مقدمة
تبدو الرموز الشريطية المتغيّرة تمامًا مثل الرموز الشريطية العادية، ولكنها تتغيّر بشكل دوري، عادةً كل دقيقة، ويتم برمجة المحطة الطرفية/القارئ لقبول أحدث رمز فقط. يحد هذا الإجراء الأمني من المخاطر المرتبطة التقاط لقطة شاشة للرموز الشريطية، ولا سيما سرقة التذاكر أو التذاكر غير المصرّح بها إعادة البيع. يمكن أيضًا استخدام الرموز الشريطية الدوارة كإجراء احتياطي للأجهزة التي لا يمكنها ذلك الاستفادة من ميزة "الدفع الذكي" بسبب عدم توافقها مع تقنية NFC (أي عدم توفُّر الأجهزة أو أو إيقاف البرنامج).
مرجع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
للاطّلاع على التفاصيل الفنية حول الرموز الشريطية المتغيّرة، يُرجى الاطّلاع على
نوع RotatingBarcode.
مثال على الحمولة
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
الآليات الاحتياطية
على جهاز المستخدم، يتم استخدام آلية واحدة فقط لتحصيل القيمة في وقت معيّن، يعتمد ذلك على كيفية إعداد البطاقة وإمكانيات الجهاز. بترتيب الأولوية، يتم استخدام أنواع تحصيل القيمة التالية:
-
الدفع الذكي: في حال تحديد حمولة الدفع الذكي وما إذا كان الجهاز يتيح
NFC/HCE
- تجدر الإشارة إلى أنه يمكن للمستخدم إلغاء هذا الإجراء بالنقر على زر "عرض الرمز" الذي ستفرض عرض الرمز الشريطي/الرمز الشريطي الثابت الدوران.
- رمز شريطي متغيّر: إذا تم تحديد حمولة رمز شريطي متغيّر
- رمز شريطي ثابت: إذا تم تحديد حمولة رمز شريطي
يمكن أن يؤدي تحديد عدة حِزم بيانات تحصيل قيمة الرمز إلى ضمان توفّر الرمز لجميع المستخدمين، ولكن قد يكون لذلك تأثيرات على الأمان. على وجه الخصوص، يؤدي استخدام رمز شريطي ثابت كبديل لرمز شريطي متغيّر إلى إلغاء معظم مزايا الأمان التي تعود على استخدام الرموز الشريطية المتغيّرة. لن يظهر الرمز الاحتياطي الثابت للرمز الشريطي إلا في طرق عرض الويب أو على العملاء الذين لا يتيحون استخدام الرموز الشريطية بالتناوب. اعتبارًا من اليوم، نتوقع أن يصبح استخدام الرموز الشريطية المتغيّرة متاحًا في جميع عملاء "محفظة Google".
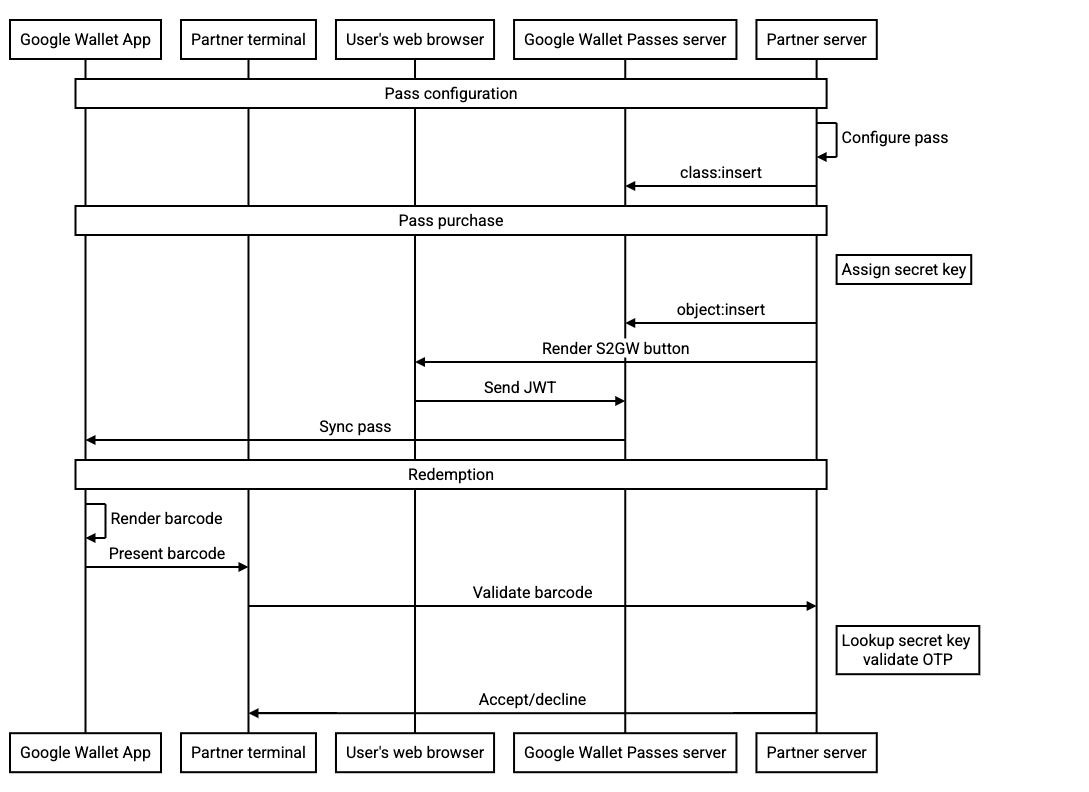
حفظ التدفق
توفّر Google Wallet API العديد من عمليات الربط، بما في ذلك:
- إنشاء فئات بطاقات الهدايا في وقت مناسب أو مُسبَق
- إرسال العناصر الكاملة في JWT أو حفظ العناصر مسبقًا ثم الإشارة إليها حسب المعرّف في JWT
- تعديل العناصر بعد حفظها
يتوافق الحقل المقترَح rotatingBarcode مع جميع هذه العمليات، ولكن لتحسين الأمان، نقترح ما يلي:
-
استخدِم واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
object:insertلإدراج البطاقة في خادم "محفظة Google" وإعداد الزر "إضافة إلى محفظة Google" لتحديد العنصر المحدّد حسب رقم التعريف في JWT. يضمن ذلك لا يتضمن JWT الناتج المفتاح السري للرمز الشريطي الدوار. - استخدِم مفتاحًا سريًا لكلمة مرور صالحة لمرة واحدة فقط ومخصّصًا لبطاقة واحدة.
- من المتوقّع أن يكون المفتاح صالحًا طوال مدة صلاحية البطاقة، ما لم يتم تعديله. لا نتوقّع أن يتم تحديث هذا المفتاح بأي تكرار أثناء مسار التشغيل الطبيعي.
يوضّح مخطّط التسلسل التالي عملية التنقّل بين الجهات المختلفة لعملية دمج نموذجية: