Введение
Вращающиеся штрих-коды выглядят так же, как обычные штрих-коды, но меняются периодически, обычно каждую минуту, а терминал/считыватель запрограммирован принимать только самый последний из них. Эта мера безопасности снижает риски, связанные со снятием скриншотов штрих-кода, в частности кражу билета или несанкционированную перепродажу билета. Вращающиеся штрих-коды также могут служить запасным вариантом для устройств, которые не могут использовать преимущества Smart Tap из-за отсутствия поддержки NFC (отсутствие оборудования или отключенное программное обеспечение).
Справочник по API
Технические подробности о вращающихся штрих-кодах см. в разделе Тип RotatingBarcode .
Пример полезной нагрузки
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } | |
Резервные механизмы
На пользовательском устройстве одновременно используется только один механизм погашения, в зависимости от того, как настроен пропуск и от возможностей устройства. В порядке приоритета используются следующие типы погашения:
- Smart Tap: если указана полезная нагрузка Smart-Tap и если устройство поддерживает NFC/HCE.
- Обратите внимание: пользователь может отменить это действие, нажав «Показать код», что приведет к принудительному отображению вращающегося/статического штрих-кода.
- Вращающийся штрих-код: если указана вращающаяся полезная нагрузка штрих-кода.
- Статический штрих-код: если указана полезная нагрузка штрих-кода.
Указание нескольких полезных данных погашения может гарантировать поддержку всех пользователей, но может иметь последствия для безопасности. В частности, использование статического штрих-кода в качестве альтернативы вращающемуся штрих-коду сводит на нет большую часть преимуществ безопасности, связанных с использованием вращающихся штрих-кодов. Резервный статический штрих-код будет отображаться только в веб-представлениях или на клиентах, которые не поддерживают вращающиеся штрих-коды. На сегодняшний день мы ожидаем, что все клиенты Google Кошелька будут поддерживать чередующиеся штрих-коды.
Сохранить поток
API Google Кошелька предлагает несколько потоков, в том числе:
- Создание классов подарочных карт в кратчайшие сроки или заранее.
- Отправка полных объектов в JWT или предварительное сохранение объектов с последующей ссылкой на них по идентификатору в JWT.
- Обновление объектов после их сохранения
Предлагаемое поле RotatingBarcode совместимо со всеми этими потоками, однако в целях повышения безопасности мы предлагаем следующее:
- Вызовите API
object:insert, чтобы вставить пропуск на сервер Google Кошелька, и настройте кнопку «Добавить в Google Кошелек» для ссылки на конкретный объект по идентификатору в вашем JWT. Это гарантирует, что полученный JWT не будет включать секретный ключ вращающегося штрих-кода. - Используйте секретный ключ OTP, ограниченный одним проходом.
- Ожидается, что ключ, если он не будет обновлен, будет действителен в течение всего срока действия пропуска. Мы не ожидаем, что этот ключ будет обновляться с какой-либо частотой в ходе нормальной работы.
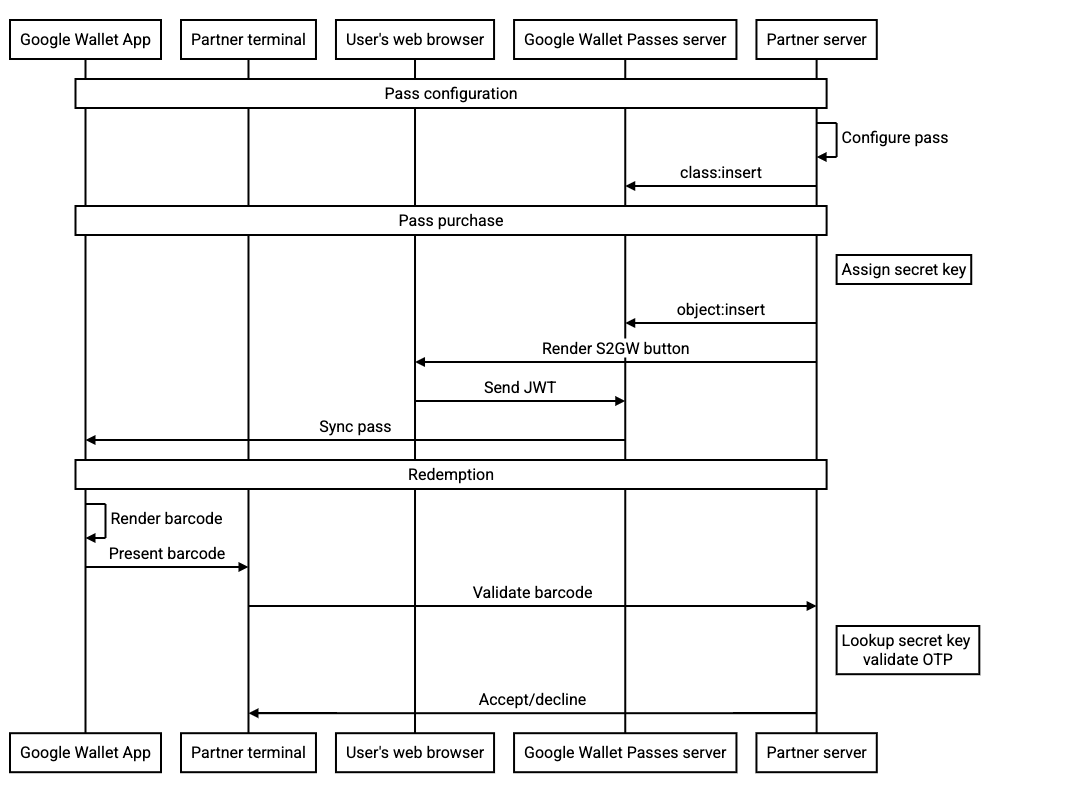
Следующая диаграмма последовательности иллюстрирует поток между различными участниками типичной интеграции: