Şu andan itibaren Çapraz egzersizleri öne çıkarın Kategorik veri modülünde, şu sınıflandırma probleminin doğrusal olmadığı unutulmamalıdır:
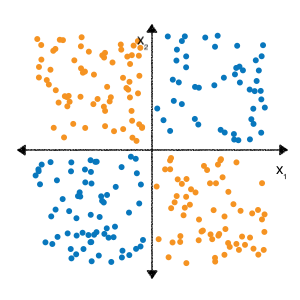
"Doğrusal olmayan" etiketi içeren bir etiketi doğru tahmin edemeyeceğiniz \(b + w_1x_1 + w_2x_2\)formunun modelidir. Başka bir deyişle, "karar yüzeyi" bir çizgi değil.
Ancak, $x_1$ ve $x_2$ özellikleri üzerinde çapraz özellik yaparsak sonra, iki özellik arasındaki doğrusal olmayan ilişkiyi bir doğrusal model: $b + w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + w_3x_3$ burada $x_3$, iki nokta arasındaki $x_1$ ve $x_2$:
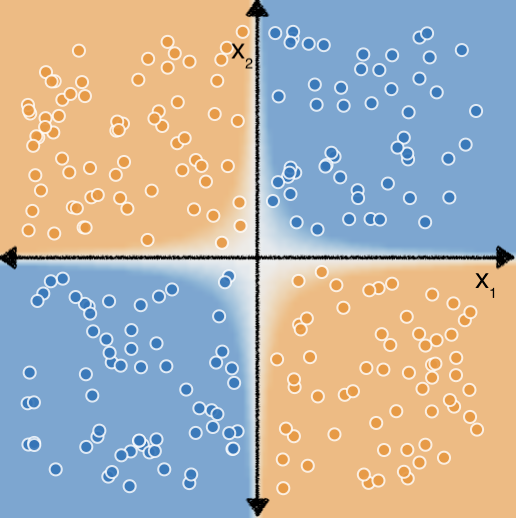
Şimdi aşağıdaki veri kümesini göz önünde bulundurun:

Özellik çaprazlama alıştırmalarında, bu verilere doğrusal bir model sığdırmak için doğru özellik çaprazlamalarının belirlenmesinin biraz daha fazla çaba ve deneme gerektirdiğini de hatırlayabilirsiniz.
Peki, tüm bu denemeleri kendiniz yapmak zorunda olmasanız ne olur? Nöral ağlar, verilerdeki doğrusal olmayan kalıpları bulmak için tasarlanmış bir model mimarileri ailesidir. Bir sinir ağının eğitimi sırasında model, kaybı en aza indirmek için giriş verilerinde gerçekleştirilecek optimum özellik kesişimlerini otomatik olarak öğrenir.
Aşağıdaki bölümlerde, sinir ağlarının işleyiş şeklini daha ayrıntılı olarak inceleyeceğiz.
