Elementy
Zadbaj o dobrą organizację dzięki kolekcji
Zapisuj i kategoryzuj treści zgodnie ze swoimi preferencjami.
Podczas pomiaru blok jest rozbity na wiersze zawierające nienakładające się elementy i odstępy elementów.
Elementy
Elementy reprezentują obiekty wizualne na bryle. Oto przykłady:
- Pola
- Ikony
- Połączenia
- Narożniki
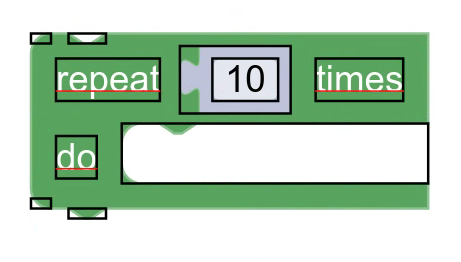
Każdy element jest prostokątem określającym granice elementu wizualnego oraz dodatkowe dane specyficzne dla każdego z nich.
Granice elementu są zwykle określane przez klasę zewnętrzną (czyli przedmiot, który reprezentuje). Na przykład elementy pól reprezentują pola, a ich rozmiar jest określany za pomocą metody getSize pola.
Odstęp elementu
Odstęp elementu to pusta przestrzeń między elementami w rzędzie.
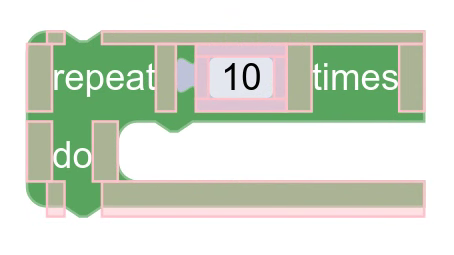
Granice odstępów są określane na podstawie informacji o renderowaniu podczas pomiaru. Po zmierzeniu wszystkich elementów bloku informacje o renderowaniu wstawiają między nimi odstępy o wybranym rozmiarze. Rozmiary nie muszą być spójne. Często różnią się w zależności od elementów po obu stronach odstępy.
O ile nie stwierdzono inaczej, treść tej strony jest objęta licencją Creative Commons – uznanie autorstwa 4.0, a fragmenty kodu są dostępne na licencji Apache 2.0. Szczegółowe informacje na ten temat zawierają zasady dotyczące witryny Google Developers. Java jest zastrzeżonym znakiem towarowym firmy Oracle i jej podmiotów stowarzyszonych.
Ostatnia aktualizacja: 2025-07-25 UTC.
[null,null,["Ostatnia aktualizacja: 2025-07-25 UTC."],[],["During the measurement phase, blocks are divided into rows with elements and spacers. Elements, such as fields, icons, connections, and corners, are represented by rectangles with specific data. Their sizes are dictated by external classes, like a field's `getSize` method. Element spacers are empty spaces inserted between elements by the render info, with varying sizes based on the adjacent elements. The render info determines spacer sizes after measuring all block elements.\n"]]


