簡介
本文說明如何結合地點洞察資料集、BigQuery 中的公開地理空間資料和 Place Details API,建構選址解決方案。
本課程是以 2025 年 Google Cloud Next 大會的示範為基礎,您可以在 YouTube 上觀看該示範。 此外,我們也提供範例 Colab 筆記本,其中包含文件所述程序的程式碼,格式可直接執行。
業務難題
假設您經營的連鎖咖啡店非常成功,並想擴展到內華達州等新州,但您在當地沒有任何業務。開設新店是重大投資,因此根據資料做出決策,對成功至關重要。但要從何著手呢?
本指南將逐步說明多層分析,協助您找出新咖啡廳的最佳地點。首先,我們會從全州的角度著手,逐步將搜尋範圍縮小至特定郡和商業區,最後執行超區域分析,為各個區域評分,並繪製競爭對手地圖,找出市場缺口。
解決方案工作流程
這個程序會遵循邏輯漏斗,從廣泛的範圍開始,逐步縮小範圍,以精確搜尋區域,並提高對最終網站選擇的信心。
事前準備和環境設定
開始分析前,您需要具備幾項重要功能的環境。本指南將逐步說明如何使用 SQL 和 Python 進行實作,但一般原則也適用於其他技術堆疊。
請先確認環境是否符合下列先決條件:
- 在 BigQuery 中執行查詢。
- 存取 Places 洞察,詳情請參閱「設定 Places 洞察」
- 訂閱
bigquery-public-data和美國人口普查局縣市人口總數
您也必須能夠在地圖上以視覺化方式呈現地理空間資料,這對於解讀每個分析步驟的結果至關重要。確認的方法有很多種,您可以使用 Looker Studio 等 BI 工具直接連線至 BigQuery,也可以使用 Python 等資料科學語言。
州層級分析:找出最佳郡/縣
首先,我們會進行廣泛分析,找出內華達州最有希望的郡。我們將「有發展潛力」定義為人口眾多且現有餐廳密度高,這代表當地擁有強大的飲食文化。
我們的 BigQuery 查詢會運用 Places 洞察資料集內建的地址元件,達成這項目的。這項查詢會先使用 administrative_area_level_1_name 欄位篩選資料,只納入內華達州的地點,然後計算餐廳數量。然後進一步篩選這個集合,只納入類型陣列包含「restaurant」的地點。最後,系統會依縣市名稱 (administrative_area_level_2_name) 將這些結果分組,計算每個縣市的數量。這種做法會使用資料集內建的預先索引地址結構。
以下節錄內容說明如何將縣市幾何圖形與地點洞察資料合併,並依特定地點類型 (restaurant) 篩選:
SELECT WITH AGGREGATION_THRESHOLD
administrative_area_level_2_name,
COUNT(*) AS restaurant_count
FROM
`places_insights___us.places`
WHERE
-- Filter for the state of Nevada
administrative_area_level_1_name = 'Nevada'
-- Filter for places that are restaurants
AND 'restaurant' IN UNNEST(types)
-- Filter for operational places only
AND business_status = 'OPERATIONAL'
-- Exclude rows where the county name is null
AND administrative_area_level_2_name IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
administrative_area_level_2_name
ORDER BY
restaurant_count DESC
光是計算餐廳數量還不夠,我們還需要搭配人口資料,才能真正瞭解市場飽和度和商機。我們會使用美國人口普查局郡級人口總數資料。
如要比較這兩個差異極大的指標 (地點數量與人口數),我們使用最小-最大正規化。這項技術會將兩項指標縮放至共同範圍 (0 到 1)。然後將這些指標合併為單一 normalized_score,並為每個指標分配 50% 的權重,以利進行平衡比較。
這段摘錄內容顯示計算分數的核心邏輯。這項指標會結合標準化人口數和餐廳數:
(
-- Normalize restaurant count (scales to a 0-1 value) and apply 50% weight
SAFE_DIVIDE(restaurant_count - min_restaurants, max_restaurants - min_restaurants) * 0.5
+
-- Normalize population (scales to a 0-1 value) and apply 50% weight
SAFE_DIVIDE(population_2023 - min_pop, max_pop - min_pop) * 0.5
) AS normalized_score
完整查詢執行完畢後,系統會傳回縣市清單、餐廳數量、人口數和正規化分數。依 normalized_score
DESC排序後,克拉克郡明顯是頂尖競爭者,值得進一步調查。
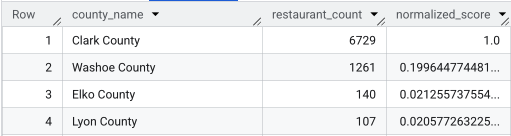
這張螢幕截圖顯示前 4 個正規化分數最高的郡。這個範例刻意省略了原始人口數。
縣級分析:找出最繁忙的商業區
現在我們已找出克拉克縣,下一步是放大畫面,找出商業活動最活躍的郵遞區號。根據現有咖啡店的資料,我們知道如果咖啡店位於主要品牌密集度高的區域,成效會比較好,因此我們會將此做為人潮眾多的指標。
這項查詢會使用 Places Insights 中的 brands 表格,其中包含特定品牌的相關資訊。您可以查詢這個表格,找出支援的品牌清單。首先,我們定義目標品牌清單,然後將這份清單與主要地點洞察資料集合併,計算克拉克郡各郵遞區號內有多少這類商店。
如要達到這個目標,最有效率的方法是採取兩步驟做法:
- 首先,我們會執行快速的非地理空間彙整作業,計算每個郵遞區號內的品牌數量。
- 接著,我們會將這些結果加入公開資料集,取得地圖界線以進行視覺化。
使用 postal_code_names 欄位計算品牌數量
第一個查詢會執行核心計數邏輯。這個函式會篩選出克拉克郡的地點,然後取消巢狀結構的 postal_code_names 陣列,依郵遞區號分組計算品牌數量。
WITH brand_names AS (
-- First, select the chains we are interested in by name
SELECT
id,
name
FROM
`places_insights___us.brands`
WHERE
name IN ('7-Eleven', 'CVS', 'Walgreens', 'Subway Restaurants', "McDonald's")
)
SELECT WITH AGGREGATION_THRESHOLD
postal_code,
COUNT(*) AS total_brand_count
FROM
`places_insights___us.places` AS places_table,
-- Unnest the built-in postal code and brand ID arrays
UNNEST(places_table.postal_code_names) AS postal_code,
UNNEST(places_table.brand_ids) AS brand_id
JOIN
brand_names
ON brand_names.id = brand_id
WHERE
-- Filter directly on the administrative area fields in the places table
places_table.administrative_area_level_2_name = 'Clark County'
AND places_table.administrative_area_level_1_name = 'Nevada'
GROUP BY
postal_code
ORDER BY
total_brand_count DESC
輸出結果是郵遞區號和對應品牌數量的表格。
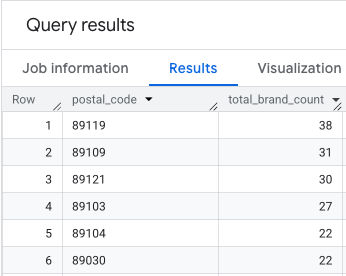
附加郵遞區號幾何圖形以供對應
現在我們有了計數,可以取得視覺化所需的 polygon 形狀。第二項查詢會採用第一項查詢,並將其包裝在名為 brand_counts_by_zip 的一般資料表運算式 (CTE) 中,然後將結果彙整至公開的 geo_us_boundaries.zip_codes table。這會將幾何圖形有效附加至預先計算的計數。
WITH brand_counts_by_zip AS (
-- This will be the entire query from the previous step, without the final ORDER BY (excluded for brevity).
. . .
)
-- Now, join the aggregated results to the boundaries table
SELECT
counts.postal_code,
counts.total_brand_count,
-- Simplify the geometry for faster rendering in maps
ST_SIMPLIFY(zip_boundaries.zip_code_geom, 100) AS geography
FROM
brand_counts_by_zip AS counts
JOIN
`bigquery-public-data.geo_us_boundaries.zip_codes` AS zip_boundaries
ON counts.postal_code = zip_boundaries.zip_code
ORDER BY
counts.total_brand_count DESC
輸出內容為郵遞區號資料表、對應的品牌數量,以及郵遞區號幾何圖形。
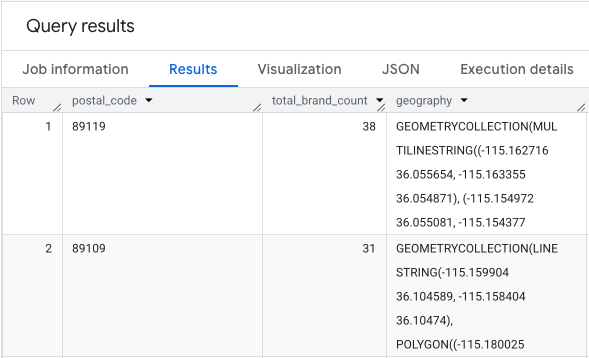
我們可以將這項資料視覺化為熱視圖。顏色越深的紅色區域代表目標品牌越密集,可協助我們找出拉斯維加斯商業最密集的區域。
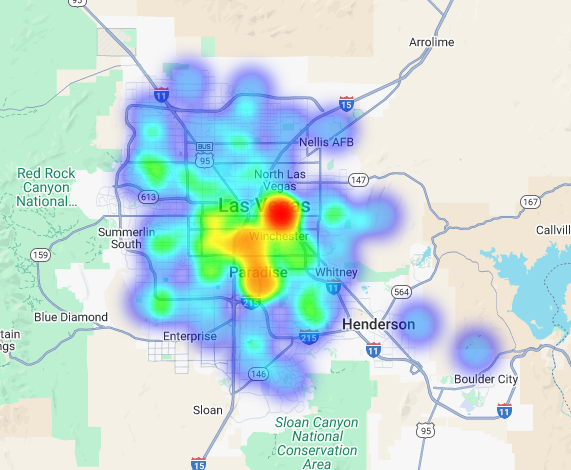
超區域分析:為個別格線區域評分
找出拉斯維加斯的大概區域後,接下來就要進行精細分析。我們會在這一層加入特定的業務知識。我們知道,如果咖啡店附近有其他商家在尖峰時段 (例如上午稍晚和午餐時段) 也很忙碌,咖啡店的生意就會興隆。
我們的下一個查詢會非常具體。首先,這項技術會使用標準 H3 地理空間索引 (解析度為 8),在拉斯維加斯都會區建立細密的六邊形格線,以便在微觀層面分析該區域。查詢會先找出所有在尖峰時段 (週一上午 10 點至下午 2 點) 營業的互補商家。
接著,我們會為每個地點類型套用加權分數。對我們來說,附近的餐廳比便利商店更有價值,因此餐廳的乘數較高。這樣我們就能為每個小區域提供自訂 suitability_score。
這段摘錄內容著重於加權評分邏輯,其中會參照預先計算的營業時間檢查旗標 (is_open_monday_window):
. . .
(
COUNTIF('restaurant' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 8 +
COUNTIF('convenience_store' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 3 +
COUNTIF('bar' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7 +
COUNTIF('tourist_attraction' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 6 +
COUNTIF('casino' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7
) AS suitability_score
. . .
展開完整查詢
-- This query calculates a custom 'suitability score' for different areas in the Las Vegas -- metropolitan area to identify prime commercial zones. It uses a weighted model based -- on the density of specific business types that are open during a target time window. -- Step 1: Pre-filter the dataset to only include relevant places. -- This CTE finds all places in our target localities (Las Vegas, Spring Valley, etc.) and -- adds a boolean flag 'is_open_monday_window' for those open during the target time. WITH PlacesInTargetAreaWithOpenFlag AS ( SELECT point, types, EXISTS( SELECT 1 FROM UNNEST(regular_opening_hours.monday) AS monday_hours WHERE monday_hours.start_time <= TIME '10:00:00' AND monday_hours.end_time >= TIME '14:00:00' ) AS is_open_monday_window FROM `places_insights___us.places` WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM UNNEST(locality_names) AS locality WHERE locality IN ('Las Vegas', 'Spring Valley', 'Paradise', 'North Las Vegas', 'Winchester') ) AND administrative_area_level_1_name = 'Nevada' ), -- Step 2: Aggregate the filtered places into H3 cells and calculate the suitability score. -- Each place's location is converted to an H3 index (at resolution 8). The query then -- calculates a weighted 'suitability_score' and individual counts for each business type -- within that cell. TileScores AS ( SELECT WITH AGGREGATION_THRESHOLD -- Convert each place's geographic point into an H3 cell index. `carto-os.carto.H3_FROMGEOGPOINT`(point, 8) AS h3_index, -- Calculate the weighted score based on the count of places of each type -- that are open during the target window. ( COUNTIF('restaurant' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 8 + COUNTIF('convenience_store' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 3 + COUNTIF('bar' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7 + COUNTIF('tourist_attraction' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 6 + COUNTIF('casino' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) * 7 ) AS suitability_score, -- Also return the individual counts for each category for detailed analysis. COUNTIF('restaurant' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS restaurant_count, COUNTIF('convenience_store' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS convenience_store_count, COUNTIF('bar' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS bar_count, COUNTIF('tourist_attraction' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS tourist_attraction_count, COUNTIF('casino' IN UNNEST(types) AND is_open_monday_window) AS casino_count FROM -- CHANGED: This now references the CTE with the expanded area. PlacesInTargetAreaWithOpenFlag -- Group by the H3 index to ensure all calculations are per-cell. GROUP BY h3_index ), -- Step 3: Find the maximum suitability score across all cells. -- This value is used in the next step to normalize the scores to a consistent scale (e.g., 0-10). MaxScore AS ( SELECT MAX(suitability_score) AS max_score FROM TileScores ) -- Step 4: Assemble the final results. -- This joins the scored tiles with the max score, calculates the normalized score, -- generates the H3 cell's polygon geometry for mapping, and orders the results. SELECT ts.h3_index, -- Generate the hexagonal polygon for the H3 cell for visualization. `carto-os.carto.H3_BOUNDARY`(ts.h3_index) AS h3_geography, ts.restaurant_count, ts.convenience_store_count, ts.bar_count, ts.tourist_attraction_count, ts.casino_count, ts.suitability_score, -- Normalize the score to a 0-10 scale for easier interpretation. ROUND( CASE WHEN ms.max_score = 0 THEN 0 ELSE (ts.suitability_score / ms.max_score) * 10 END, 2 ) AS normalized_suitability_score FROM -- A cross join is efficient here as MaxScore contains only one row. TileScores ts, MaxScore ms -- Display the highest-scoring locations first. ORDER BY normalized_suitability_score DESC;
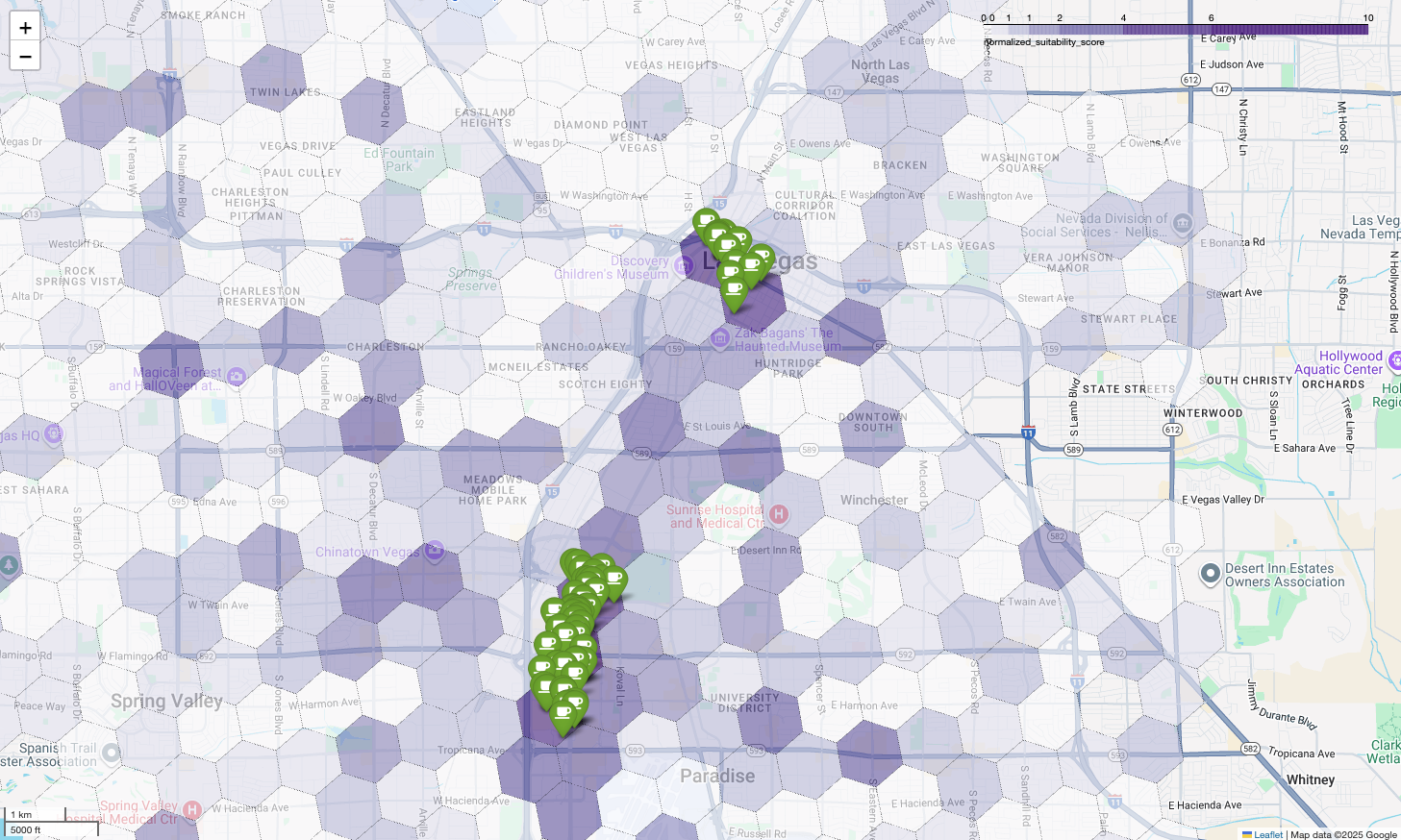
在地圖上顯示這些分數,即可清楚看出哪些地點最適合開店。深紫色方塊主要位於拉斯維加斯大道和市中心附近,是我們新咖啡廳最有潛力的區域。
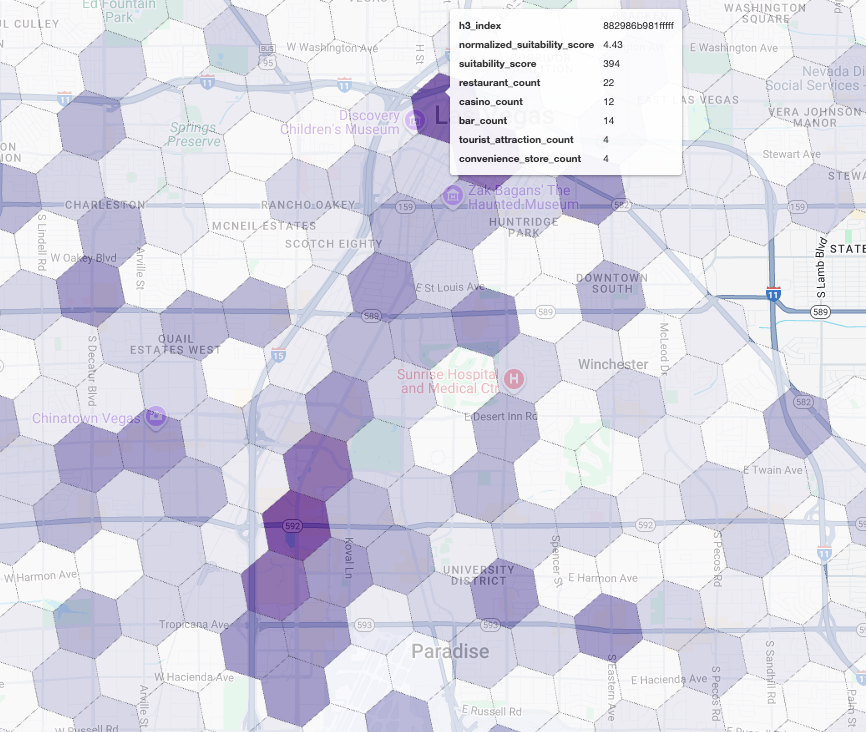
競品分析:找出現有咖啡廳
我們的適當性模型已成功找出最有希望的區域,但高分並不保證一定能成功。現在我們必須將這項資料與競爭對手資料疊加。理想地點是現有咖啡廳密度較低的潛力區域,因為我們希望找到明顯的市場缺口。
為此,我們會使用 PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 函式。這個函式的設計宗旨,是有效率地傳回指定地理區域內 H3 儲存格中的地點數量。
首先,我們會動態定義整個拉斯維加斯都會區的地理位置。
我們不會只依賴單一地區,而是查詢公開的 Overture 地圖資料集,取得拉斯維加斯及其周圍主要地區的邊界,並使用 ST_UNION_AGG 將這些邊界合併為單一多邊形。接著,我們會將這個區域傳遞至函式,要求函式計算所有營業中的咖啡館。
這項查詢會定義都會區,並呼叫函式來取得 H3 儲存格中的咖啡廳數量:
-- Define a variable to hold the combined geography for the Las Vegas metro area.
DECLARE las_vegas_metro_area GEOGRAPHY;
-- Set the variable by fetching the shapes for the five localities from Overture Maps
-- and merging them into a single polygon using ST_UNION_AGG.
SET las_vegas_metro_area = (
SELECT
ST_UNION_AGG(geometry)
FROM
`bigquery-public-data.overture_maps.division_area`
WHERE
country = 'US'
AND region = 'US-NV'
AND names.primary IN ('Las Vegas', 'Spring Valley', 'Paradise', 'North Las Vegas', 'Winchester')
);
-- Call the PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 function with our defined area and parameters.
SELECT
*
FROM
`places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3`(
JSON_OBJECT(
-- Use the metro area geography we just created.
'geography', las_vegas_metro_area,
-- Specify 'coffee_shop' as the place type to count.
'types', ["coffee_shop"],
-- Best practice: Only count places that are currently operational.
'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'],
-- Set the H3 grid resolution to 8.
'h3_resolution', 8
)
);
函式會傳回表格,其中包含 H3 儲存格索引、幾何圖形、咖啡店總數,以及咖啡店的 Place ID 樣本:

雖然匯總計數很有用,但查看實際競爭對手至關重要。
我們將在此從 Places 洞察資料集轉換至 Places API。從正規化合適度分數最高的儲存格中擷取 sample_place_ids,即可呼叫 Place Details API,擷取每個競爭對手的詳細資料,例如名稱、地址、評分和位置。
這需要比較先前查詢 (產生適用性分數) 和 PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 查詢的結果。您可以使用 H3 儲存格索引,從正規化適用性分數最高的儲存格取得咖啡店數量和 ID。
這段 Python 程式碼示範如何執行這項比較。
# Isolate the Top 5 Most Suitable H3 Cells
top_suitability_cells = gdf_suitability.head(5)
# Extract the 'h3_index' values from these top 5 cells into a list.
top_h3_indexes = top_suitability_cells['h3_index'].tolist()
print(f"The top 5 H3 indexes are: {top_h3_indexes}")
# Now, we find the rows in our DataFrame where the
# 'h3_cell_index' matches one of the indexes from our top 5 list.
coffee_counts_in_top_zones = gdf_coffee_shops[
gdf_coffee_shops['h3_cell_index'].isin(top_h3_indexes)
]
現在我們已取得 H3 儲存格中現有咖啡店的地點 ID 清單,這些儲存格的適用性分數最高,因此可以要求取得每個地點的詳細資料。
如要執行這項操作,您可以針對每個地點 ID 直接向 Place Details API 傳送要求,也可以使用用戶端程式庫執行呼叫。請記得設定 FieldMask 參數,只要求所需的資料。
最後,我們將所有內容整合為單一的強大視覺化效果。我們以紫色適宜性等值線地圖做為基礎圖層,然後為從 Places API 擷取的每間咖啡店新增圖釘。這張最終地圖會整合所有分析結果,提供一目瞭然的檢視畫面:深紫色區域代表潛力,綠色圖釘則代表當前市場的實際情況。
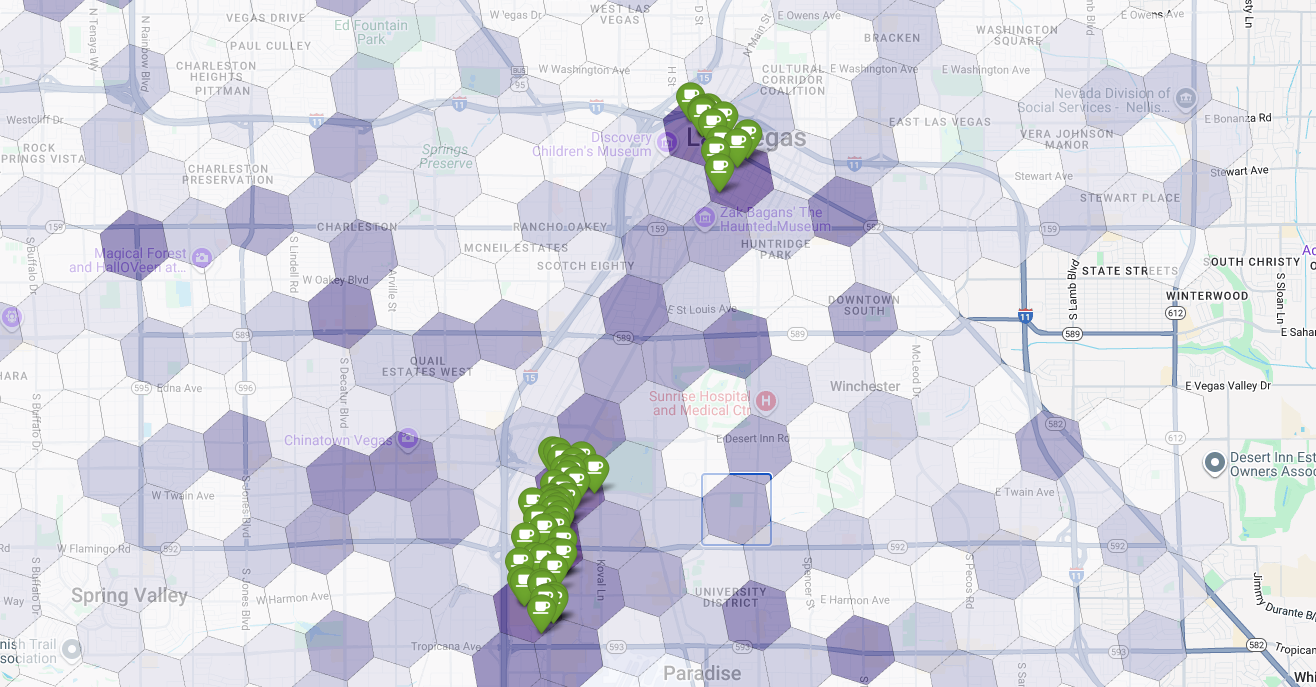
只要找出沒有或只有少量圖釘的深紫色儲存格,就能準確找出最適合新地點的區域。

上述兩個儲存格的適用性分數很高,但仍有一些明顯的差距,可能適合做為新咖啡店的地點。
結論
在本文件中,我們從全州範圍的問題「要在哪裡擴展?」,轉向以資料為依據的當地答案。您可以疊加不同的資料集,並套用自訂的業務邏輯,有系統地降低重大業務決策的相關風險。這個工作流程結合了 BigQuery 的規模、地點洞察的豐富性,以及 Places API 的即時詳細資料,為任何想運用位置情報實現策略性成長的機構提供強大的範本。
後續步驟
- 請根據您的業務邏輯、目標地理區域和專有資料集,調整這個工作流程。
- 探索 Places Insights 資料集中的其他資料欄位,例如評論數、價格等級和使用者評分,進一步豐富模型。
- 自動執行這項程序,建立內部網站選取資訊主頁,用於動態評估新市場。
深入瞭解說明文件:
貢獻者
Henrik Valve | DevX 工程師

