目標
高ボリューム アドレス検証のチュートリアルでは、高ボリューム アドレス検証を使用できるさまざまなシナリオについて説明しました。このチュートリアルでは、大量の住所確認を実行するための Google Cloud Platform 内のさまざまな設計パターンを紹介します。
まず、Cloud Run、Compute Engine、Google Kubernetes Engine を使用して Google Cloud Platform で高ボリューム アドレス検証を 1 回実行する概要について説明します。次に、この機能をデータ パイプラインの一部として組み込む方法について説明します。
この記事を読み終えるころには、Google Cloud 環境で大量の住所確認を実行するためのさまざまなオプションを十分に理解できているはずです。
Google Cloud Platform のリファレンス アーキテクチャ
このセクションでは、Google Cloud Platform を使用した大容量アドレス検証のさまざまな設計パターンについて詳しく説明します。Google Cloud Platform で実行することで、既存のプロセスやデータ パイプラインと統合できます。
Google Cloud Platform で大容量住所検証を 1 回実行する
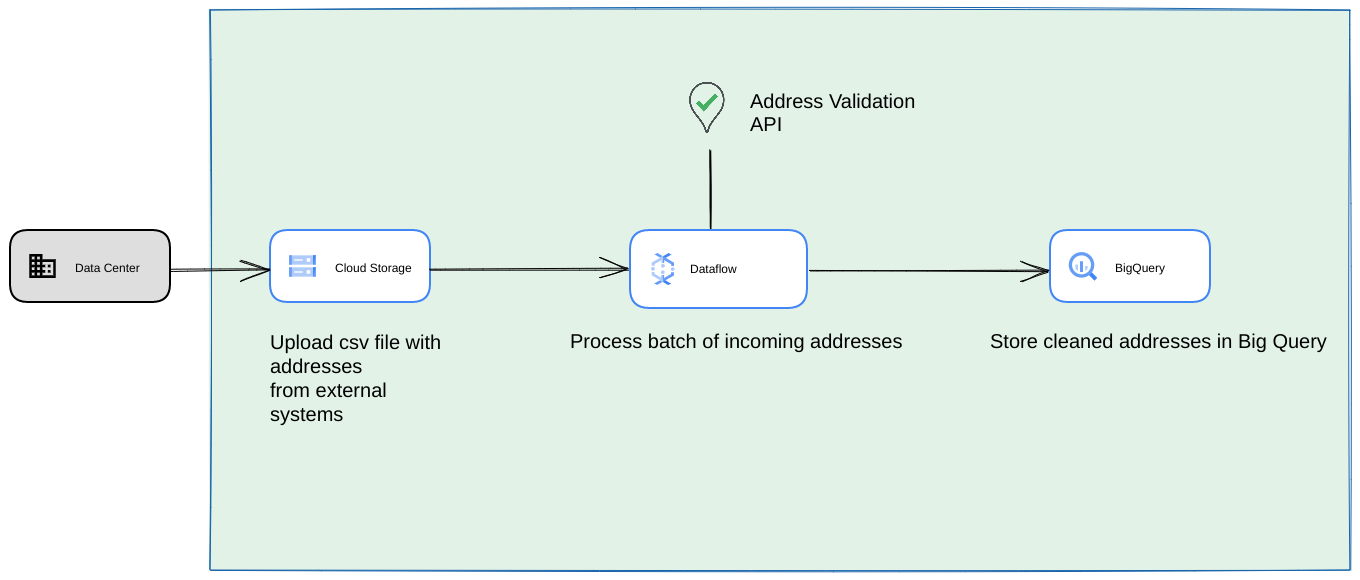
以下は、Google Cloud Platform で統合を構築する方法のリファレンス アーキテクチャです。これは、1 回限りのオペレーションやテストに適しています。
この場合は、CSV ファイルを Cloud Storage バケットにアップロードすることをおすすめします。その後、高容量の住所検証スクリプトを Cloud Run 環境から実行できます。ただし、Compute Engine や Google Kubernetes Engine などの他のランタイム環境で実行することもできます。出力 CSV を Cloud Storage バケットにアップロードすることもできます。
Google Cloud Platform データ パイプラインとして実行する
前のセクションで示したデプロイ パターンは、1 回限りの使用で High Volume Address Validation をすばやくテストする場合に最適です。ただし、データ パイプラインの一部として定期的に使用する必要がある場合は、Google Cloud Platform のネイティブ機能を活用して、より堅牢にすることができます。たとえば、次のような変更が可能です。
- この場合、CSV ファイルを Cloud Storage バケットにダンプできます。
- Dataflow ジョブは、処理するアドレスを取得して BigQuery にキャッシュに保存できます。
- Dataflow Python ライブラリを拡張して、大容量アドレス検証のロジックを追加し、Dataflow ジョブからアドレスを検証できます。
データ パイプラインからスクリプトを長時間実行される定期的なプロセスとして実行する
もう 1 つの一般的なアプローチは、ストリーミング データ パイプラインの一部として、アドレスのバッチを定期的なプロセスとして検証することです。BigQuery データストアにアドレスがある場合もあります。このアプローチでは、定期的なデータ パイプライン(毎日、毎週、毎月トリガーする必要がある)を構築する方法について説明します。
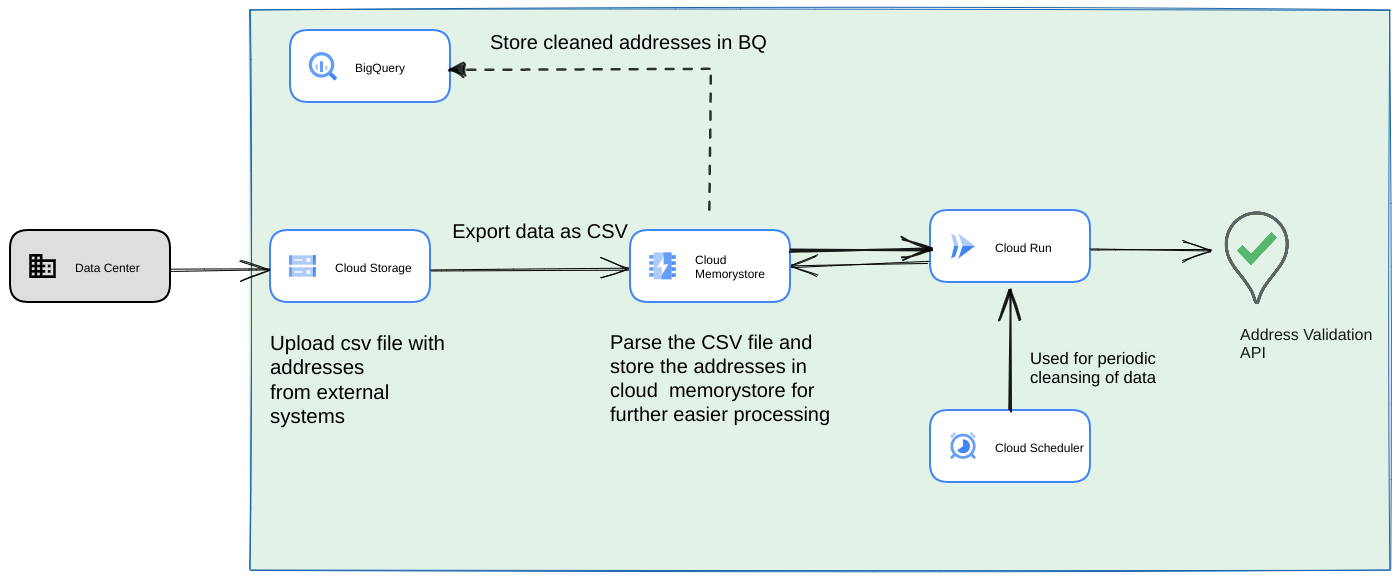
- 最初の CSV ファイルを Cloud Storage バケットにアップロードします。
- Memorystore を永続データストアとして使用して、長時間実行されるプロセスの中間状態を維持します。
- 最終的なアドレスを BigQuery データストアにキャッシュに保存します。
- スクリプトを定期的に実行するように Cloud Scheduler を設定します。
このアーキテクチャには、次のメリットがあります。
- Cloud Scheduler を使用すると、アドレスの検証を定期的に行うことができます。アドレスの再検証を毎月行うか、新しいアドレスの検証を毎月または四半期ごとに行うことをおすすめします。このアーキテクチャは、このユースケースの解決に役立ちます。
顧客データが BigQuery にある場合、検証済みの住所または検証フラグをそこに直接キャッシュに保存できます。注: キャッシュに保存できるものとその方法については、大容量アドレス検証に関する記事で詳しく説明しています。
Memorystore を使用すると、復元力が高まり、より多くのアドレスを処理できるようになります。この手順では、非常に大規模なアドレス データセットの処理に必要な状態が処理パイプライン全体に追加されます。Cloud SQL[https://cloud.google.com/sql] などの他のデータベース テクノロジーや、Google Cloud Platform が提供する他のデータベースのフレーバーも使用できます。ただし、Memorystore はスケーリングとシンプルさのニーズを完璧にバランスさせているため、第一の選択肢とすべきです。
まとめ
ここで説明するパターンを適用すると、Google Cloud Platform のさまざまなユースケースで Address Validation API を使用できます。
上記のユースケースを簡単に開始できるように、オープンソースの Python ライブラリを作成しました。これは、パソコンのコマンドラインから呼び出すことも、Google Cloud Platform や他のクラウド プロバイダから呼び出すこともできます。
ライブラリの使用方法について詳しくは、こちらの記事をご覧ください。
次のステップ
確実な住所で購入手続き、配送、オペレーションを改善する ホワイトペーパーをダウンロードし、Address Validation で購入手続き、配送、オペレーションを改善する ウェビナーをご覧ください。
参考資料:
寄稿者
この記事は Google が管理しています。このページは、以下の投稿者が作成しました。
主な著者:
Henrik Valve | ソリューション エンジニア
Thomas Anglaret | ソリューション エンジニア
Sarthak Ganguly | ソリューション エンジニア

