Introdução
Os códigos de barras rotativos são semelhantes aos normais, mas mudam com frequência periódica, normalmente a cada minuto, e o terminal/leitor é programado para aceitar apenas o código mais recente. Essa medida de segurança reduz os riscos associados Captura de tela com código de barras, especificamente em caso de roubo ou não autorização da passagem revenda. Os códigos de barras rotativos também podem funcionar como um substituto para dispositivos que não conseguem usar o Toque inteligente porque não têm suporte para NFC (por falta de hardware ou software desativado).
Referência da API
Para ver detalhes técnicos sobre códigos de barras rotativos, consulte a
Tipo RotatingBarcode.
Exemplo de payload
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
Mecanismos substitutos
No dispositivo do usuário, somente um mecanismo de resgate é usado por vez, dependendo de como o cartão está configurado e dos recursos do dispositivo. Em ordem de prioridade, os seguintes tipos de resgate são usados:
-
Toque inteligente: se um payload de toque inteligente for especificado e se o dispositivo oferecer suporte
NFC/HCE
- Isso pode ser substituído pelo usuário clicando em "Mostrar código", que forçará a exibição do código de barras rotativo/estático.
- Código de barras rotativo: se um payload de código de barras rotativo for especificado
- Código de barras estático: se um payload de código de barras for especificado
Especificar vários payloads de resgate é uma forma de garantir que haja suporte para todos os usuários, mas isso pode gerar implicações de segurança. Mais especificamente, o uso de um código de barras estático como um código de barras rotativo, por sua vez, anula a maioria dos benefícios de segurança códigos de barras rotativos. Um código de barras estático substituto só vai aparecer nas visualizações da Web ou em clientes que não suportam códigos de barras rotativos. A partir de hoje, esperamos todos os clientes da Carteira virtual do Google para oferecer suporte a códigos de barras rotativos.
Salvar fluxo
A API Google Wallet oferece vários fluxos, incluindo:
- Criar classes de vale-presente no horário salvo ou com antecedência
- Enviar objetos completos no JWT ou salvá-los com antecedência e depois se referir a eles pelo ID no JWT
- Atualizar os objetos depois de salvá-los
O campo generateBarcode proposto é compatível com todos esses fluxos, No entanto, para melhorar a segurança, sugerimos o seguinte:
-
Chame a API
object:insertpara inserir o cartão no servidor da Carteira do Google e configure o botão "Adicionar à Carteira do Google" para fazer referência ao objeto específico por ID no JWT. Isso garante que o O JWT resultante não inclui a chave secreta do código de barras rotativo. - Use uma chave secreta de OTP com escopo para um único cartão
- A menos que seja atualizada, espera-se que a chave seja válida durante a vida útil do o passe. Não esperamos que essa chave seja atualizada em qualquer frequência durante o curso da operação normal.
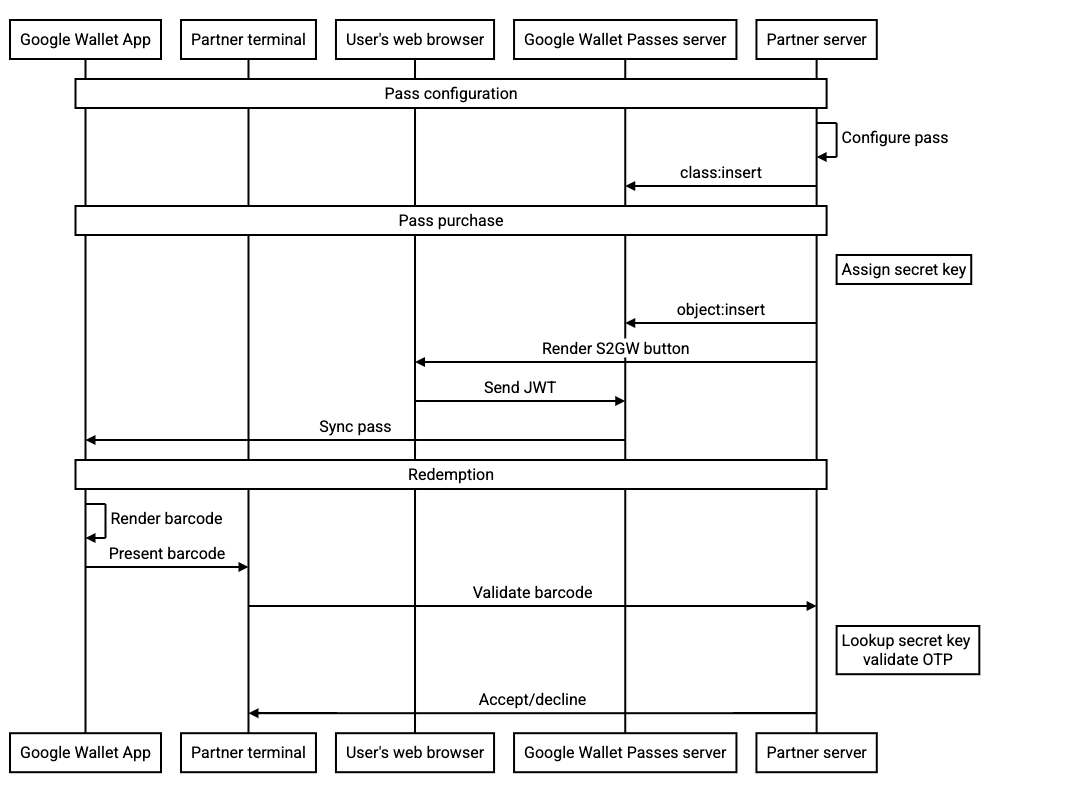
O diagrama de sequência a seguir ilustra o fluxo entre os vários atores para uma integração típica: