Wprowadzenie
Kody paskowe wyglądają jak zwykłe kody kreskowe, ale zmieniają się okresowo zwykle co minutę, a terminal/czytnik jest tak zaprogramowany, aby najnowszego. To zabezpieczenie zmniejsza ryzyko związane z robienie zrzutów ekranu z kodem kreskowym, w szczególności kradzież biletu lub nieautoryzowany bilet sprzedaż. Rotacja kodów kreskowych może też służyć jako działanie zastępcze w przypadku urządzeń, które nie mogą korzystają z technologii smart tap ze względu na brak obsługi NFC (brak sprzętu lub wyłączone oprogramowanie).
Dokumentacja API
Szczegółowe informacje techniczne dotyczące rotacji kodów kreskowych znajdziesz w dokumentacji
Typ RotatingBarcode.
Przykładowy ładunek
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
Mechanizmy awaryjne
Na urządzeniu użytkownika w danym momencie używany jest tylko jeden mechanizm wykorzystania karty. w zależności od konfiguracji karty i możliwości urządzenia. Używane są te typy promocji (w kolejności według priorytetu):
-
Smart Tap: jeśli określono dane payload dla smart tap i urządzenie obsługuje NFC/HCE.
- Użytkownik może to zmienić, klikając „Pokaż kod”, co spowoduje wyświetlenie obracającego się lub statycznego kodu kreskowego.
- Rotacja kodu kreskowego: jeśli określono rotację kodu kreskowego
- Kod kreskowy statyczny: jeśli określono ładunek danych kodu kreskowego.
Określenie wielu ładunków do wykupu może zapewnić obsługę wszystkich użytkowników, ale może mieć wpływ na bezpieczeństwo. W szczególności użycie kodu kreskowego stałego jako zapasowego dla kodu kreskowego rotacyjnego niweczy większość korzyści związanych z bezpieczeństwem wynikających ze stosowania kodów kreskowych rotacyjnych. Statyczny zamiennik kodu kreskowego będzie wyświetlany tylko w widokach internetowych lub w klientach, które nie obsługują obracających się kodów kreskowych. Od dzisiaj wszystkich klientów Portfela Google z obsługą rotacji kodów kreskowych.
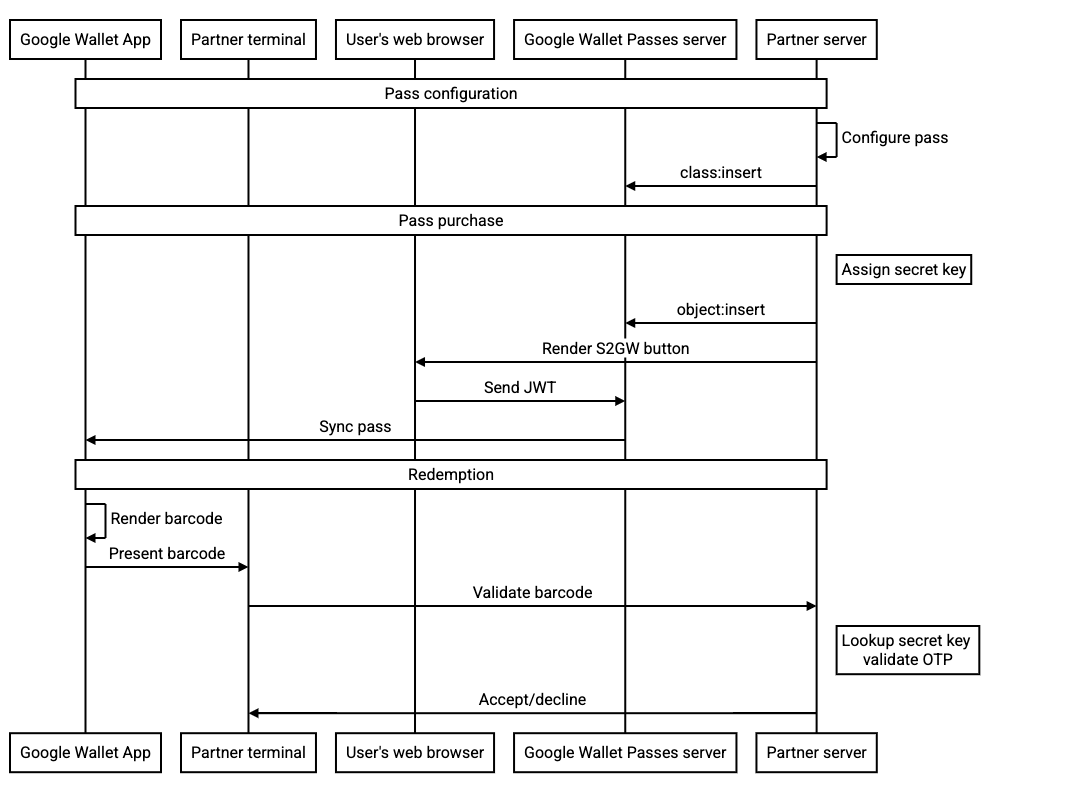
Zapisywanie przepływu
Interfejs API Portfela Google oferuje kilka procesów, w tym:
- tworzenie zajęć z karty podarunkowej w celu zaoszczędzenia czasu lub z wyprzedzeniem.
- Wysyłanie w tokenie JWT kompletnych obiektów lub zapisywanie obiektów z wyprzedzeniem, a potem odwoływanie się do nich według identyfikatora w tokenie JWT.
- Aktualizowanie obiektów po ich zapisaniu
Proponowane pole rotacji kodu kreskowego jest zgodne ze wszystkimi tymi przepływami. jednak w celu poprawy bezpieczeństwa sugerujemy wykonanie tych czynności:
-
Wywołaj interfejs API
object:insert, aby wstawić kartę do serwera Portfela Google i skonfigurować przycisk Dodaj do Portfela Google, aby odwołują się do konkretnego obiektu za pomocą identyfikatora w tokenie JWT. Dzięki temu powstały w ten sposób token JWT nie zawiera tajnego klucza rotacji kodu kreskowego. - Użyj klucza obiektu tajnego dla hasła jednorazowego z zakresu pojedynczej karty
- Klucz, o ile nie zostanie zaktualizowany, jest ważny przez cały okres ważności karty. Nie spodziewamy się, aby ten klucz był aktualizowany w żadnej częstotliwości w trakcie normalnego działania.
Ten diagram sekwencji przedstawia przepływ danych między różnymi podmiotami w przypadku typowej integracji: