简介
本文档介绍了如何通过结合使用 Places Insights 数据集、BigQuery 中的公共地理空间数据和 Place Details API 来构建选址解决方案。
它基于 Google Cloud Next 2025 大会上展示的演示,可在 YouTube 上观看。 此外,我们还提供了一个示例 Colab 笔记本,其中包含本文档中所述流程的代码,并且采用可直接运行的格式。
业务挑战
假设您拥有一家成功的连锁咖啡店,并希望扩展到内华达州等您尚未涉足的新州。开设新店是一项重大投资,因此做出数据驱动型决策对于成功至关重要。您甚至不知道从何处入手?
本指南将引导您完成多层分析,以确定新咖啡店的最佳位置。我们将从全州范围的视角开始,逐步将搜索范围缩小到特定县和商业区,最后进行超本地化分析,通过绘制竞争对手地图来评估各个区域并找出市场空白。
解决方案工作流
此流程遵循逻辑漏斗,从宽泛开始,逐渐变得更加精细,以缩小搜索范围并提高对最终选定地点的信心。
前提条件和环境设置
在深入分析之前,您需要一个具备一些关键功能的环境。虽然本指南将介绍如何使用 SQL 和 Python 进行实现,但一般原则可应用于其他技术堆栈。
作为前提条件,请确保您的环境可以:
- 在 BigQuery 中执行查询。
- 访问“地点数据洞见”,如需了解详情,请参阅设置“地点数据洞见”
- 订阅来自
bigquery-public-data和 US Census Bureau County Population Totals 的公共数据集
您还需要能够在地图上直观呈现地理空间数据,这对于解读每个分析步骤的结果至关重要。您可以通过多种方式来达到这个目的。您可以使用直接连接到 BigQuery 的 Looker Studio 等 BI 工具,也可以使用 Python 等数据科学语言。
州级分析:找到最佳县/郡
我们的第一步是进行广泛的分析,以确定内华达州最有前景的县。我们将有前景定义为人口众多且现有餐厅密度高,这表明当地的餐饮文化浓厚。
我们的 BigQuery 查询利用 Places Insights 数据集中提供的内置地址组件实现了这一目标。该查询通过先过滤数据以仅包含内华达州境内的地点(使用 administrative_area_level_1_name 字段),然后统计餐厅数量。然后,它进一步细化此组,仅包含类型数组包含“restaurant”的位置。最后,它按县名 (administrative_area_level_2_name) 对这些结果进行分组,以生成每个县的计数。此方法利用了数据集的内置预索引地址结构。
以下代码段展示了如何将县级几何图形与 Places Insights 数据联接,并按特定地点类型 restaurant 进行过滤:
SELECT WITH AGGREGATION_THRESHOLD
administrative_area_level_2_name,
COUNT(*) AS restaurant_count
FROM
`places_insights___us.places`
WHERE
-- Filter for the state of Nevada
administrative_area_level_1_name = 'Nevada'
-- Filter for places that are restaurants
AND 'restaurant' IN UNNEST(types)
-- Filter for operational places only
AND business_status = 'OPERATIONAL'
-- Exclude rows where the county name is null
AND administrative_area_level_2_name IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
administrative_area_level_2_name
ORDER BY
restaurant_count DESC
餐厅的原始数量并不够;我们需要将其与人口数据进行平衡,才能真正了解市场饱和度和机遇。我们将使用美国人口调查局县级人口总数中的人口数据。
为了比较这两个截然不同的指标(地点数量与庞大的人口数量),我们使用最小-最大值归一化。此技术可将两个指标都缩放到一个共同的范围(0 到 1)。然后,我们将它们合并为一个 normalized_score,为每个指标赋予 50% 的权重,以实现平衡的比较。
此摘录显示了用于计算得分的核心逻辑。它结合了归一化的人口和餐厅数量:
(
-- Normalize restaurant count (scales to a 0-1 value) and apply 50% weight
SAFE_DIVIDE(restaurant_count - min_restaurants, max_restaurants - min_restaurants) * 0.5
+
-- Normalize population (scales to a 0-1 value) and apply 50% weight
SAFE_DIVIDE(population_2023 - min_pop, max_pop - min_pop) * 0.5
) AS normalized_score
运行完整查询后,系统会返回一个列表,其中包含各个县、餐厅数量、人口和归一化得分。按 normalized_score
DESC 排序后,我们发现克拉克县是明显的胜出者,因此可以将其作为头号竞争者进行进一步调查。
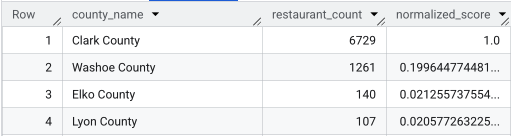
此屏幕截图显示了按标准化得分排名的前 4 个县。此示例中有意省略了原始人口数量。
县级分析:找出最繁忙的商业区
现在,我们已经确定了克拉克县,下一步是放大地图,找到商业活动最频繁的邮政编码。根据现有咖啡店的数据,我们知道,如果咖啡店位于主要品牌密集区域附近,效果会更好,因此我们将此作为高客流量的代理变量。
此查询使用“地点数据洞见”中的 brands 表,其中包含有关特定品牌的信息。您可以查询此表,以了解受支持的品牌列表。我们首先定义目标品牌列表,然后将其与主 Places Insights 数据集联接,以统计克拉克县每个邮政编码中包含的这些特定商店的数量。
实现此目的的最有效方法是采用两步法:
- 首先,我们将执行快速的非地理空间聚合,以统计每个邮政编码中的品牌数量。
- 其次,我们将这些结果与公共数据集联接,以获取用于可视化的地图边界。
使用 postal_code_names 字段统计品牌数量
第一个查询执行核心计数逻辑。它会过滤克拉克县的地点,然后取消嵌套 postal_code_names 数组,以按邮政编码对品牌数量进行分组。
WITH brand_names AS (
-- First, select the chains we are interested in by name
SELECT
id,
name
FROM
`places_insights___us.brands`
WHERE
name IN ('7-Eleven', 'CVS', 'Walgreens', 'Subway Restaurants', "McDonald's")
)
SELECT WITH AGGREGATION_THRESHOLD
postal_code,
COUNT(*) AS total_brand_count
FROM
`places_insights___us.places` AS places_table,
-- Unnest the built-in postal code and brand ID arrays
UNNEST(places_table.postal_code_names) AS postal_code,
UNNEST(places_table.brand_ids) AS brand_id
JOIN
brand_names
ON brand_names.id = brand_id
WHERE
-- Filter directly on the administrative area fields in the places table
places_table.administrative_area_level_2_name = 'Clark County'
AND places_table.administrative_area_level_1_name = 'Nevada'
GROUP BY
postal_code
ORDER BY
total_brand_count DESC
输出是一个表格,其中包含邮政编码及其对应的品牌数量。

附加邮政编码几何图形以进行地图绘制
现在,我们有了这些数量,就可以获取可视化所需的多边形形状。第二个查询采用第一个查询,将其封装在名为 brand_counts_by_zip 的通用表表达式 (CTE) 中,并将其结果与公开的 geo_us_boundaries.zip_codes table 联接。这样可高效地将几何图形附加到预先计算的计数中。
WITH brand_counts_by_zip AS (
-- This will be the entire query from the previous step, without the final ORDER BY (excluded for brevity).
. . .
)
-- Now, join the aggregated results to the boundaries table
SELECT
counts.postal_code,
counts.total_brand_count,
-- Simplify the geometry for faster rendering in maps
ST_SIMPLIFY(zip_boundaries.zip_code_geom, 100) AS geography
FROM
brand_counts_by_zip AS counts
JOIN
`bigquery-public-data.geo_us_boundaries.zip_codes` AS zip_boundaries
ON counts.postal_code = zip_boundaries.zip_code
ORDER BY
counts.total_brand_count DESC
输出结果是一个表格,其中包含邮政编码、相应的品牌数量和邮政编码几何图形。

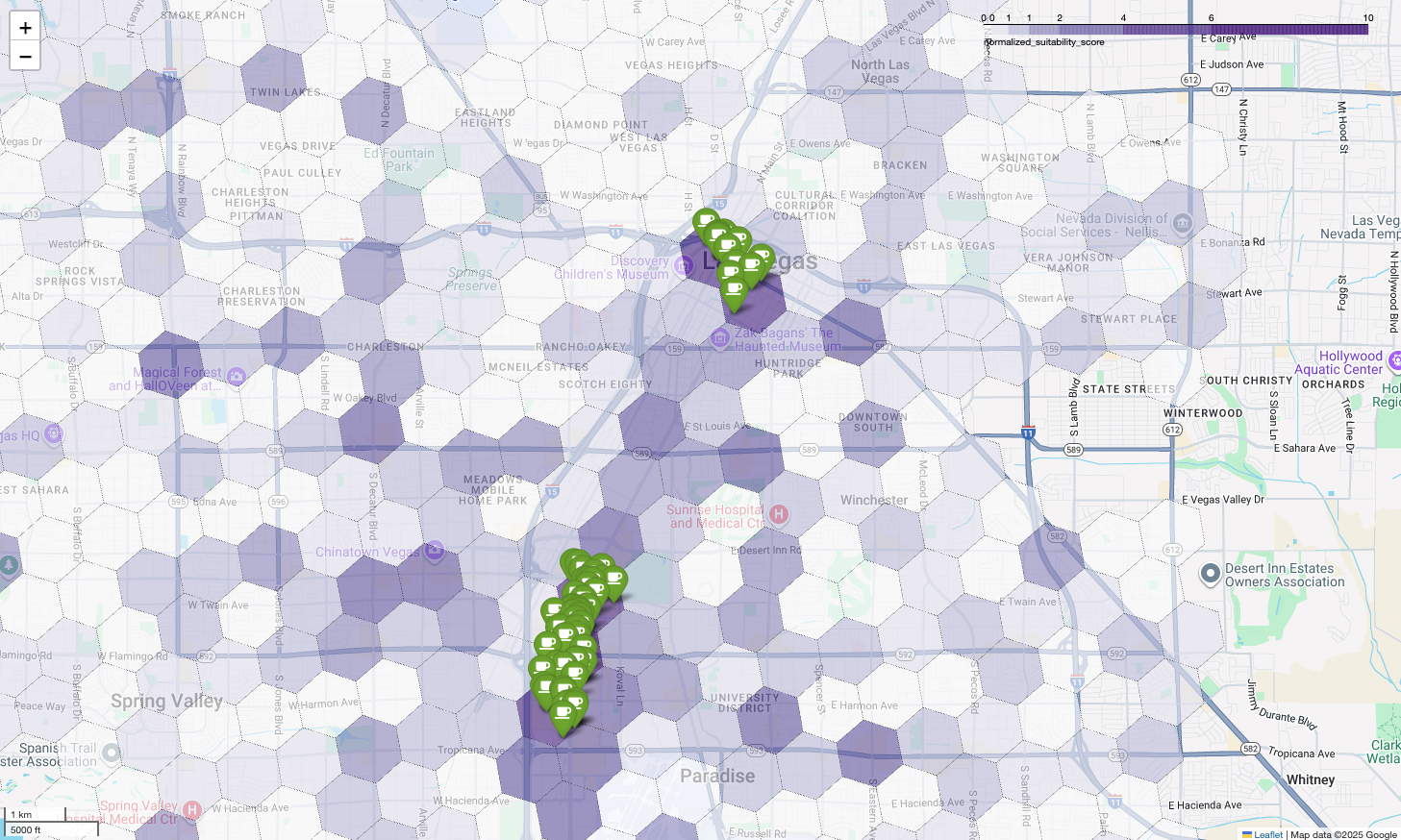
我们可以将这些数据直观呈现为热图。颜色越深的红色区域表示目标品牌的集中度越高,这表明拉斯维加斯商业密度最高的区域。

超本地分析:为各个网格区域评分
确定拉斯维加斯的大致区域后,接下来就要进行精细分析了。我们可以在这里添加特定的业务知识。我们知道,如果咖啡馆附近有在高峰时段(例如上午晚些时候和午餐时段)生意兴隆的其他商家,那么咖啡馆也会生意兴隆。
我们的下一个查询非常具体。首先,使用标准 H3 地理空间索引(分辨率为 8)在拉斯维加斯都市区创建精细的六边形网格,以便在微观层面上分析该区域。该查询首先确定在我们的高峰时段(周一上午 10 点到下午 2 点)营业的所有互补型商家。
然后,我们会为每种地点类型应用加权得分。附近的餐厅对我们来说比便利店更有价值,因此餐厅的乘数更高。这样,我们就可以为每个小区域获得自定义的 suitability_score。
此摘录重点介绍了加权得分逻辑,该逻辑引用了预先计算的标志 (is_open_monday_window) 以进行营业时间检查:
. . .
(
COUNTIF('restaurant' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 8 +
COUNTIF('convenience_store' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 3 +
COUNTIF('bar' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7 +
COUNTIF('tourist_attraction' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 6 +
COUNTIF('casino' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7
) AS suitability_score
. . .
展开即可显示完整查询
-- This query calculates a custom 'suitability score' for different areas in the Las Vegas -- metropolitan area to identify prime commercial zones. It uses a weighted model based -- on the density of specific business types that are open during a target time window. -- Step 1: Pre-filter the dataset to only include relevant places. -- This CTE finds all places in our target localities (Las Vegas, Spring Valley, etc.) and -- adds a boolean flag 'is_open_monday_window' for those open during the target time. WITH PlacesInTargetAreaWithOpenFlag AS ( SELECT point, types, EXISTS( SELECT 1 FROM UNNEST(regular_opening_hours.monday) AS monday_hours WHERE monday_hours.start_time <= TIME '10:00:00' AND monday_hours.end_time >= TIME '14:00:00' ) AS is_open_monday_window FROM `places_insights___us.places` WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM UNNEST(locality_names) AS locality WHERE locality IN ('Las Vegas', 'Spring Valley', 'Paradise', 'North Las Vegas', 'Winchester') ) AND administrative_area_level_1_name = 'Nevada' ), -- Step 2: Aggregate the filtered places into H3 cells and calculate the suitability score. -- Each place's location is converted to an H3 index (at resolution 8). The query then -- calculates a weighted 'suitability_score' and individual counts for each business type -- within that cell. TileScores AS ( SELECT WITH AGGREGATION_THRESHOLD -- Convert each place's geographic point into an H3 cell index. `carto-os.carto.H3_FROMGEOGPOINT`(point, 8) AS h3_index, -- Calculate the weighted score based on the count of places of each type -- that are open during the target window. ( COUNTIF('restaurant' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 8 + COUNTIF('convenience_store' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 3 + COUNTIF('bar' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7 + COUNTIF('tourist_attraction' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 6 + COUNTIF('casino' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7 ) AS suitability_score, -- Also return the individual counts for each category for detailed analysis. COUNTIF('restaurant' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS restaurant_count, COUNTIF('convenience_store' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS convenience_store_count, COUNTIF('bar' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS bar_count, COUNTIF('tourist_attraction' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS tourist_attraction_count, COUNTIF('casino' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS casino_count FROM -- CHANGED: This now references the CTE with the expanded area. PlacesInTargetAreaWithOpenFlag -- Group by the H3 index to ensure all calculations are per-cell. GROUP BY h3_index ), -- Step 3: Find the maximum suitability score across all cells. -- This value is used in the next step to normalize the scores to a consistent scale (e.g., 0-10). MaxScore AS ( SELECT MAX(suitability_score) AS max_score FROM TileScores ) -- Step 4: Assemble the final results. -- This joins the scored tiles with the max score, calculates the normalized score, -- generates the H3 cell's polygon geometry for mapping, and orders the results. SELECT ts.h3_index, -- Generate the hexagonal polygon for the H3 cell for visualization. `carto-os.carto.H3_BOUNDARY`(ts.h3_index) AS h3_geography, ts.restaurant_count, ts.convenience_store_count, ts.bar_count, ts.tourist_attraction_count, ts.casino_count, ts.suitability_score, -- Normalize the score to a 0-10 scale for easier interpretation. ROUND( CASE WHEN ms.max_score = 0 THEN 0 ELSE (ts.suitability_score / ms.max_score) * 10 END, 2 ) AS normalized_suitability_score FROM -- A cross join is efficient here as MaxScore contains only one row. TileScores ts, MaxScore ms -- Display the highest-scoring locations first. ORDER BY normalized_suitability_score DESC;
在地图上直观呈现这些得分后,便可清晰地看出哪些位置胜出。最深的紫色方块主要位于拉斯维加斯大道和市中心附近,是开设新咖啡店最具潜力的区域。
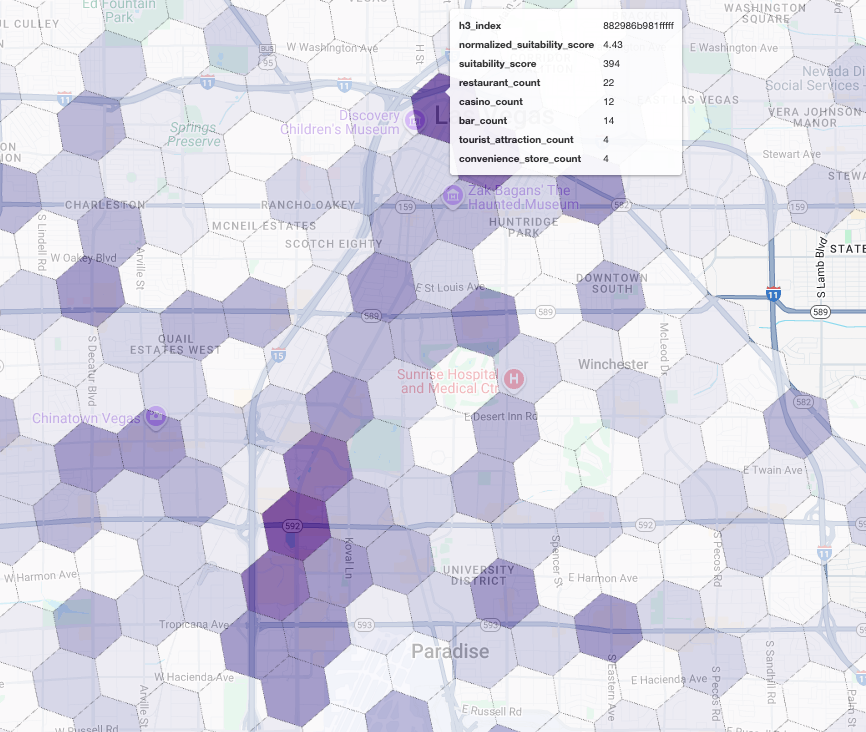
竞争对手分析:确定现有咖啡馆
我们的适宜性模型已成功识别出最有前景的区域,但仅凭高得分并不能保证成功。现在,我们必须将此数据与竞争对手的数据叠加。理想的地点是具有高潜力但现有咖啡店密度较低的区域,因为我们希望找到明显的市场空白。
为此,我们使用 PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 函数。此函数旨在按 H3 单元格高效返回指定地理位置内的地点数量。
首先,我们动态定义整个拉斯维加斯都市区的地理位置。
我们没有依赖单个地理位置,而是查询公开的 Overture Maps 数据集,以获取拉斯维加斯及其周边主要地理位置的边界,并使用 ST_UNION_AGG 将它们合并为单个多边形。然后,我们将此区域传递给该函数,要求它统计所有正在营业的咖啡店。
此查询定义了都市区,并调用该函数以获取 H3 单元格中的咖啡店数量:
-- Define a variable to hold the combined geography for the Las Vegas metro area.
DECLARE las_vegas_metro_area GEOGRAPHY;
-- Set the variable by fetching the shapes for the five localities from Overture Maps
-- and merging them into a single polygon using ST_UNION_AGG.
SET las_vegas_metro_area = (
SELECT
ST_UNION_AGG(geometry)
FROM
`bigquery-public-data.overture_maps.division_area`
WHERE
country = 'US'
AND region = 'US-NV'
AND names.primary IN ('Las Vegas', 'Spring Valley', 'Paradise', 'North Las Vegas', 'Winchester')
);
-- Call the PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 function with our defined area and parameters.
SELECT
*
FROM
`places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3`(
JSON_OBJECT(
-- Use the metro area geography we just created.
'geography', las_vegas_metro_area,
-- Specify 'coffee_shop' as the place type to count.
'types', ["coffee_shop"],
-- Best practice: Only count places that are currently operational.
'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'],
-- Set the H3 grid resolution to 8.
'h3_resolution', 8
)
);
该函数会返回一个表,其中包含 H3 单元格索引、其几何图形、咖啡店总数以及咖啡店的 Place ID 示例:

虽然汇总统计信息很有用,但查看实际的竞争对手至关重要。
在此阶段,我们将从 Places Insights 数据集过渡到 Places API。通过从具有最高归一化适宜性得分的单元格中提取 sample_place_ids,我们可以调用 Place Details API 来检索每个竞争对手的丰富详细信息,例如其名称、地址、评分和位置。
这需要比较生成了适宜性得分的先前查询的结果与 PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 查询的结果。H3 Cell Index 可用于从具有最高归一化适宜性得分的单元格中获取咖啡店数量和 ID。
以下 Python 代码演示了如何执行此比较。
# Isolate the Top 5 Most Suitable H3 Cells
top_suitability_cells = gdf_suitability.head(5)
# Extract the 'h3_index' values from these top 5 cells into a list.
top_h3_indexes = top_suitability_cells['h3_index'].tolist()
print(f"The top 5 H3 indexes are: {top_h3_indexes}")
# Now, we find the rows in our DataFrame where the
# 'h3_cell_index' matches one of the indexes from our top 5 list.
coffee_counts_in_top_zones = gdf_coffee_shops[
gdf_coffee_shops['h3_cell_index'].isin(top_h3_indexes)
]
现在,我们已经获得了 H3 单元格中具有最高适宜性得分的咖啡店的地点 ID 列表,接下来可以请求有关每个地点的更多详细信息。
为此,您可以直接向地点详情 API 发送针对每个地点 ID 的请求,也可以使用客户端库来执行调用。请务必设置 FieldMask 参数,以便仅请求所需的数据。
最后,我们将所有内容整合到一个强大的可视化图表中。我们将紫色适宜性等值线地图绘制为基础层,然后为从 Places API 检索到的每个咖啡店添加图钉。这张最终地图可让您一目了然地了解整个分析过程:深紫色区域表示潜在市场,绿色图钉表示当前市场的实际情况。
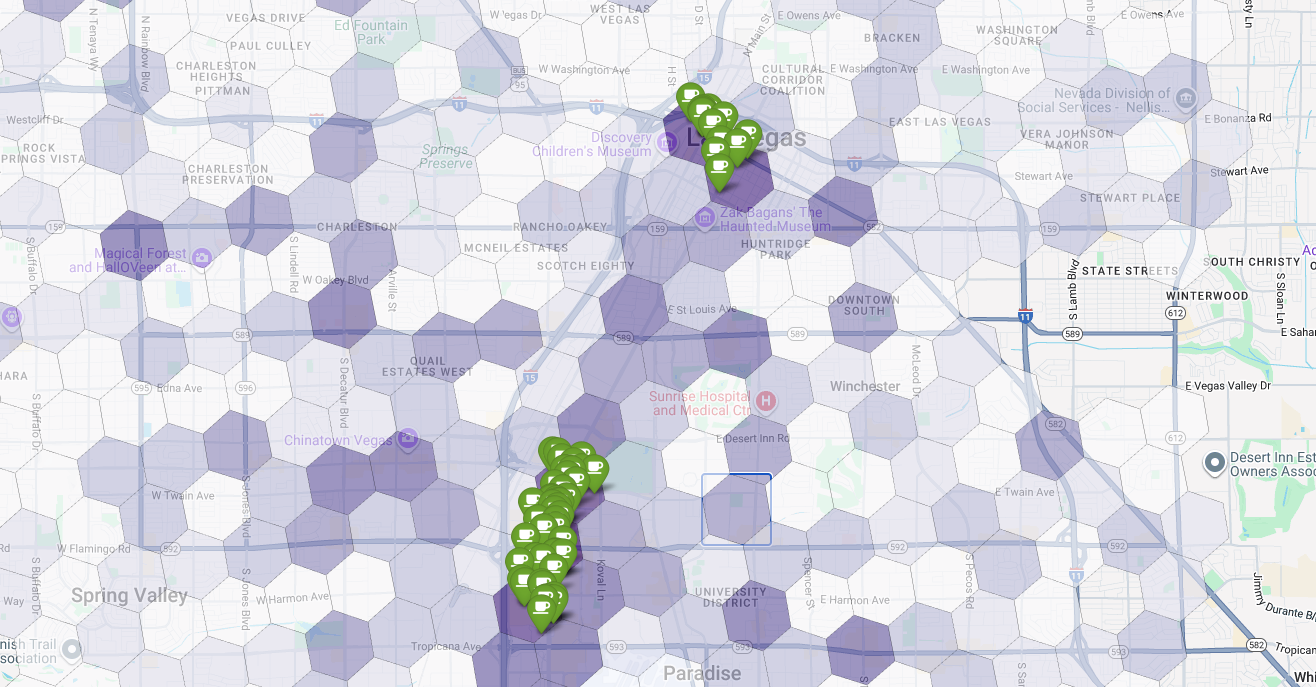
通过寻找图钉较少或没有图钉的深紫色单元格,我们可以放心地精确定位最适合开设新店的区域。

上述两个小区的适宜性得分较高,但存在一些明显的差距,这些差距可能就是我们新咖啡店的潜在位置。
总结
在本文档中,我们从在何处扩张?这一州级问题入手,最终得出了有数据支持的本地答案。通过分层处理不同的数据集并应用自定义业务逻辑,您可以系统性地降低与重大业务决策相关的风险。此工作流结合了 BigQuery 的大规模数据处理能力、Places Insights 的丰富信息和 Places API 的实时详细信息,为希望利用位置情报实现战略性增长的任何组织提供了一个强大的模板。
后续步骤
- 您可以根据自己的业务逻辑、目标地理位置和专有数据集调整此工作流。
- 探索 Places Insights 数据集中的其他数据字段,例如评价数量、价格水平和用户评分,以进一步丰富您的模型。
- 自动执行此流程,以创建可用于动态评估新市场的内部网站选择信息中心。
深入了解相关文档:
贡献者
Henrik Valve | DevX 工程师

