Una de las funciones exclusivas de las aplicaciones para dispositivos móviles es el reconocimiento de la ubicación. Los usuarios de dispositivos móviles los llevan a todas partes. Por eso, si agregas la función de reconocimiento de la ubicación a tu app, podrás brindarles una experiencia más contextual.
Muestras de código
El repositorio ApiDemos en GitHub incluye ejemplos que muestran el uso de la ubicación en un mapa:
Kotlin
- MyLocationDemoActivity: Uso de la capa Mi ubicación, incluidos los permisos de tiempo de ejecución
- LocationSourceDemoActivity: Uso de una interfaz
LocationSourcepersonalizada - CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap: Búsqueda de la ubicación actual de un dispositivo Android y visualización de la información del lugar (una empresa o cualquier otro lugar de interés) en esa ubicación (consulta el instructivo sobre cómo mostrar la información del lugar actual en un mapa)
Java
- MyLocationDemoActivity: Uso de la capa Mi ubicación, incluidos los permisos de tiempo de ejecución
- LocationSourceDemoActivity: Uso de una interfaz
LocationSourcepersonalizada - CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap: Búsqueda de la ubicación actual de un dispositivo Android y visualización de la información del lugar (una empresa o cualquier otro lugar de interés) en esa ubicación (consulta el instructivo sobre cómo mostrar la información del lugar actual en un mapa)
Cómo trabajar con datos de ubicación
Entre los datos de ubicación disponibles para un dispositivo Android, se incluyen la ubicación actual del dispositivo (identificada a través de una combinación de tecnologías), la dirección y el método de movimiento, y si el dispositivo cruzó un límite geográfico predefinido, lo que también se conoce como perímetro virtual. Según las necesidades de tu aplicación, puedes elegir entre varias formas de trabajar con datos de ubicación:
- La capa Mi ubicación proporciona una forma sencilla de mostrar la ubicación de un dispositivo en el mapa. No proporciona datos.
- La API de Location de Servicios de Google Play se recomienda para todas las solicitudes programáticas de datos de ubicación.
- La interfaz
LocationSourcete permite definir un proveedor de ubicación personalizado.
Permisos de ubicación
Si tu app necesita acceder a la ubicación del usuario, primero debes solicitar el permiso correspondiente. Para ello, agrega los permisos de ubicación de Android pertinentes a tu app.
Android ofrece dos permisos de ubicación: ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION y ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. El permiso que elijas determinará la exactitud de la ubicación que mostrará la API.
android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION: Permite que la API muestre la ubicación aproximada del dispositivo. El permiso proporciona una estimación de la ubicación del dispositivo a partir de los servicios de ubicación, como se describe en la documentación sobre la exactitud de la ubicación aproximada.android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION: Permite que la API determine la ubicación más precisa posible mediante los proveedores de ubicación disponibles, incluido el sistema de posicionamiento global (GPS), así como Wi-Fi y datos móviles.
Agrega los permisos al manifiesto de la app
Si solo se necesita la ubicación aproximada para que tu app funcione, agrega el permiso ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION al archivo de manifiesto de tu app:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.myapp" >
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
...
</manifest>
Sin embargo, si se necesita la ubicación precisa, agrega los permisos ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION y ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION al archivo de manifiesto de tu app:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.myapp" >
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
...
</manifest>
Solicita permisos de tiempo de ejecución
Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) presenta un nuevo modelo para administrar los permisos, que simplifica el proceso de instalación y actualización de apps para los usuarios. Si tu app tiene como objetivo un nivel de API 23 o posterior, puedes utilizar el nuevo modelo de permisos.
Si tu app admite el nuevo modelo de permisos y el dispositivo ejecuta Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) o una versión posterior, el usuario no tendrá que otorgar ningún permiso al instalar o actualizar la app. Esta deberá comprobar si tiene los permisos necesarios de tiempo de ejecución y solicitarlos en caso de no tenerlos. El sistema le mostrará un diálogo al usuario para solicitarle los permisos correspondientes.
Para ofrecer una mejor experiencia del usuario, es importante solicitar los permisos en contexto. Si conocer la ubicación es fundamental para el funcionamiento de tu app, debes solicitar el permiso de ubicación cuando se inicia la app. Se recomienda hacerlo con una pantalla de bienvenida o mediante un asistente que les explique a los usuarios por qué se requiere el permiso.
Si la app requiere el permiso de ubicación solo para una parte de su funcionalidad, deberás solicitarlo cuando la app esté por realizar la acción que lo necesita.
La app debe manejar correctamente los casos en los que los usuarios no otorguen su permiso. Por ejemplo, si el permiso se necesita para una función específica, la app puede inhabilitarla. Si el permiso es fundamental para que la app funcione, esta podrá inhabilitar todas sus funcionalidades y notificarle al usuario que es indispensable conceder el permiso.
La siguiente muestra de código comprueba si se otorgó el permiso con la biblioteca de AndroidX antes de habilitar la capa Mi ubicación. Luego, controla el resultado de la solicitud de permiso implementando ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback desde la biblioteca de compatibilidad:
Kotlin
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package com.example.kotlindemos
import android.Manifest
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.content.pm.PackageManager
import android.location.Location
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat
import com.example.kotlindemos.PermissionUtils.PermissionDeniedDialog.Companion.newInstance
import com.example.kotlindemos.PermissionUtils.isPermissionGranted
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener
import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback
import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment
/**
* This demo shows how GMS Location can be used to check for changes to the users location. The
* "My Location" button uses GMS Location to set the blue dot representing the users location.
* Permission for [Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] and [Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION]
* are requested at run time. If either permission is not granted, the Activity is finished with an error message.
*/
class MyLocationDemoActivity : AppCompatActivity(),
OnMyLocationButtonClickListener,
OnMyLocationClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback,
OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback {
/**
* Flag indicating whether a requested permission has been denied after returning in
* [.onRequestPermissionsResult].
*/
private var permissionDenied = false
private lateinit var map: GoogleMap
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.my_location_demo)
val mapFragment =
supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment?
mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this)
}
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) {
map = googleMap
googleMap.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this)
googleMap.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this)
enableMyLocation()
}
/**
* Enables the My Location layer if the fine location permission has been granted.
*/
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
private fun enableMyLocation() {
// 1. Check if permissions are granted, if so, enable the my location layer
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(
this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(
this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED
) {
map.isMyLocationEnabled = true
return
}
// 2. If if a permission rationale dialog should be shown
if (ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(
this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
) || ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(
this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
)
) {
PermissionUtils.RationaleDialog.newInstance(
LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE, true
).show(supportFragmentManager, "dialog")
return
}
// 3. Otherwise, request permission
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(
this,
arrayOf(
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
),
LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE
)
}
override fun onMyLocationButtonClick(): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show()
// Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs
// (the camera animates to the user's current position).
return false
}
override fun onMyLocationClick(location: Location) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n$location", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show()
}
override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(
requestCode: Int,
permissions: Array<String>,
grantResults: IntArray
) {
if (requestCode != LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(
requestCode,
permissions,
grantResults
)
return
}
if (isPermissionGranted(
permissions,
grantResults,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
) || isPermissionGranted(
permissions,
grantResults,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
)
) {
// Enable the my location layer if the permission has been granted.
enableMyLocation()
} else {
// Permission was denied. Display an error message
// Display the missing permission error dialog when the fragments resume.
permissionDenied = true
}
}
override fun onResumeFragments() {
super.onResumeFragments()
if (permissionDenied) {
// Permission was not granted, display error dialog.
showMissingPermissionError()
permissionDenied = false
}
}
/**
* Displays a dialog with error message explaining that the location permission is missing.
*/
private fun showMissingPermissionError() {
newInstance(true).show(supportFragmentManager, "dialog")
}
companion object {
/**
* Request code for location permission request.
*
* @see .onRequestPermissionsResult
*/
private const val LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE = 1
}
}
Java
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package com.example.mapdemo;
import android.Manifest.permission;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment;
import android.Manifest;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.location.Location;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat;
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* This demo shows how GMS Location can be used to check for changes to the users location. The "My
* Location" button uses GMS Location to set the blue dot representing the users location.
* Permission for {@link android.Manifest.permission#ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION} and {@link
* android.Manifest.permission#ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION} are requested at run time. If either
* permission is not granted, the Activity is finished with an error message.
*/
public class MyLocationDemoActivity extends AppCompatActivity
implements
OnMyLocationButtonClickListener,
OnMyLocationClickListener,
OnMapReadyCallback,
ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback {
/**
* Request code for location permission request.
*
* @see #onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])
*/
private static final int LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE = 1;
/**
* Flag indicating whether a requested permission has been denied after returning in {@link
* #onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])}.
*/
private boolean permissionDenied = false;
private GoogleMap map;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.my_location_demo);
SupportMapFragment mapFragment =
(SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.map);
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
}
@Override
public void onMapReady(@NonNull GoogleMap googleMap) {
map = googleMap;
map.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this);
map.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this);
enableMyLocation();
}
/**
* Enables the My Location layer if the fine location permission has been granted.
*/
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
private void enableMyLocation() {
// 1. Check if permissions are granted, if so, enable the my location layer
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)
== PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED
|| ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)
== PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
map.setMyLocationEnabled(true);
return;
}
// 2. Otherwise, request location permissions from the user.
PermissionUtils.requestLocationPermissions(this, LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE, true);
}
@Override
public boolean onMyLocationButtonClick() {
Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs
// (the camera animates to the user's current position).
return false;
}
@Override
public void onMyLocationClick(@NonNull Location location) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n" + location, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions,
@NonNull int[] grantResults) {
if (requestCode != LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
return;
}
if (PermissionUtils.isPermissionGranted(permissions, grantResults,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) || PermissionUtils
.isPermissionGranted(permissions, grantResults,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)) {
// Enable the my location layer if the permission has been granted.
enableMyLocation();
} else {
// Permission was denied. Display an error message
// Display the missing permission error dialog when the fragments resume.
permissionDenied = true;
}
}
@Override
protected void onResumeFragments() {
super.onResumeFragments();
if (permissionDenied) {
// Permission was not granted, display error dialog.
showMissingPermissionError();
permissionDenied = false;
}
}
/**
* Displays a dialog with error message explaining that the location permission is missing.
*/
private void showMissingPermissionError() {
PermissionUtils.PermissionDeniedDialog
.newInstance(true).show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "dialog");
}
}
Capa Mi ubicación
Puedes utilizar la capa y el botón Mi ubicación para mostrarle al usuario su posición actual en el mapa. Llama a mMap.setMyLocationEnabled() para habilitar la capa Mi ubicación en el mapa.
A continuación, se muestra un ejemplo de uso simple de la capa Mi ubicación:
Kotlin
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package com.google.maps.example.kotlin
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.location.Location
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener
import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback
import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment
import com.google.maps.example.R
internal class MyLocationLayerActivity : AppCompatActivity(),
OnMyLocationButtonClickListener,
OnMyLocationClickListener,
OnMapReadyCallback {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_my_location)
val mapFragment =
supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this)
}
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) {
// TODO: Before enabling the My Location layer, you must request
// location permission from the user. This sample does not include
// a request for location permission.
map.isMyLocationEnabled = true
map.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this)
map.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this)
}
override fun onMyLocationClick(location: Location) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n$location", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show()
}
override fun onMyLocationButtonClick(): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show()
// Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs
// (the camera animates to the user's current position).
return false
}
}
Java
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package com.google.maps.example;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.location.Location;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment;
class MyLocationLayerActivity extends AppCompatActivity
implements GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener,
GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener,
OnMapReadyCallback {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_my_location);
SupportMapFragment mapFragment =
(SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.map);
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
}
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
@Override
public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) {
// TODO: Before enabling the My Location layer, you must request
// location permission from the user. This sample does not include
// a request for location permission.
map.setMyLocationEnabled(true);
map.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this);
map.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onMyLocationClick(@NonNull Location location) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n" + location, Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
@Override
public boolean onMyLocationButtonClick() {
Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
// Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs
// (the camera animates to the user's current position).
return false;
}
}
Cuando la capa Mi ubicación está habilitada, aparece el botón correspondiente en la esquina superior derecha del mapa. Cuando un usuario hace clic en el botón, la cámara centra el mapa en la ubicación actual del dispositivo, si se conoce. La ubicación se indica en el mapa con un pequeño punto azul si el dispositivo está quieto o como un corchete angular si está en movimiento.
En la siguiente captura de pantalla, se muestra el botón Mi ubicación en la esquina superior derecha y el punto azul de Mi ubicación en el centro del mapa:
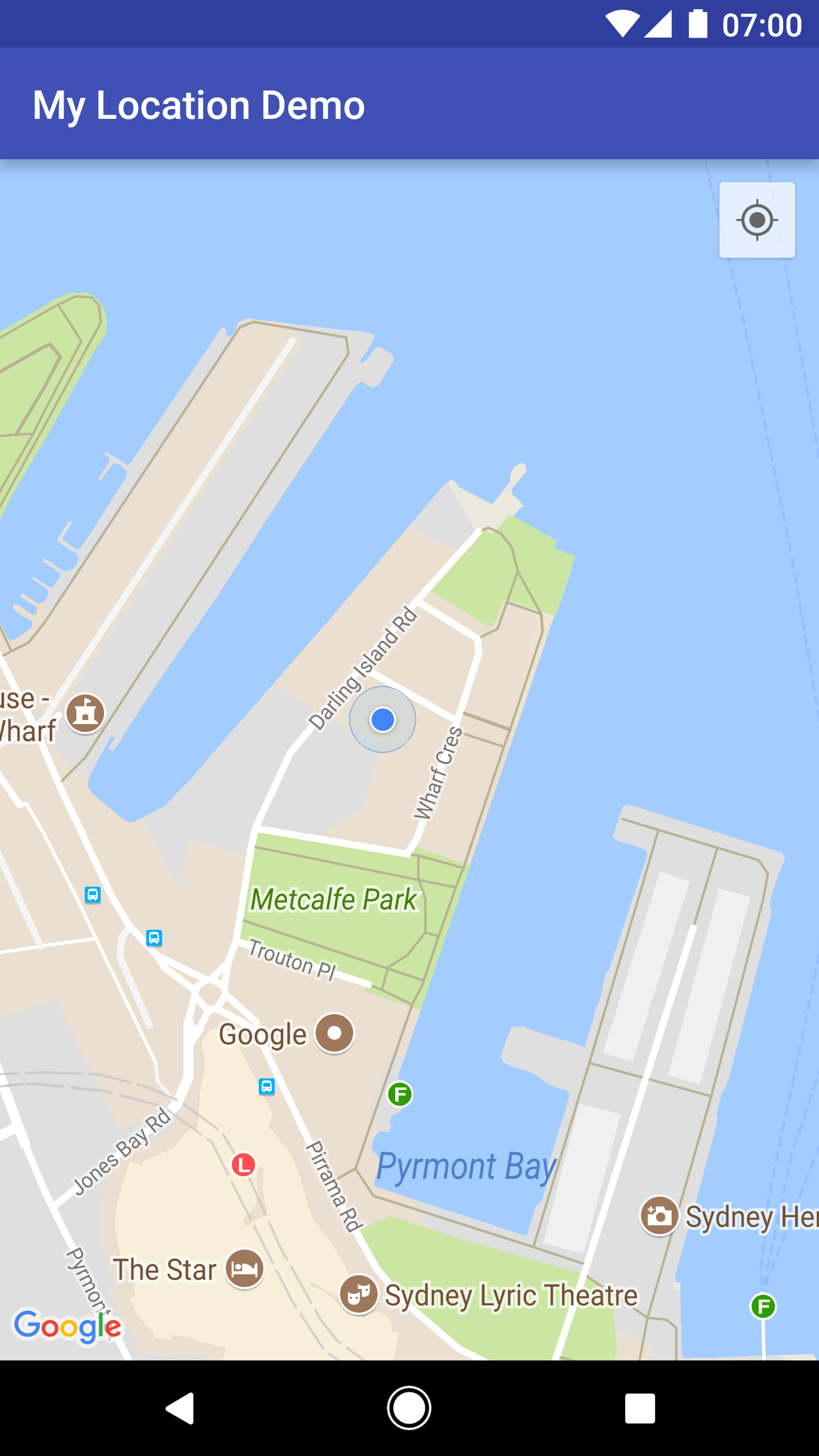
Si no deseas mostrar el botón Mi ubicación, llama a UiSettings.setMyLocationButtonEnabled(false).
Tu app puede responder a los siguientes eventos:
- Si el usuario hace clic en el botón Mi ubicación, tu app recibirá una devolución de llamada
onMyLocationButtonClick()del objeto de escuchaGoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener. - Si el usuario hace clic en el punto azul de Mi ubicación, tu app recibirá una devolución de llamada
onMyLocationClick()del objeto de escuchaGoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener.
API de Location de Servicios de Google Play
La API de Location de Servicios de Google Play es el método preferido para agregar la función de reconocimiento de la ubicación a tu aplicación para Android. Incluye funcionalidades que te permitirán hacer lo siguiente:
- Determinar la ubicación del dispositivo
- Escuchar cambios en la ubicación
- Determinar el medio de transporte si el dispositivo está en movimiento
- Crear y supervisar regiones geográficas predefinidas, conocidas como perímetros virtuales
Las APIs de ubicación te permiten compilar fácilmente aplicaciones con capacidad de ahorro de energía y reconocimiento de la ubicación. Al igual que el SDK de Maps para Android, la API de Location se distribuye como parte del SDK de Servicios de Google Play. Para obtener más información sobre la API de Location, consulta la clase de capacitación de Android Cómo conocer la ubicación con tu app o la Referencia de la API de Location. Los ejemplos de código se incluyen como parte del SDK de Servicios de Google Play.
