaceDetailsFragment ) سطح بزرگتری را برای نمایش اطلاعات جزئیات مکان ارائه می دهد و به شما امکان می دهد انواع بیشتری از اطلاعات را نمایش دهید.
گزینه های نمایش محتوا
میتوانید با استفاده از فهرستهای موجود در PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.Content یا PlaceDetailsFragment.Content مشخص کنید که کدام محتوا نمایش داده شود.
| نمای فشرده | نمای کامل |
|---|---|
|
|
صورتحساب
هنگام استفاده از Place Details UI Kit، برای هر بار فراخوانی روش .loadWithPlaceId() .loadWithResourceName() یا loadWithCoordinates() صورتحساب دریافت می کنید. اگر یک مکان را چندین بار بارگیری کنید، برای هر درخواست صورتحساب دریافت می کنید.
برای اینکه چندین بار شارژ نشوید، مستقیماً .loadWithPlaceId() یا .loadWithResourceName() را در روش های چرخه عمر Android اضافه نکنید. برای مثال، در متد onResume() مستقیماً .loadWithPlaceId() یا .loadWithResourceName() را فراخوانی نکنید.
جزئیات مکان را به برنامه خود اضافه کنید
می توانید با افزودن یک قطعه به یک طرح، جزئیات مکان را به برنامه خود اضافه کنید. وقتی قطعه را نمونهسازی میکنید، میتوانید ظاهر و احساس اطلاعات جزئیات مکان را مطابق با نیازهایتان و مطابقت با ظاهر برنامهتان سفارشی کنید. درباره سفارشی سازی بیشتر بیاموزید .
شما سه روش در Kotlin و Java در دسترس دارید: یکی برای بارگیری قطعه با شناسه مکان ( loadWithPlaceId() )، یکی برای بارگیری قطعه با نام منبع ( loadWithResourceName() ) و دیگری برای بارگیری قطعه با مختصات طول و عرض جغرافیایی ( loadWithCoordinates() ). شما می توانید هر روش یا چند روش را انتخاب کنید.
موقعیت پیش فرض برای نمای فشرده، عمودی است. اگر میخواهید یک طرح افقی داشته باشید، Orientation.HORIZONTAL مشخص کنید. همچنین می توانید به صورت اختیاری Orientation.VERTICAL برای وضوح مشخص کنید. نمای کامل فقط به صورت عمودی قابل نمایش است.
نمونههایی را در بخش نمونههای جزء جزئیات مکان ببینید.
ظاهر بصری را سفارشی کنید
یک ظاهر طراحی سفارشی
میتوانید رنگها، تایپوگرافی، فاصلهها، حاشیهها و گوشههای جزء جزئیات مکان خود را سفارشی کنید.
کیت UI Places یک رویکرد سیستم طراحی را برای سفارشیسازی بصری تقریباً بر اساس طراحی متریال (با برخی تغییرات خاص Google-Maps) ارائه میکند. به مرجع طراحی متریال برای رنگ و تایپوگرافی مراجعه کنید. به طور پیش فرض، این سبک به زبان طراحی بصری Google Maps پایبند است.
Places UI Kit به طور پیشفرض یک تم تیره ارائه میکند، بنابراین ممکن است لازم باشد هر دو تم تاریک و روشن را سفارشی کنید. برای سفارشی کردن تم تیره، یک ورودی برای رنگ در values-night/colors.xml اضافه کنید.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد استایل به بخش استایل سفارشی مراجعه کنید.
سفارشی سازی عرض و ارتفاع
نماهای فشرده
عرض های پیشنهادی:
- جهت عمودی: بین 180 و 300dp.
- جهت افقی: بین 180dp تا 500dp.
عرض های کوچکتر از 160dp ممکن است به درستی نمایش داده نشوند.
بهترین روش این است که ارتفاعی را برای نماهای فشرده تنظیم نکنید. این به محتوای پنجره اجازه می دهد تا ارتفاع را تنظیم کند و اجازه می دهد تمام اطلاعات نمایش داده شوند.
نماهای کامل
برای نماهای کامل، عرض توصیه شده بین 250dp تا 450dp است. عرض کوچکتر از 250dp ممکن است به درستی نمایش داده نشود.
می توانید ارتفاع مؤلفه را تنظیم کنید: نمای عمودی جزئیات مکان به صورت عمودی در فضای اختصاص داده شده حرکت می کند.
بهترین روش این است که ارتفاع را برای نمایش کامل تنظیم کنید. این به محتوای پنجره اجازه می دهد تا به درستی اسکرول شود.
نمونههای جزء جزئیات مکان
یک نمای فشرده یا کامل ایجاد کنید
کاتلین
// We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } }
جاوا
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( Orientation.HORIZONTAL, Arrays.asList(Content.ADDRESS, Content.TYPE, Content.RATING, Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE_ICON), R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme); fragment.setPlaceLoadListener( new PlaceLoadListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Place place) { ... } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { ... } }); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commitNow(); // Load the fragment with a Place ID. fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId); // Load the fragment with a resource name. fragment.loadWithResourceName(resourceName);
این نمونه کد کامل جهت نمای فشرده را به صورت برنامه نویسی بر اساس پیکربندی دستگاه کاربر تعیین می کند.
کاتلین
package com.example.placedetailsuikit import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.content.res.Configuration import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.activity.viewModels import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import com.example.placedetailsuikit.databinding.ActivityMainBinding import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PointOfInterest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceDetailsCompactFragment import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceLoadListener import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.Orientation private const val TAG = "PlacesUiKit" /** * A simple ViewModel to store UI state that needs to survive configuration changes. * In this case, it holds the ID of the selected place. Using a ViewModel is good practice * as it prevents data loss during events like screen rotation, ensuring a * seamless user experience. */ class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { var selectedPlaceId: String? = null } /** * This activity serves as a basic example of integrating the Place Details UI Kit. * It demonstrates the fundamental steps required: * 1. Setting up a Google Map. * 2. Requesting location permissions to center the map. * 3. Handling clicks on Points of Interest (POIs) to get a Place ID. * 4. Using the Place ID to load and display place details in a [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. */ class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPoiClickListener { // ViewBinding provides type-safe access to views defined in the XML layout, // eliminating the need for `findViewById` and preventing null pointer exceptions. private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding private var googleMap: GoogleMap? = null // The FusedLocationProviderClient is the main entry point for interacting with the // fused location provider, which intelligently manages the underlying location technologies. private lateinit var fusedLocationClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // Using registerForActivityResult is the modern, recommended approach for handling // permission requests. It decouples the request from the handling logic, making the // code cleaner and easier to manage compared to the older `onRequestPermissionsResult` callback. private lateinit var requestPermissionLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<Array<String>> // The `by viewModels()` delegate provides a lazy-initialized ViewModel scoped to this Activity. // This ensures that we get the same ViewModel instance across configuration changes. private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // The ActivityResultLauncher is initialized here. The lambda defines the callback // that will be executed once the user responds to the permission dialog. requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestMultiplePermissions()) { permissions -> // We check if either fine or coarse location permission was granted. if (permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] == true || permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] == true) { Log.d(TAG, "Location permission granted by user.") fetchLastLocation() } else { // If permission is denied, we inform the user and default to a known location. // This ensures the app remains functional even without location access. Log.d(TAG, "Location permission denied by user.") Toast.makeText( this, "Location permission denied. Showing default location.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() moveToSydney() } } // enableEdgeToEdge() allows the app to draw behind the system bars for a more immersive experience. enableEdgeToEdge() binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.dismissButton.setOnClickListener { dismissPlaceDetails() } // --- Crucial: Initialize Places SDK --- // It's essential to initialize the Places SDK before making any other Places API calls. // This should ideally be done once, for example, in the Application's `onCreate`. val apiKey = BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY if (apiKey.isEmpty() || apiKey == "YOUR_API_KEY") { // A valid API key is required for the Places SDK to function. Log.e(TAG, "No api key") Toast.makeText( this, "Add your own API_KEY in local.properties", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() finish() return } // `initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled` is used to opt-in to the new SDK version. Places.initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled(applicationContext, apiKey) fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // ------------------------------------ // The SupportMapFragment is the container for the map. `getMapAsync` allows us to // work with the GoogleMap object via a callback once it's fully initialized. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map_fragment) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) // This block handles restoration after a configuration change (e.g., screen rotation). // If a place was selected before the rotation, its ID is stored in the ViewModel. // We use this ID to immediately show the details fragment again. if (viewModel.selectedPlaceId != null) { viewModel.selectedPlaceId?.let { placeId -> Log.d(TAG, "Restoring PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } } } /** * This callback is triggered when the GoogleMap object is ready to be used. * All map setup logic should be placed here. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { Log.d(TAG, "Map is ready") googleMap = map // Setting the OnPoiClickListener allows us to capture user taps on points of interest. googleMap?.setOnPoiClickListener(this) // After the map is ready, we determine the initial camera position based on location permissions. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fetchLastLocation() } else { requestLocationPermissions() } } /** * A helper function to centralize the check for location permissions. */ private fun isLocationPermissionGranted(): Boolean { return ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED } /** * This function triggers the permission request flow. The result is handled by the * ActivityResultLauncher defined in `onCreate`. */ private fun requestLocationPermissions() { Log.d(TAG, "Requesting location permissions.") requestPermissionLauncher.launch( arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) } /** * Fetches the device's last known location. This is a fast and battery-efficient way * to get a location fix. It should only be called after verifying permissions. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun fetchLastLocation() { // Double-checking permissions here is a good practice, although the call sites are already guarded. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fusedLocationClient.lastLocation .addOnSuccessListener { location: Location? -> if (location != null) { val userLocation = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(userLocation, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to user's last known location.") } else { // `lastLocation` can be null if the location has never been recorded. // In this case, we fall back to a default location. Log.d(TAG, "Last known location is null. Falling back to Sydney.") moveToSydney() } } .addOnFailureListener { // This listener handles errors in the location fetching process. Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get location.", it) moveToSydney() } } } /** * Moves the map camera to a default, hardcoded location (Sydney). * This serves as a reliable fallback. */ private fun moveToSydney() { val sydney = LatLng(-33.8688, 151.2093) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(sydney, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to Sydney") } /** * This is the callback for the `OnPoiClickListener`. It's triggered when a user * taps a POI on the map. */ override fun onPoiClick(poi: PointOfInterest) { val placeId = poi.placeId Log.d(TAG, "Place ID: $placeId") // We save the selected place ID to the ViewModel. This is critical for surviving // configuration changes. If the user rotates the screen now, the `onCreate` // method will be able to restore the place details view. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = placeId showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } /** * This function is the core of the integration. It creates, configures, and displays * the [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. * @param placeId The unique identifier for the place to be displayed. */ private fun showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId: String) { Log.d(TAG, "Showing PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") // We manage the visibility of UI elements to provide feedback to the user. // The wrapper is shown, and a loading indicator is displayed while the data is fetched. binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.GONE binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.VISIBLE // The Place Details widget can be displayed vertically or horizontally. // We dynamically choose the orientation based on the device's current configuration. val orientation = if (resources.configuration.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) { Orientation.HORIZONTAL } else { Orientation.VERTICAL } // We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } } /** * Hides the place details view and clears the selected place ID from the ViewModel. */ private fun dismissPlaceDetails() { binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.GONE // Clearing the ID in the ViewModel is important so that if the user rotates the // screen after dismissing, the details view doesn't reappear. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = null } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() // It's a good practice to nullify references to objects that have a lifecycle // tied to the activity, like the GoogleMap object, to prevent potential memory leaks. googleMap = null } }
یک تم ایجاد کنید
هنگام نمونه سازی یک قطعه، می توانید موضوعی را تعیین کنید که هر یک از ویژگی های سبک پیش فرض را لغو کند. هر ویژگی موضوعی که لغو نشده است از سبک های پیش فرض استفاده می کند. اگر میخواهید از یک تم تیره پشتیبانی کنید، میتوانید یک ورودی برای رنگ در values-night/colors.xml اضافه کنید.
Places UI Kit به طور پیشفرض یک تم تیره ارائه میکند، بنابراین ممکن است لازم باشد هر دو تم تاریک و روشن را سفارشی کنید. برای سفارشی کردن تم تیره، یک ورودی برای رنگ در values-night/colors.xml اضافه کنید.
<style name="CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme" parent="PlacesMaterialTheme"> <item name="placesColorPrimary">@color/app_primary_color</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurface">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurfaceVariant">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesTextAppearanceBodySmall">@style/app_text_appearence_small</item> <item name="placesCornerRadius">20dp</item> </style>
از محتوای استاندارد استفاده کنید
این نمونه از محتوای استاندارد استفاده می کند.
val fragmentStandardContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.STANDARD_CONTENT,
orientation,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)محتوای خاص را سفارشی کنید
این نمونه فقط گزینه های آدرس، ورودی قابل دسترسی و Content رسانه را برای نمای فشرده انتخاب می کند و آنها را با CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme رندر می کند.
val placeDetailsFragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
listOf(
Content.ADDRESS,
Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE,
Content.MEDIA
),
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)از همه مطالب استفاده کنید
این نمونه از تمام گزینه های Content یک نمای فشرده استفاده می کند.
val fragmentAllContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)

