本指南介绍了如何使用 Google Chat API 的 Message 资源中的 create() 方法执行以下任一操作:
- 发送包含文字、卡片和互动式微件的消息。
- 向特定 Chat 用户私下发送消息。
- 发起或回复消息串。
- 为消息命名,以便您可以在其他 Chat API 请求中指定该消息。
消息大小上限(包括任何文本或卡片)为 32,000 字节。 如需发送超出此大小的邮件,您的 Chat 应用必须改为发送多条邮件。
除了调用 Chat API 来创建消息之外,Chat 应用还可以创建和发送消息来回复用户互动,例如在用户将 Chat 应用添加到聊天室后发布欢迎消息。在响应互动时,Chat 应用可以使用其他类型的消息传递功能,包括互动对话框和链接预览界面。如需回复用户,Chat 应用会同步返回消息,而无需调用 Chat API。如需了解如何发送消息来响应互动,请参阅接收和响应与 Google Chat 应用的互动。
Chat 如何显示和归因于使用 Chat API 创建的消息
您可以使用应用身份验证和用户身份验证来调用 create() 方法。聊天会根据您使用的身份验证类型,以不同的方式将消息归因于消息发送者。
当您以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证时,Chat 应用会发送消息。

App。当您以用户身份进行身份验证时,Chat 应用会代表用户发送消息。Chat 还会通过显示聊天应用的名称来将聊天应用归因于消息。

身份验证类型还决定了您可以在消息中包含哪些消息传递功能和界面。借助应用身份验证,Chat 应用可以发送包含富文本、基于卡片的界面和互动式 widget 的消息。由于 Chat 用户只能在消息中发送文本,因此在使用用户身份验证创建消息时,您只能添加文本。 如需详细了解 Chat API 提供的消息传递功能,请参阅 Google Chat 消息概览。
本指南介绍如何使用任一身份验证类型通过 Chat API 发送消息。
前提条件
Node.js
- 拥有可访问 Google Chat 的 Google Workspace 商务版或企业版账号。
- 设置环境:
- 创建 Google Cloud 项目。
- 配置 OAuth 权限请求页面。
- 启用并配置 Google Chat API,为您的 Chat 应用指定名称、图标和说明。
- 安装 Node.js Cloud 客户端库。
- 根据您希望在 Google Chat API 请求中进行身份验证的方式,创建访问凭据:
- 如需以 Chat 用户身份进行身份验证,请创建 OAuth 客户端 ID 凭据,并将该凭据保存为名为
credentials.json的 JSON 文件,保存到您的本地目录。 - 如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请创建服务账号凭据,并将凭据保存为名为
credentials.json的 JSON 文件。
- 如需以 Chat 用户身份进行身份验证,请创建 OAuth 客户端 ID 凭据,并将该凭据保存为名为
- 选择授权范围,具体取决于您是想以用户身份还是以 Chat 应用身份进行身份验证。
- 经过身份验证的用户或调用 Chat 应用所属的 Google Chat 聊天室。如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请将 Chat 应用添加到聊天室。
Python
- 拥有可访问 Google Chat 的 Google Workspace 商务版或企业版账号。
- 设置环境:
- 创建 Google Cloud 项目。
- 配置 OAuth 权限请求页面。
- 启用并配置 Google Chat API,为您的 Chat 应用指定名称、图标和说明。
- 安装 Python Cloud 客户端库。
- 根据您希望在 Google Chat API 请求中进行身份验证的方式,创建访问凭据:
- 如需以 Chat 用户身份进行身份验证,请创建 OAuth 客户端 ID 凭据,并将该凭据保存为名为
credentials.json的 JSON 文件,保存到您的本地目录。 - 如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请创建服务账号凭据,并将凭据保存为名为
credentials.json的 JSON 文件。
- 如需以 Chat 用户身份进行身份验证,请创建 OAuth 客户端 ID 凭据,并将该凭据保存为名为
- 选择授权范围,具体取决于您是想以用户身份还是以 Chat 应用身份进行身份验证。
- 经过身份验证的用户或调用 Chat 应用所属的 Google Chat 聊天室。如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请将 Chat 应用添加到聊天室。
Java
- 拥有可访问 Google Chat 的 Google Workspace 商务版或企业版账号。
- 设置环境:
- 创建 Google Cloud 项目。
- 配置 OAuth 权限请求页面。
- 启用并配置 Google Chat API,为您的 Chat 应用指定名称、图标和说明。
- 安装 Java Cloud 客户端库。
- 根据您希望在 Google Chat API 请求中进行身份验证的方式,创建访问凭据:
- 如需以 Chat 用户身份进行身份验证,请创建 OAuth 客户端 ID 凭据,并将该凭据保存为名为
credentials.json的 JSON 文件,保存到您的本地目录。 - 如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请创建服务账号凭据,并将凭据保存为名为
credentials.json的 JSON 文件。
- 如需以 Chat 用户身份进行身份验证,请创建 OAuth 客户端 ID 凭据,并将该凭据保存为名为
- 选择授权范围,具体取决于您是想以用户身份还是以 Chat 应用身份进行身份验证。
- 经过身份验证的用户或调用 Chat 应用所属的 Google Chat 聊天室。如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请将 Chat 应用添加到聊天室。
Apps 脚本
- 拥有可访问 Google Chat 的 Google Workspace 商务版或企业版账号。
- 设置环境:
- 创建 Google Cloud 项目。
- 配置 OAuth 权限请求页面。
- 启用并配置 Google Chat API,为您的 Chat 应用指定名称、图标和说明。
- 创建独立的 Apps 脚本项目,然后启用高级聊天服务。
- 在本指南中,您必须使用用户或应用身份验证。如需以 Chat 应用身份进行身份验证,请创建服务账号凭据。如需了解具体步骤,请参阅以 Google Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证和授权。
- 选择授权范围,具体取决于您是想以用户身份还是以 Chat 应用身份进行身份验证。
- 经过身份验证的用户或调用 Chat 应用所属的 Google Chat 聊天室。如需以 Chat 应用的身份进行身份验证,请将 Chat 应用添加到聊天室。
以 Chat 应用的身份发送消息
本部分介绍了如何使用应用身份验证发送包含文本、卡片和互动辅助功能 widget 的消息。

如需使用应用身份验证来调用 CreateMessage() 方法,您必须在请求中指定以下字段:
chat.bot授权范围。- 您要发布消息的
Space资源。Chat 应用必须是聊天室的成员。 - 要创建的
Message资源。如需定义消息的内容,您可以添加富文本 (text)、一个或多个卡片界面 (cardsV2),也可以同时添加这两者。
您还可以选择性地添加以下内容:
- 用于在消息底部添加互动按钮的
accessoryWidgets字段。 - 用于向指定用户私下发送消息的
privateMessageViewer字段。 messageId字段,可用于命名消息,以便在其他 API 请求中使用。- 用于发起或回复话题的
thread.threadKey和messageReplyOption字段。如果空间不使用线程,则系统会忽略此字段。
以下代码展示了一个示例,说明了 Chat 应用如何发送以 Chat 应用身份发布的包含文本、卡片和消息底部可点击按钮的消息:
Node.js
Python
Java
Apps 脚本
如需运行此示例,请将 SPACE_NAME 替换为空间 name 字段中的 ID。您可以通过调用 ListSpaces() 方法或从会议室的网址中获取 ID。
在消息底部添加互动式微件
在本指南的第一个代码示例中,聊天应用消息会在消息底部显示一个可点击的按钮,称为辅助 widget。辅助功能 widget 会显示在消息中的任何文本或卡片之后。您可以使用这些 widget 以多种方式提示用户与您的消息互动,包括:
- 评价消息的准确性或满意度。
- 报告“信息”应用或 Chat 应用存在的问题。
- 打开指向相关内容(例如文档)的链接。
- 在特定时间段内关闭或推迟接收来自 Chat 应用的类似消息。
如需添加辅助 widget,请在请求正文中添加 accessoryWidgets[] 字段,并指定要添加的一个或多个 widget。
下图展示了一个 Chat 应用,该应用会在文本消息中附加辅助 widget,以便用户评价其使用 Chat 应用的体验。
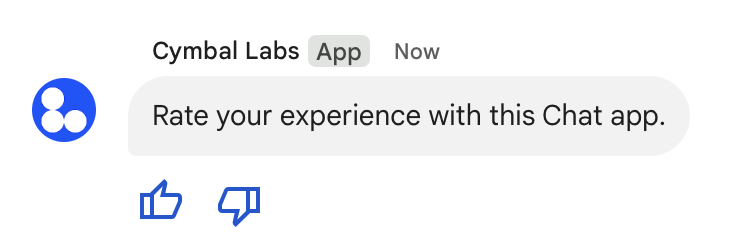
以下示例展示了创建包含两个附件按钮的文本消息的请求正文。当用户点击按钮时,相应的函数(例如 doUpvote)会处理互动:
{
text: "Rate your experience with this Chat app.",
accessoryWidgets: [{ buttonList: { buttons: [{
icon: { material_icon: {
name: "thumb_up"
}},
color: { red: 0, blue: 255, green: 0 },
onClick: { action: {
function: "doUpvote"
}}
}, {
icon: { material_icon: {
name: "thumb_down"
}},
color: { red: 0, blue: 255, green: 0 },
onClick: { action: {
function: "doDownvote"
}}
}]}}]
}
私密地发送消息
聊天应用可以私下发送消息,以便消息仅对聊天室中的特定用户可见。当聊天应用发送私信时,该消息会显示一个标签,通知用户该消息仅对其可见。
如需使用 Chat API 私下发送消息,请在请求正文中指定 privateMessageViewer 字段。如需指定用户,请将值设置为表示 Chat 用户的 User 资源。您还可以使用 User 资源的 name 字段,如以下示例所示:
{
text: "Hello private world!",
privateMessageViewer: {
name: "users/USER_ID"
}
}
如需使用此示例,请将 USER_ID 替换为用户的唯一 ID,例如 12345678987654321 或 hao@cymbalgroup.com。如需详细了解如何指定用户,请参阅识别和指定 Google Chat 用户。
如需私下发送消息,您必须在请求中省略以下内容:
代表用户发送短信
本部分介绍如何使用用户身份验证代表用户发送消息。如果使用用户身份验证,消息内容只能包含文本,并且必须省略仅适用于 Chat 应用的消息传递功能,包括卡片界面和互动式 widget。

如需使用用户身份验证来调用 CreateMessage() 方法,您必须在请求中指定以下字段:
- 支持此方法的用户身份验证的授权范围。以下示例使用
chat.messages.create范围。 - 您要发布消息的
Space资源。经过身份验证的用户必须是相应聊天室的成员。 - 要创建的
Message资源。如需定义消息的内容,您必须添加text字段。
您还可以选择性地添加以下内容:
messageId字段,可用于命名消息,以便在其他 API 请求中使用。- 用于发起或回复话题的
thread.threadKey和messageReplyOption字段。如果空间不使用线程,则系统会忽略此字段。
以下代码展示了 Chat 应用如何代表已通过身份验证的用户在指定聊天室中发送文本消息的示例:
Node.js
Python
Java
Apps 脚本
如需运行此示例,请将 SPACE_NAME 替换为空间 name 字段中的 ID。您可以通过调用 ListSpaces() 方法或从会议室的网址中获取 ID。
发起或回复消息串
对于使用话题的聊天室,您可以指定新消息是发起新话题,还是回复现有话题。
默认情况下,使用 Chat API 创建的消息会启动新线程。为了帮助您识别相应消息串并在日后回复,您可以在请求中指定消息串键:
- 在请求正文中,指定
thread.threadKey字段。 - 指定查询参数
messageReplyOption以确定在键已存在时会发生什么情况。
如需创建回复现有对话串的消息,请执行以下操作:
以下代码展示了 Chat 应用如何代表已通过身份验证的用户发送一条文本消息,该消息会启动或回复给定聊天室中由键标识的给定线程:
Node.js
Python
Java
Apps 脚本
如需运行此示例,请替换以下内容:
THREAD_KEY:空间中的现有线程密钥,或者要创建新线程,则为线程的唯一名称。SPACE_NAME:来自空间的name字段的 ID。您可以通过调用ListSpaces()方法或从会议室的网址中获取 ID。
为消息命名
如需在未来的 API 调用中检索或指定消息,您可以在请求中设置 messageId 字段来为消息命名。为消息命名后,您无需存储消息资源名称(以 name 字段表示)中系统分配的 ID,即可指定消息。
例如,如需使用 get() 方法检索消息,您可以使用资源名称来指定要检索的消息。资源名称的格式为 spaces/{space}/messages/{message},其中 {message} 表示系统分配的 ID 或您在创建消息时设置的自定义名称。
如需为消息命名,请在创建消息时在 messageId 字段中指定自定义 ID。messageId 字段用于设置 Message 资源的 clientAssignedMessageId 字段的值。
您只能在创建消息时为其命名。您无法为现有消息命名或修改自定义 ID。自定义 ID 必须满足以下要求:
- 以
client-开头。例如,client-custom-name是有效的自定义 ID,但custom-name不是。 - 最多包含 63 个字符,并且只能包含小写字母、数字和连字符。
- 在空间内是唯一的。一个聊天应用不能为不同的消息使用相同的自定义 ID。
以下代码展示了 Chat 应用如何代表已通过身份验证的用户向指定聊天室发送包含 ID 的文本消息:
Node.js
Python
Java
Apps 脚本
如需运行此示例,请替换以下内容:
SPACE_NAME:来自空间的name字段的 ID。您可以通过调用ListSpaces()方法或从会议室的网址中获取 ID。MESSAGE-ID:以custom-开头的消息的名称。必须与 Chat 应用在指定空间中创建的任何其他消息名称不同。
引用消息
您可以通过调用 CreateMessage()(rpc, rest) 并在请求中设置 quotedMessageMetadata(rpc, rest) 来引用另一条消息。
您可以在消息串或主聊天中引用消息,但无法引用其他消息串中的消息。
以下代码展示了如何创建引用另一条消息的消息:
Node.js
import {createClientWithUserCredentials} from './authentication-utils.js';
const USER_AUTH_OAUTH_SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.create'];
// This sample shows how to create a message that quotes another message.
async function main() {
// Create a client
const chatClient = await createClientWithUserCredentials(USER_AUTH_OAUTH_SCOPES);
// Initialize request argument(s)
const request = {
// TODO(developer): Replace SPACE_NAME .
parent: 'spaces/SPACE_NAME',
message: {
text: 'I am responding to a quoted message!',
// quotedMessageMetadata lets chat apps respond to a message by quoting it.
quotedMessageMetadata: {
// TODO(developer): Replace QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME
// and QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME.
name: 'QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME',
lastUpdateTime: 'QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME'
}
}
};
// Make the request
const response = await chatClient.createMessage(request);
// Handle the response
console.log(response);
}
main().catch(console.error);
Python
from authentication_utils import create_client_with_user_credentials
from google.apps import chat_v1 as google_chat
from google.protobuf.timestamp_pb2 import Timestamp
SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.create']
# This sample shows how to create a message that quotes another message.
def create_message_quote_message():
'''Creates a message that quotes another message.'''
# Create a client
client = create_client_with_user_credentials(SCOPES)
# Create a timestamp from the RFC-3339 string.
# TODO(developer): Replace QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME.
last_update_time = Timestamp()
last_update_time.FromJsonString('QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME')
# Initialize request argument(s)
request = google_chat.CreateMessageRequest(
# TODO(developer): Replace SPACE_NAME.
parent='spaces/SPACE_NAME',
# Create the message.
message = google_chat.Message(
text='I am responding to a quoted message!',
# quotedMessageMetadata lets chat apps respond to a message by quoting it.
quoted_message_metadata=google_chat.QuotedMessageMetadata(
name='QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME',
last_update_time=last_update_time
)
)
)
# Make the request
response = client.create_message(request)
# Handle the response
print(response)
create_message_quote_message()
Java
import com.google.chat.v1.ChatServiceClient;
import com.google.chat.v1.CreateMessageRequest;
import com.google.chat.v1.Message;
import com.google.chat.v1.QuotedMessageMetadata;
import com.google.protobuf.util.Timestamps;
import com.google.workspace.api.chat.samples.utils.AuthenticationUtils;
import java.text.ParseException;
// This sample shows how to create a message that quotes another message.
public class CreateMessageQuoteMessage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, ParseException {
// Create a client.
ChatServiceClient chatClient = AuthenticationUtils.createClientWithUserCredentials();
// Initialize request argument(s).
// TODO(developer): Replace SPACE_NAME, QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME,
// and QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME here.
String parent = "spaces/SPACE_NAME";
String quotedMessageName = "QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME";
String lastUpdateTime = "QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME";
QuotedMessageMetadata quotedMessageMetadata =
QuotedMessageMetadata.newBuilder()
.setName(quotedMessageName)
.setLastUpdateTime(Timestamps.parse(lastUpdateTime))
.build();
Message message = Message.newBuilder()
.setText("I am responding to a quoted message!")
.setQuotedMessageMetadata(quotedMessageMetadata)
.build();
CreateMessageRequest request =
CreateMessageRequest.newBuilder()
.setParent(parent)
.setMessage(message)
.build();
// Make the request.
Message response = chatClient.createMessage(request);
// Handle the response.
System.out.println(response);
}
}
Apps 脚本
/**
* Creates a message that quotes another message.
*
* Relies on the OAuth2 scope 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.create'
* referenced in the manifest file (appsscript.json).
*/
function createMessageQuoteMessage() {
// Initialize request argument(s)
// TODO(developer): Replace SPACE_NAME here.
const parent = 'spaces/SPACE_NAME';
const message = {
// The text content of the message.
text: 'I am responding to a quoted message!',
// quotedMessageMetadata lets chat apps respond to a message by quoting it.
//
// TODO(developer): Replace QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME
// and QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME .
quotedMessageMetadata: {
name: 'QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME',
lastUpdateTime: 'QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME',
}
};
// Make the request
const response = Chat.Spaces.Messages.create(message, parent);
// Handle the response
console.log(response);
}
如需运行此示例,请替换以下内容:
SPACE_NAME:来自空间的name字段的 ID。您可以通过调用ListSpaces()(rpc、rest)方法或从会议室的网址中获取 ID。QUOTED_MESSAGE_NAME:要引用消息的消息资源name(rpc、rest),格式为spaces/{space}/messages/{message}。QUOTED_MESSAGE_LAST_UPDATE_TIME:要引用消息的上次更新时间。如果消息从未经过修改,则与createTime(rpc、rest)相对应。如果消息经过修改,则与lastUpdateTime(rpc、rest)相对应。
问题排查
当 Google Chat 应用或卡片返回错误时,Chat 界面会显示一条消息,提示“出了点问题”。 或“无法处理您的请求”。有时,Chat 界面不会显示任何错误消息,但 Chat 应用或卡片会产生意外结果;例如,卡片消息可能不会显示。
虽然聊天界面中可能不会显示错误消息,但当您为聊天应用启用错误日志记录功能后,系统会提供描述性错误消息和日志数据,帮助您修复错误。如需查看、调试和修复错误方面的帮助,请参阅排查和修复 Google Chat 错误。
相关主题
- 使用卡片构建器设计和预览 Chat 应用的 JSON 卡片消息。
- 设置邮件格式。
- 获取有关消息的详细信息。
- 列出聊天室中的消息。
- 更新消息。
- 删除消息。
- 在 Google Chat 消息中提及用户。
- 使用传入的网络钩子向 Google Chat 发送消息。