מבוא
ברקודים מסתובבים נראים בדיוק כמו ברקודים רגילים, אבל הם משתנים מדי פעם, בדרך כלל כל דקה, והמסוף/הקורא מתוכנת לקבל נתונים רק העדכנית ביותר. אמצעי האבטחה הזה מפחית את הסיכונים שקשורים לצילום מסך של ברקוד, במיוחד לגבי גניבת כרטיסים או מכירת כרטיסים לא מורשית. ברקודים מסתובבים יכולים גם לשמש כחלופה למכשירים שלא יכולים לנצל את התכונה 'הקשה חכמה' עקב אי תמיכה ב-NFC (אין מספיק חומרה, שהתוכנה מושבתת).
הפניית API
לקבלת פרטים טכניים על סיבוב ברקודים, אפשר לעיין ב
סוג RotatingBarcode.
מטען ייעודי (payload) לדוגמה
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
מנגנונים חלופיים
במכשיר של המשתמש, נעשה שימוש במנגנון מימוש אחד בכל רגע נתון, בהתאם לאופן שבו הכרטיס מוגדר וליכולות של המכשיר. סוגי המימוש הבאים לפי סדר העדיפות:
-
הקשה חכמה: אם צוין עומס עבודה של הקשה חכמה והמכשיר תומך ב-NFC/HCE
- הערה: המשתמש יכול לשנות את ההגדרה הזו בלחיצה על 'הצגת הקוד', וכך לאלץ את הצגת הברקוד המסתובב או הברקוד הסטטי.
- ברקוד מסתובב: אם צוין עומס עבודה של ברקוד מסתובב
- ברקוד סטטי: אם צוין מטען ייעודי (payload) של ברקוד
ציון מטענים ייעודיים (payloads) מרובים של מימוש יכול להבטיח שכל המשתמשים נתמכים, אבל עשויות להיות השלכות על האבטחה. באופן ספציפי, שימוש בברקוד סטטי כחלופה לברקוד נע מבטל את רוב יתרונות האבטחה של שימוש בברקודים נעים. חלופה לברקוד סטטי תוצג רק בתצוגות אינטרנט או לקוחות שלא תומכים בברקודים מסתובבים. נכון להיום, אנחנו צופים כל הלקוחות של Google Wallet כדי לתמוך בברקודים מסתובבים.
שמירת תהליך העבודה
ב-Google Wallet API יש כמה תהליכים, כולל:
- יצירת הכיתות של כרטיסי המתנה בזמן חיסכון בזמן או מראש
- שליחת האובייקטים המלאים ב-JWT, או שמירת האובייקטים מראש ולאחר מכן הפניה אליהם לפי מזהה ב-JWT
- עדכון האובייקטים אחרי שהם נשמרו
השדה רוטingBarcode המוצע תואם לכל התהליכים האלה, עם זאת, כדי לשפר את האבטחה, מומלץ לבצע את הפעולות הבאות:
-
קוראים ל-API של
object:insertכדי להוסיף את הכרטיס לשרת של Google Wallet, ומגדירים את הלחצן 'הוספה ל-Google Wallet' כך שיפנה לאובייקט הספציפי לפי המזהה שלו ב-JWT. כך מוודאים שה-JWT שנוצר לא כולל את המפתח הסודי של הברקוד המנווט. - שימוש במפתח סודי מסוג OTP שמוגדרת לו היקף של כניסה אחת
- המפתח, אלא אם הוא מעודכן, צפוי להיות בתוקף כל משך החיים של עובר. אנחנו לא צופים שהמפתח הזה יתעדכן בתדירות כלשהי במהלך הפעולה הרגילה.
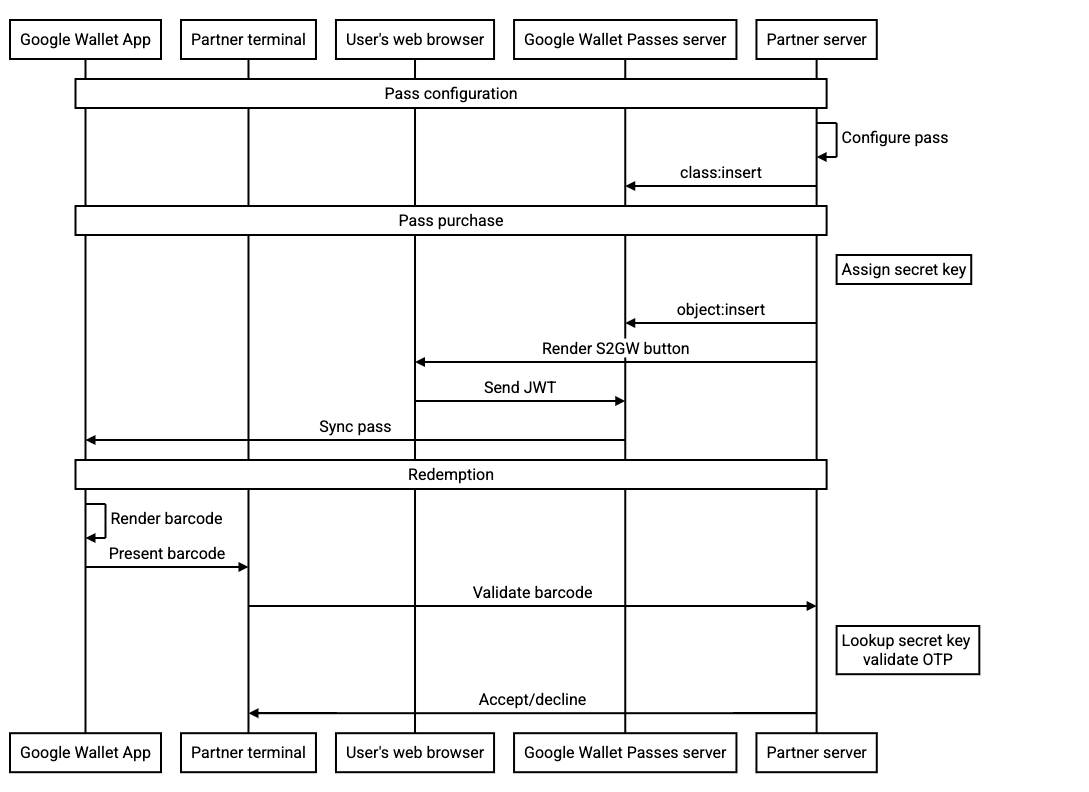
תרשים הרצף הבא ממחיש את הזרימה בין הגורמים השונים לשילוב אופייני: